1:先看看current宏的含义:
这个宏是本篇文章的思路口,内核中有一个很常用的current宏,执向当前任务结构体。
#define current get_current()
static __always_inline struct task_struct *get_current(void)
{
unsigned long sp_el0;
asm ("mrs %0, sp_el0" : "=r" (sp_el0));
return (struct task_struct *)sp_el0;
}
可知sp_el0 指向task_struct。sp_el0本身是用于用户态的栈sp(异常级别EL0)。到了内核态,该寄存器被用来执行当前进程的任务结构。也就意味着,原来的sp_el0的值肯定在内核中某个地方保存了起来,不然返回用户态都找不到原来的值了。为了解答这个问题,先看看启动核的__primary_switched函数:最早的第一个进程由启动核运行的一段汇编代码。
arch/arm64/kernel/head.S
__primary_switched:
adrp x4, init_thread_union
add sp, x4, #THREAD_SIZE //SP在内核态就是SP_EL1
adr_l x5, init_task
msr sp_el0, x5 // Save thread_info
adr_l x8, vectors // load VBAR_EL1 with virtual
msr vbar_el1, x8 // vector table address
isb
stp xzr, x30, [sp, #-16]!
mov x29, sp
str_l x21, __fdt_pointer, x5 // Save FDT pointer
ldr_l x4, kimage_vaddr // Save the offset between
sub x4, x4, x0 // the kernel virtual and
str_l x4, kimage_voffset, x5 // physical mappings
// Clear BSS
adr_l x0, __bss_start
mov x1, xzr
adr_l x2, __bss_stop
sub x2, x2, x0
bl __pi_memset
dsb ishst // Make zero page visible to PTW
第一:sp的值 init_thread_union+#THREAD_SIZE大小地址。
第二:sp_el0的值init_task的地址。init_task就是内核静态定义的0号内核线程。
init_thread_union的地址:
./include/linux/sched/task.h:extern union thread_union init_thread_union;
./include/asm-generic/vmlinux.lds.h
#define INIT_TASK_DATA(align)
. = ALIGN(align);
__start_init_task = .;
init_thread_union = .;
init_stack = .;
KEEP(*(.data..init_task))
KEEP(*(.data..init_thread_info))
. = __start_init_task + THREAD_SIZE;
__end_init_task = .;
KEEP中的两个段 include/linux/init_task.h
/* Attach to the init_task data structure for proper alignment */
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_TASK_STRUCT_ON_STACK
#define __init_task_data __attribute__((__section__(".data..init_task")))
#else
#define __init_task_data /**/
#endif
/* Attach to the thread_info data structure for proper alignment */
#define __init_thread_info __attribute__((__section__(".data..init_thread_info")))
//
include/linux/sched.h
union thread_union {
#ifndef CONFIG_ARCH_TASK_STRUCT_ON_STACK
struct task_struct task;
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
struct thread_info thread_info;
#endif
unsigned long stack[THREAD_SIZE/sizeof(long)];
};
THEAD_SIZE 是内核栈的大小 (arch/arm64/include/asm/memory.h) #ifdef CONFIG_KASAN #define KASAN_SHADOW_SCALE_SHIFT 3 #define KASAN_SHADOW_SIZE (UL(1) << (VA_BITS - KASAN_SHADOW_SCALE_SHIFT)) #define KASAN_THREAD_SHIFT 1 #else #define KASAN_SHADOW_SIZE (0) #define KASAN_THREAD_SHIFT 0 #endif #define MIN_THREAD_SHIFT (14 + KASAN_THREAD_SHIFT) #if defined(CONFIG_VMAP_STACK) && (MIN_THREAD_SHIFT < PAGE_SHIFT) #define THREAD_SHIFT PAGE_SHIFT #else #define THREAD_SHIFT MIN_THREAD_SHIFT #endif #if THREAD_SHIFT >= PAGE_SHIFT #define THREAD_SIZE_ORDER (THREAD_SHIFT - PAGE_SHIFT) #endif #define THREAD_SIZE (UL(1) << THREAD_SHIFT)应该就是一个页面大小 64K。
struct task_struct init_task
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_TASK_STRUCT_ON_STACK
__init_task_data //将该init_task放在".data..init_task"段。正好被链接器使用
#endif
= {
#ifdef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
.thread_info = INIT_THREAD_INFO(init_task),
.stack_refcount = ATOMIC_INIT(1),
#endif
.state = 0,
.stack = init_stack,
.usage = ATOMIC_INIT(2),
.flags = PF_KTHREAD,
......
}
struct thread_info init_thread_info __init_thread_info = INIT_THREAD_INFO(init_task);
//将该段放在".data..init_thread_info"0号进行的栈和task_struct 图:
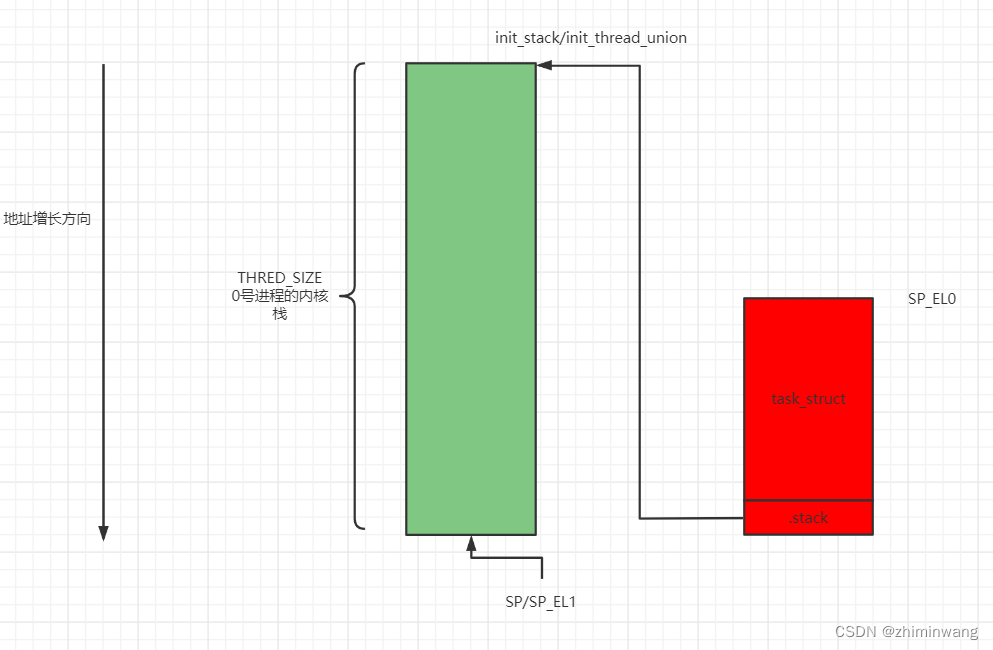
2:新创建的进程创建的内核栈。
copy_process
dup_task_struct
alloc_thread_stack_node
__vmalloc_node_range分配stack大小THREAD_SIZE
static struct task_struct *dup_task_struct(struct task_struct *orig, int node)
{
struct task_struct *tsk;
unsigned long *stack;
struct vm_struct *stack_vm_area;
int err;
if (node == NUMA_NO_NODE)
node = tsk_fork_get_node(orig);
tsk = alloc_task_struct_node(node);
if (!tsk)
return NULL;
stack = alloc_thread_stack_node(tsk, node);
if (!stack)
goto free_tsk;
stack_vm_area = task_stack_vm_area(tsk);
err = arch_dup_task_struct(tsk, orig);
/*
* arch_dup_task_struct() clobbers the stack-related fields. Make
* sure they're properly initialized before using any stack-related
* functions again.
*/
tsk->stack = stack;
#ifdef CONFIG_VMAP_STACK
tsk->stack_vm_area = stack_vm_area;
。。。。。。。省略
}
tatic unsigned long *alloc_thread_stack_node(struct task_struct *tsk, int node)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_VMAP_STACK
void *stack;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < NR_CACHED_STACKS; i++) {
struct vm_struct *s;
s = this_cpu_xchg(cached_stacks[i], NULL);
if (!s)
continue;
/* Clear stale pointers from reused stack. */
memset(s->addr, 0, THREAD_SIZE);
tsk->stack_vm_area = s;
return s->addr;
}
stack = __vmalloc_node_range(THREAD_SIZE, THREAD_ALIGN,
VMALLOC_START, VMALLOC_END,
THREADINFO_GFP,
PAGE_KERNEL,
0, node, __builtin_return_address(0));
/*
* We can't call find_vm_area() in interrupt context, and
* free_thread_stack() can be called in interrupt context,
* so cache the vm_struct.
*/
if (stack)
tsk->stack_vm_area = find_vm_area(stack);
return stack;
#else
struct page *page = alloc_pages_node(node, THREADINFO_GFP,
THREAD_SIZE_ORDER);
return page ? page_address(page) : NULL;
#endif
}
3:通过fork创建的新进程其pc地址和sp是在那里设置?
arch/arm64/kernel/process.c::copy_thread函数
_do
_fork->copy_process->copy_thread_tls->copy_thread
#define task_pt_regs(p)
((struct pt_regs *)(THREAD_SIZE + task_stack_page(p)) - 1)
#define current_pt_regs() task_pt_regs(current)
#define task_stack_page(task) ((void *)(task)->stack)
/
int copy_thread(unsigned long clone_flags, unsigned long stack_start,
unsigned long stk_sz, struct task_struct *p)
{
printk("===copy_thread pid %d stack_start %llx stk_sz %llx kernel_stack %llx n",p->pid,stack_start,stk_sz,p->stack);
struct pt_regs *childregs = task_pt_regs(p); //在p的内核栈最后保留pt_regs大小
memset(&p->thread.cpu_context, 0, sizeof(struct cpu_context));
/*
* Unalias p->thread.sve_state (if any) from the parent task
* and disable discard SVE state for p:
*/
clear_tsk_thread_flag(p, TIF_SVE);
p->thread.sve_state = NULL;
/*
* In case p was allocated the same task_struct pointer as some
* other recently-exited task, make sure p is disassociated from
* any cpu that may have run that now-exited task recently.
* Otherwise we could erroneously skip reloading the FPSIMD
* registers for p.
*/
fpsimd_flush_task_state(p);
if (likely(!(p->flags & PF_KTHREAD))) {//用户进程
*childregs = *current_pt_regs(); //使用父进程的寄存器
childregs->regs[0] = 0;
/*
* Read the current TLS pointer from tpidr_el0 as it may be
* out-of-sync with the saved value.
*/
*task_user_tls(p) = read_sysreg(tpidr_el0);
if (stack_start) {
if (is_compat_thread(task_thread_info(p)))
childregs->compat_sp = stack_start;
else
childregs->sp = stack_start; //用户空间的栈.
}
/*
* If a TLS pointer was passed to clone (4th argument), use it
* for the new thread.
*/
if (clone_flags & CLONE_SETTLS)
p->thread.uw.tp_value = childregs->regs[3];
} else {
memset(childregs, 0, sizeof(struct pt_regs));
childregs->pstate = PSR_MODE_EL1h;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ARM64_UAO) &&
cpus_have_const_cap(ARM64_HAS_UAO))
childregs->pstate |= PSR_UAO_BIT;
p->thread.cpu_context.x19 = stack_start;
p->thread.cpu_context.x20 = stk_sz;
}
p->thread.cpu_context.pc = (unsigned long)ret_from_fork; //新进程唤醒后需要执行的第一段代码入口。
p->thread.cpu_context.sp = (unsigned long)childregs; //新进程的sp寄存器值,其执行当前内核栈往后pt_regs大小。
ptrace_hw_copy_thread(p);
return 0;
}
上述打印如下:stack_start 地址范围确实在用户空间。部分为0 应该是内核线程。
[ 29.460947] ===copy_thread pid 848 stack_start ffffc25ea670 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff00000eba0000
[ 29.473410] ===copy_thread pid 1046 stack_start ffffaeb0c710 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff000023880000
[ 29.509338] ===copy_thread pid 848 stack_start ffffc25ea670 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff000023a00000
[ 29.786659] ===copy_thread pid 1 stack_start 0 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff00000e920000
[ 29.792466] ===copy_thread pid 848 stack_start ffffc25eb220 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff000023ae0000
[ 29.819915] ===copy_thread pid 848 stack_start ffffc25eb220 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff000023ca0000
[ 29.824324] ===copy_thread pid 848 stack_start ffffc25eb220 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff000023e40000
[ 29.853700] ===copy_thread pid 848 stack_start ffffc25eb220 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff000024000000
[ 29.856679] ===copy_thread pid 848 stack_start ffffc25eb220 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff0000241c0000
[ 29.909747] ===copy_thread pid 1 stack_start 0 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff00000de20000
[ 29.931232] ===copy_thread pid 1 stack_start 0 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff0000251a0000
[ 29.933685] ===copy_thread pid 1074 stack_start ffff9d53e760 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff00000f380000
[ 29.934775] ===copy_thread pid 848 stack_start ffff7ad5eae0 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff000024000000
[ 29.953477] ===copy_thread pid 1046 stack_start ffffadaaeae0 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff0000251c0000
[ 29.961483] ===copy_thread pid 1074 stack_start ffff9cd2e760 stk_sz 0 kernel_stack ffff00000f3a0000
5 任务切换核心函数cpu_switch_to
上述函数会创建新进程,在内核栈中预留pt_regs大小的空间,用来设置用户空间所需要的寄存器,新创建的进程被唤醒最终通过cpu_switch_to切换:
//x0 是prev ,x1是next 任务
ENTRY(cpu_switch_to)
mov x10, #THREAD_CPU_CONTEXT //task_struct.thread.cpu_context
add x8, x0, x10
mov x9, sp
stp x19, x20, [x8], #16 // store callee-saved registers
stp x21, x22, [x8], #16
stp x23, x24, [x8], #16
stp x25, x26, [x8], #16
stp x27, x28, [x8], #16
stp x29, x9, [x8], #16
str lr, [x8]
add x8, x1, x10
ldp x19, x20, [x8], #16 // restore callee-saved registers
ldp x21, x22, [x8], #16
ldp x23, x24, [x8], #16
ldp x25, x26, [x8], #16
ldp x27, x28, [x8], #16
ldp x29, x9, [x8], #16
ldr lr, [x8]
mov sp, x9 //将next进程的cpu_context.sp 放到sp寄存器(sp_el1)。
msr sp_el0, x1 //将next进程task_struct 地址放入sp_el0
ret
ENDPROC(cpu_switch_to)新建进程前面提到过task_struct.thread.cpu_context.SP 执行内核栈往前pt_regs大小处:
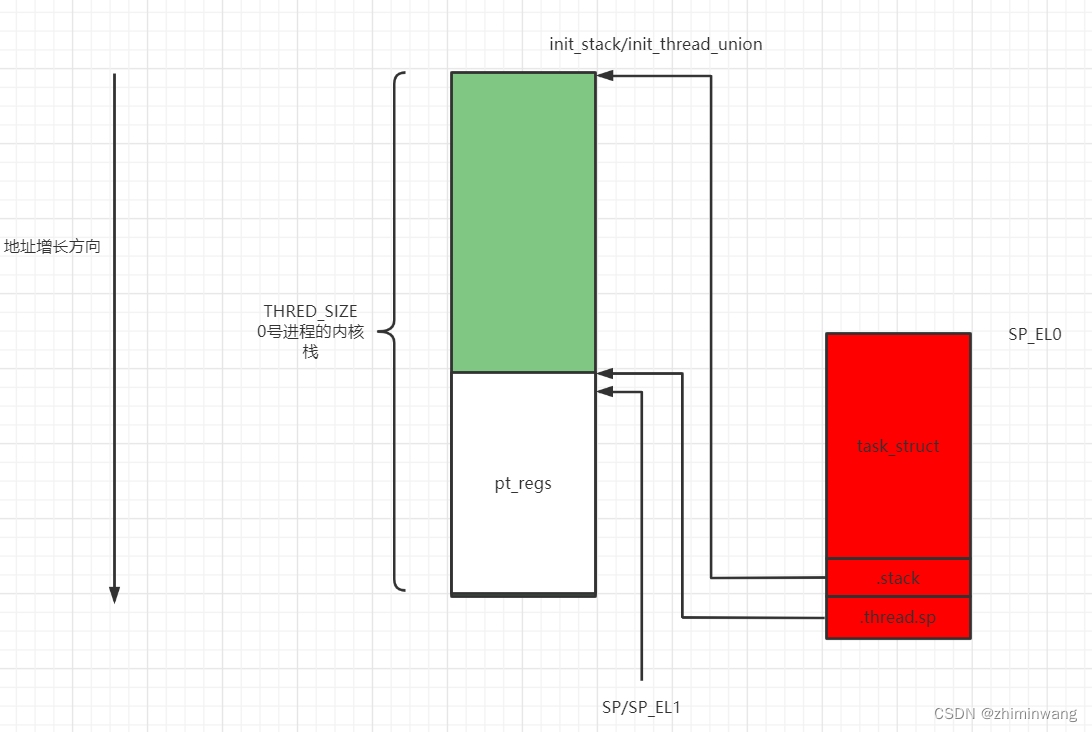
新进程的被首次唤醒运行的第一个函数是ret_from_fork。最终调用ret_to_user->kernel_exit 0:
.macro kernel_exit, el
.if el != 0
disable_daif
/* Restore the task's original addr_limit. */
ldr x20, [sp, #S_ORIG_ADDR_LIMIT]
str x20, [tsk, #TSK_TI_ADDR_LIMIT]
/* No need to restore UAO, it will be restored from SPSR_EL1 */
.endif
ldp x21, x22, [sp, #S_PC] // load ELR, SPSR
.if el == 0
ct_user_enter
.endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_SW_TTBR0_PAN
/*
* Restore access to TTBR0_EL1. If returning to EL0, no need for SPSR
* PAN bit checking.
*/
alternative_if ARM64_HAS_PAN
b 2f // skip TTBR0 PAN
alternative_else_nop_endif
.if el != 0
tbnz x22, #22, 1f // Skip re-enabling TTBR0 access if the PSR_PAN_BIT is set
.endif
__uaccess_ttbr0_enable x0, x1
.if el == 0
/*
* Enable errata workarounds only if returning to user. The only
* workaround currently required for TTBR0_EL1 changes are for the
* Cavium erratum 27456 (broadcast TLBI instructions may cause I-cache
* corruption).
*/
bl post_ttbr_update_workaround
.endif
1:
.if el != 0
and x22, x22, #~PSR_PAN_BIT // ARMv8.0 CPUs do not understand this bit
.endif
2:
#endif
.if el == 0
ldr x23, [sp, #S_SP] // load return stack pointer
msr sp_el0, x23 //还原用户空间栈,该栈保存在内核栈往前pt_regs的机构中。
tst x22, #PSR_MODE32_BIT // native task?
b.eq 3f
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_ERRATUM_845719
alternative_if ARM64_WORKAROUND_845719
#ifdef CONFIG_PID_IN_CONTEXTIDR
mrs x29, contextidr_el1
msr contextidr_el1, x29
#else
msr contextidr_el1, xzr
#endif
alternative_else_nop_endif
#endif
3:
apply_ssbd 0, x0, x1
.endif
msr elr_el1, x21 // set up the return data
msr spsr_el1, x22
ldp x0, x1, [sp, #16 * 0]
ldp x2, x3, [sp, #16 * 1]
ldp x4, x5, [sp, #16 * 2]
ldp x6, x7, [sp, #16 * 3]
ldp x8, x9, [sp, #16 * 4]
ldp x10, x11, [sp, #16 * 5]
ldp x12, x13, [sp, #16 * 6]
ldp x14, x15, [sp, #16 * 7]
ldp x16, x17, [sp, #16 * 8]
ldp x18, x19, [sp, #16 * 9]
ldp x20, x21, [sp, #16 * 10]
ldp x22, x23, [sp, #16 * 11]
ldp x24, x25, [sp, #16 * 12]
ldp x26, x27, [sp, #16 * 13]
ldp x28, x29, [sp, #16 * 14]
ldr lr, [sp, #S_LR]
add sp, sp, #S_FRAME_SIZE // restore sp //准备返回用户空间,将内核栈加S_FRAME_SIZE(pt_regs大小)。即还原成内核栈。
/*
* ARCH_HAS_MEMBARRIER_SYNC_CORE rely on eret context synchronization
* when returning from IPI handler, and when returning to user-space.
*/
.if el == 0 //eret 将恢复elr_el1 。spsr_el1等寄存器
alternative_insn eret, nop, ARM64_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0
#ifdef CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0
bne 4f
msr far_el1, x30
tramp_alias x30, tramp_exit_native
br x30
4:
tramp_alias x30, tramp_exit_compat
br x30
#endif
.else
eret
.endif
.endm
既然提到进程首次运行并返回用户空间,那么来看看内核通过异常进入内核空间。,主要看看内核如何处理内核SP和用户SP。
kernel_ventry:是异常的第一个函数。
.macro kernel_ventry, el, label, regsize = 64
.align 7
#ifdef CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0
alternative_if ARM64_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0
.if el == 0
.if regsize == 64
mrs x30, tpidrro_el0
msr tpidrro_el0, xzr
.else
mov x30, xzr
.endif
.endif
alternative_else_nop_endif
#endif
sub sp, sp, #S_FRAME_SIZE //内核栈sp 直接减S_FRAME_SIZE, 依然预留pt_regs大小空间。为后面kernel_entry 压入寄存器准备。
上面:内核栈sp 直接减S_FRAME_SIZE, 依然预留pt_regs大小空间。为后面kernel_entry 压入寄存器准备。
.macro kernel_entry, el, regsize = 64
.if regsize == 32
mov w0, w0 // zero upper 32 bits of x0
.endif
stp x0, x1, [sp, #16 * 0]
stp x2, x3, [sp, #16 * 1]
stp x4, x5, [sp, #16 * 2]
stp x6, x7, [sp, #16 * 3]
stp x8, x9, [sp, #16 * 4]
stp x10, x11, [sp, #16 * 5]
stp x12, x13, [sp, #16 * 6]
stp x14, x15, [sp, #16 * 7]
stp x16, x17, [sp, #16 * 8]
stp x18, x19, [sp, #16 * 9]
stp x20, x21, [sp, #16 * 10]
stp x22, x23, [sp, #16 * 11]
stp x24, x25, [sp, #16 * 12]
stp x26, x27, [sp, #16 * 13]
stp x28, x29, [sp, #16 * 14]
.if el == 0
clear_gp_regs
mrs x21, sp_el0 //先保存用户态栈寄存器sp_el0到x21
ldr_this_cpu tsk, __entry_task, x20 // Ensure MDSCR_EL1.SS is clear,
ldr x19, [tsk, #TSK_TI_FLAGS] // since we can unmask debug
disable_step_tsk x19, x20 // exceptions when scheduling.
apply_ssbd 1, x22, x23
.else
add x21, sp, #S_FRAME_SIZE
get_thread_info tsk
/* Save the task's original addr_limit and set USER_DS */
ldr x20, [tsk, #TSK_TI_ADDR_LIMIT]
str x20, [sp, #S_ORIG_ADDR_LIMIT]
mov x20, #USER_DS
str x20, [tsk, #TSK_TI_ADDR_LIMIT]
/* No need to reset PSTATE.UAO, hardware's already set it to 0 for us */
.endif /* el == 0 */
mrs x22, elr_el1
mrs x23, spsr_el1
stp lr, x21, [sp, #S_LR] //将x21中保存的用户态栈寄存器值压入pt_regs中。
/*
* In order to be able to dump the contents of struct pt_regs at the
* time the exception was taken (in case we attempt to walk the call
* stack later), chain it together with the stack frames.
*/
.if el == 0
stp xzr, xzr, [sp, #S_STACKFRAME]
.else
stp x29, x22, [sp, #S_STACKFRAME]
.endif
add x29, sp, #S_STACKFRAME
..........................................
.if el == 0
mov w21, #NO_SYSCALL
str w21, [sp, #S_SYSCALLNO]
.endif
/*
* Set sp_el0 to current thread_info.
*/
.if el == 0
msr sp_el0, tsk // 从用户态进入,tsk放入sp_el0用户栈寄存器。
.endif
/*
* Registers that may be useful after this macro is invoked:
*
* x21 - aborted SP
* x22 - aborted PC
* x23 - aborted PSTATE
*/
.endm
用户态通过异常进入到内核态:
1;内核栈寄存器预留pt_regs大小保留当前cpu寄存,其中就有用户态的栈寄存器sp_el0:
stp lr, x21, [sp, #S_LR] //S_LR的偏移位置,一次搞两个。
DEFINE(S_LR, offsetof(struct pt_regs, regs[30])); //regs[30] 就是第31个寄存器的位置。下一个就是SP。
2:;从内核态返回用户态将弹出之前保存的部分寄存器:
ldr x23, [sp, #S_SP] // load return stack pointer
msr sp_el0, x23
/
前面提到。用户的栈在进程创建的时候在copy_thread的时候被赋值。0号内核线程自然是没有用户栈,那么1号进程的用户栈在那里确定呢?在init/main.c的run_init_process函数增加打印日志:
6 用户1号进程的用户态栈怎么确定的?
static int run_init_process(const char *init_filename)
{
argv_init[0] = init_filename;
int ret ;
pr_info("0 Run %s as init process user_stack %llx kernel_stack %llx n""
, init_filename,current_pt_regs()->sp,current->stack);
ret = do_execve(getname_kernel(init_filename),
(const char __user *const __user *)argv_init,
(const char __user *const __user *)envp_init);
pr_info("1 Run %s as init process user_stack %llx kernel_stack %llx n""
, init_filename,current_pt_regs()->sp,current->stack);
return ret;
}
[ 9.086479] 0 Run /init as init process user_stack 0 kernel_stack ffff00000b640000
[ 9.094441] 1 Run /init as init process user_stack ffffc33ad8f0 kernel_stack ffff00000b640000
说明是在do_execv中确定的。
static struct linux_binfmt elf_format = {
.module = THIS_MODULE,
.load_binary = load_elf_binary,
.load_shlib = load_elf_library,
.core_dump = elf_core_dump,
.min_coredump = ELF_EXEC_PAGESIZE,
};
do_execve
do_execveat_common
__do_execve_file
bprm_mm_init
__bprm_mm_init //创建一个vm_area_alloc 代表进程的栈设置bprm->p
exec_binprm
search_binary_handler
fmt->load_binary(bprm);
load_elf_binary
start_thread(regs, elf_entry, bprm->p);
static inline void start_thread_common(struct pt_regs *regs, unsigned long pc)
{
memset(regs, 0, sizeof(*regs));
forget_syscall(regs);
regs->pc = pc;
}
static inline void start_thread(struct pt_regs *regs, unsigned long pc,
unsigned long sp)
{
start_thread_common(regs, pc);
regs->pstate = PSR_MODE_EL0t;
regs->sp = sp;
}
__bprm_mm_init函数:
static int __bprm_mm_init(struct linux_binprm *bprm)
{
int err;
struct vm_area_struct *vma = NULL;
struct mm_struct *mm = bprm->mm;
bprm->vma = vma = vm_area_alloc(mm);
if (!vma)
return -ENOMEM;
vma_set_anonymous(vma);
if (down_write_killable(&mm->mmap_sem)) {
err = -EINTR;
goto err_free;
}
/*
* Place the stack at the largest stack address the architecture
* supports. Later, we'll move this to an appropriate place. We don't
* use STACK_TOP because that can depend on attributes which aren't
* configured yet.
*/
BUILD_BUG_ON(VM_STACK_FLAGS & VM_STACK_INCOMPLETE_SETUP);
vma->vm_end = STACK_TOP_MAX; //0x1000000000000
vma->vm_start = vma->vm_end - PAGE_SIZE; //0xffffffff0000 相差一页
vma->vm_flags = VM_SOFTDIRTY | VM_STACK_FLAGS | VM_STACK_INCOMPLETE_SETUP;
vma->vm_page_prot = vm_get_page_prot(vma->vm_flags);
err = insert_vm_struct(mm, vma);
if (err)
goto err;
mm->stack_vm = mm->total_vm = 1;
arch_bprm_mm_init(mm, vma);
up_write(&mm->mmap_sem);
bprm->p = vma->vm_end - sizeof(void *);
return 0;
err:
up_write(&mm->mmap_sem);
err_free:
...............................................省略
}load_elf_binary函数:
static int load_elf_binary(struct linux_binprm *bprm)
{
。。。。。。。
setup_new_exec(bprm); //__set_task_comm 更新进程comm
install_exec_creds(bprm);
/* Do this so that we can load the interpreter, if need be. We will
change some of these later */
retval = setup_arg_pages(bprm, randomize_stack_top(STACK_TOP),
executable_stack); //设置进程参数,更新栈。 通过randomize_stack_top 设置一个随机栈给用户空间。
。。。。。。
}最后
以上就是勤劳纸飞机最近收集整理的关于arm64内核进程创建从内核态到用户态过程分析。1:先看看current宏的含义:2:新创建的进程创建的内核栈。3:通过fork创建的新进程其pc地址和sp是在那里设置?5 任务切换核心函数cpu_switch_to6 用户1号进程的用户态栈怎么确定的?的全部内容,更多相关arm64内核进程创建从内核态到用户态过程分析。1:先看看current宏的含义:2:新创建的进程创建的内核栈。3:通过fork创建的新进程其pc地址和sp是在那里设置?5内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复