MapReduce概述
MapReduce定义
MapReduce是一个分布式运算程序的编程框架,是用户开发“基于Hadoop的数据分析应用”的核心框架。
MapReduce核心功能是将用户编写的业务逻辑代码和自带默认组件整合成一个完整的分布式运算程序,并发运行在一个Hadoop集群上
MapReduce优缺点
优点
1)MapReduce易于编程
它简单的实现一些接口,就可以完成一个分布式程序,这个分布式程序可以分布到大量廉价的PC机器上运行。也就是说你写一个分布式程序,跟写一个简单的串行程序是一模一样的。就是因为这个特点使得MapReduce编程变得非常流行。
2)良好的扩展性
当你的计算资源不能得到满足的时候,你可以通过简单的增加机器来扩展它的计算能力。
3)高容错性
MapReduce设计的初衷就是使程序能够部署在廉价的PC机器上,这就要求它具有很高的容错性。比如其中一台机器挂了,它可以把上面的计算任务转移到另外一个节点上运行,不至于这个任务运行失败,而且这个过程不需要人工参与,而完全是由Hadoop内部完成的。
4)适合PB级以上海量数据的离线处理
可以实现上千台服务器集群并发工作,提供数据处理能力。
缺点
1)不擅长实时计算
MapReduce无法像MySQL一样,在毫秒或者秒级内返回结果。
2)不擅长流式计算
流式计算的输入数据是动态的,而MapReduce的输入数据集是静态的,不能动态变化。这是因为MapReduce自身的设计特点决定了数据源必须是静态的。
3)不擅长DAG(有向无环图)计算
多个应用程序存在依赖关系,后一个应用程序的输入为前一个的输出。在这种情况下,MapReduce并不是不能做,而是使用后,每个MapReduce作业的输出结果都会写入到磁盘,会造成大量的磁盘IO,导致性能非常的低下。
MapReduce核心思想
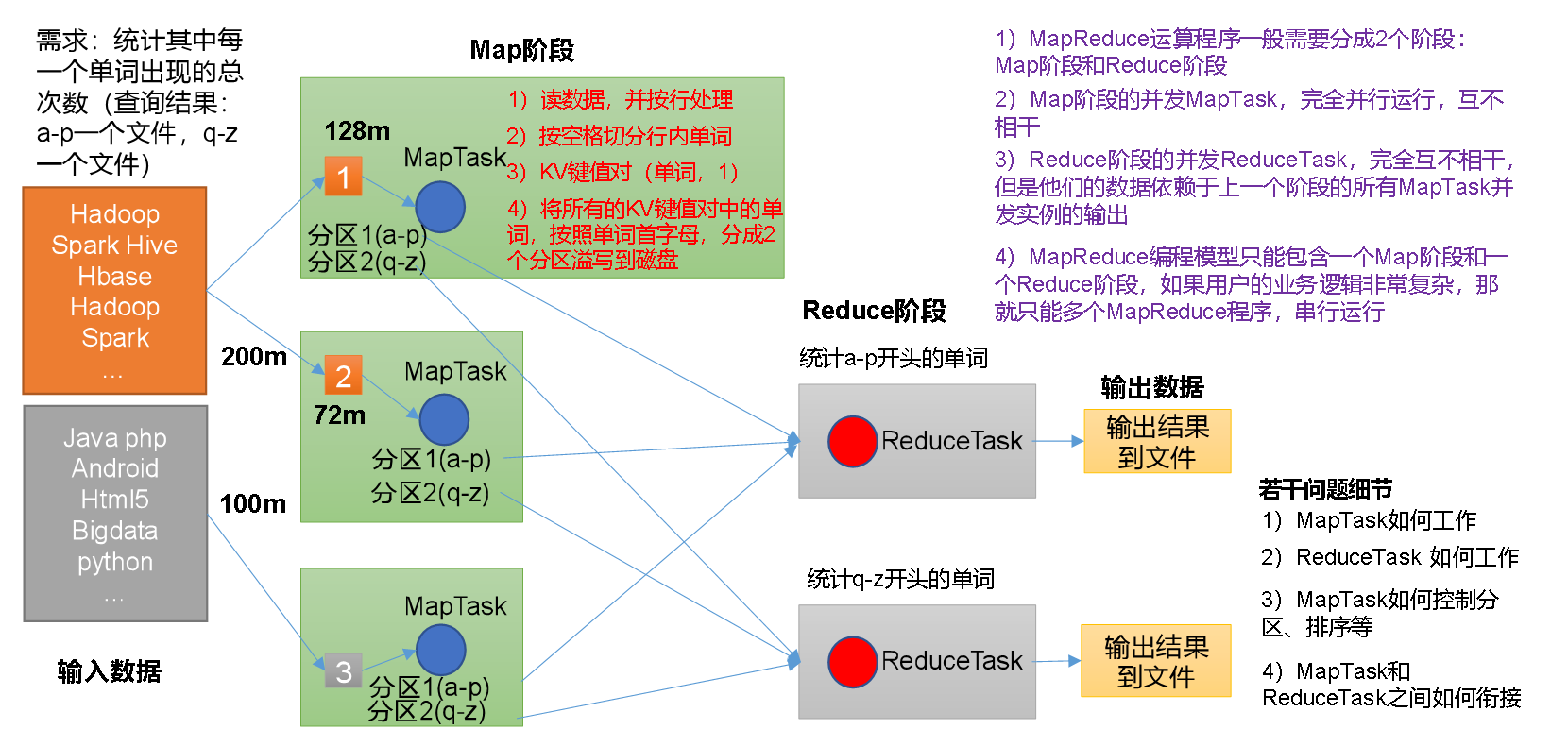
(1)分布式的运算程序往往需要分成至少2个阶段。
(2)第一个阶段的MapTask并发实例,完全并行运行,互不相干。
(3)第二个阶段的ReduceTask并发实例互不相干,但是他们的数据依赖于上一个阶段的所有MapTask并发实例的输出。
(4)MapReduce编程模型只能包含一个Map阶段和一个Reduce阶段,如果用户的业务逻辑非常复杂,那就只能多个MapReduce程序,串行运行。
注意
这里之所以不擅长串行执行是因为将结果放在了磁盘,每次都要进行磁盘的io操作,如果使用spark就可以在内存中进行,效率会高很多。
总结:分析WordCount数据流走向深入理解MapReduce核心思想。
MapReduce进程
一个完整的MapReduce程序在分布式运行时有三类实例进程:
(1)MrAppMaster:负责整个程序的过程调度及状态协调。
(2)MapTask:负责Map阶段的整个数据处理流程。
(3)ReduceTask:负责Reduce阶段的整个数据处理流程。
官方WordCount源码
采用反编译工具反编译源码,发现WordCount案例有Map类、Reduce类和驱动类。且数据的类型是Hadoop自身封装的序列化类型
可以先下载hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar这个文件查看
文件存储在这里/opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/share/hadoop/mapreduce
public class WordCount {
public WordCount() {
}
// 这里同样分成三个类,主类,map,reduce
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = (new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args)).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> [<in>...] <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(WordCount.TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(WordCount.IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCount.IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
for(int i = 0; i < otherArgs.length - 1; ++i) {
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[i]));
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[otherArgs.length - 1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
public static class IntSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public IntSumReducer() {
}
// 这里同样需要重写reduce然后写自己的业务逻辑代码
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
IntWritable val;
for(Iterator var5 = values.iterator(); var5.hasNext(); sum += val.get()) {
val = (IntWritable)var5.next();
}
this.result.set(sum);
context.write(key, this.result);
}
}
// 使用自己mapper继承Mapper这个类,里面的是泛型对应的KV
// 这里泛型的类型使用的是hadoop自己的类型,和Java的不太一样,Text是String,IntWritable是Int
public static class TokenizerMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private static final IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public TokenizerMapper() {
}
// 重写map方法实现自己的业务逻辑
public void map(Object key, Text value, Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while(itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
this.word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(this.word, one);
}
}
}
}
常用数据序列化类型
| Java类型 | Hadoop Writable类型 |
|---|---|
| Boolean | BooleanWritable |
| Byte | ByteWritable |
| Int | IntWritable |
| Float | FloatWritable |
| Long | LongWritable |
| Double | DoubleWritable |
| String | Text |
| Map | MapWritable |
| Array | ArrayWritable |
| Null | NullWritable |
MapReduce编程规范
用户编写的程序分成三个部分:Mapper、Reducer和Driver。
Mapper阶段
(1)用户自定义的Mapper要继承自己的父类
(2)Mapper的输入数据是KV对的形式(KV的类型可自定义)
public static class TokenizerMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private static final IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public TokenizerMapper() {
}
public void map(Object key, Text value, Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while(itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
this.word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(this.word, one);
}
}
}
| key | value |
|---|---|
| wordcount | 0:word |
| flink | 10:flink |
| key对应的是偏移量,value对应的是这一行的内容 | |
| (3)Mapper中的业务逻辑写在map()方法中 | |
| (4)Mapper的输出数据是KV对的形式(KV的类型可自定义) (5)map()方法(MapTask进程)对每一个<K,V>调用一次 |
Reducer阶段
(1)用户自定义的Reducer要继承自己的父类
(2)Reducer的输入数据类型对应Mapper的输出数据类型,也是KV
也就是说map输出的结果然后放到reduce中处理
(3)Reducer的业务逻辑写在reduce()方法中
(4)ReduceTask进程对每一组相同k的<k,v>组调用一次reduce()方法
| 输入原始数据 | map处理之后 | 输出reduce |
|---|---|---|
| a a b c c d | (a,1),(a,1),(b,1),(c,1),(c,1),(d,1) | a(1,1),b(1,1),c(1,1) |
| 具体怎么处理要看相应的业务 |
Word count案例实操
本地测试
需求
在给定的文本文件中统计输出每一个单词出现的总次数
(1)输入数据
hello.txt
atguigu atguigu
ss ss
cls cls
jiao
banzhang
xue
hadoop
(2)期望输出数据
atguigu 2
banzhang 1
cls 2
hadoop 1
jiao 1
ss 2
xue 1
需求分析
按照MapReduce编程规范,分别编写Mapper,Reducer,Driver。

这里转将text换成String是因为处理text的api太少了,String处理起来比较方便
环境准备
(1)创建maven工程,MapReduceDemo
(2)在pom.xml文件中添加如下依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.cern.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-hdfs</artifactId>
<version>3.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
编写程序
(1)编写Mapper类
/**
* 泛型中的<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT
* KEYIN:map阶段输入的key,一般是偏移量类型为LongWritable
* VALUEIN: map阶段输入的value,一般类型为Text
* KETOUT:Text
* VALUEOUT:LongWritable
* Text导包需要注意org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
*/
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,Text, IntWritable> {
Text temp= new Text();
IntWritable LONGVALUE=new IntWritable(1);
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String[] words = line.split(" ");
for (String word : words) {
temp.set(word);
context.write(temp,LONGVALUE);
}
}
}
(2) 编写Reducer类
/**
* KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT
*/
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
int count = 0;
IntWritable outV=new IntWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (IntWritable value : values) {
count+=value.get();
outV.set(count);
}
context.write(key,outV);
count=0;
}
}
(3) 编写Driver
public class WordCountDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 1 获取Job
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
// 2 设置jar包路径
job.setJarByClass(WordCountDriver.class);
// 3 关联mapper和reducer
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
// 4 设置map输出的kv类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 5 设置最终输出的KV类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 6 设置输出路径和输出路径
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path("D:\Javabigdata\Hadoop\我的Hadoop笔记\日常文件\11_input\inputword"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("D:\Javabigdata\Hadoop\我的Hadoop笔记\日常文件\output1"));
// 7 提交job
job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(0);
}
}
之后可以进行本地的测试,输出输入的结构都在windows的环境下面
运行在集群上
打jar包
引入构建的插件,将依赖也打入包中
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.6.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<descriptorRefs>
<descriptorRef>jar-with-dependencies</descriptorRef>
</descriptorRefs>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>make-assembly</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
修改路径和上传
public class WordCountDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 1 获取Job
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
// 2 设置jar包路径
job.setJarByClass(WordCountDriver.class);
// 3 关联mapper和reducer
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
// 4 设置map输出的kv类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 5 设置最终输出的KV类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 6 设置输出路径和输出路径
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path(args[1]));
// 7 提交job
job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(0);
}
}
上传到Liunx上之后运行脚本
hadoop jar wc.jar com.atguigu.mapreduce.wordcount2.WordCountDriver /wcinput /output
e.class);
// 6 设置输出路径和输出路径
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path(args[1]));
// 7 提交job
job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(0);
}
}
上传到Liunx上之后运行脚本
```shell
hadoop jar wc.jar com.atguigu.mapreduce.wordcount2.WordCountDriver /wcinput /output
最后
以上就是调皮胡萝卜最近收集整理的关于手写WordCount案例和MapReduce入门MapReduce概述的全部内容,更多相关手写WordCount案例和MapReduce入门MapReduce概述内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复