概述总览
理解Dubbo服务调用的过程,需要对Dubbo里的组件有一定的了解。以下是Dubbo服务调用组件关系
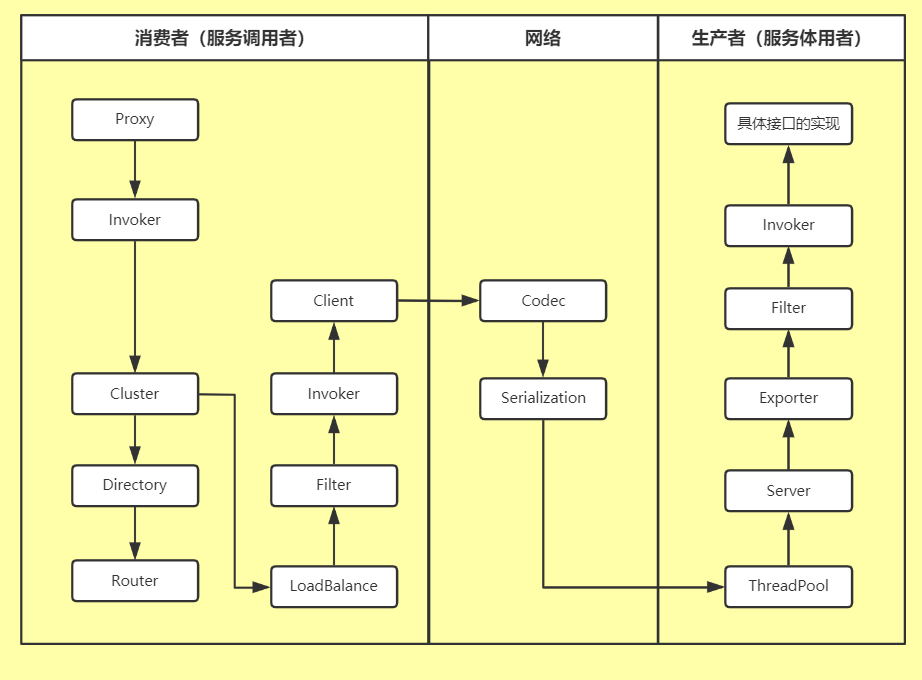
调用过程从一个Proxy开始,Proxy持有了一个Invoker对象。然后触发invoke调用。在invoke调用过程中,需要使用Cluster,Cluster负责容错。Cluster在调用之前会通过Directory获取所有可以调用的远程服务Invoker列表。由于可以调用的远程服务可能会有很多,如果用户配置了路由规则,那么还会根据路由规则将Invoker过滤一遍。
然后,存活下来的Invoker可能还会有很多。接下来就会调用LoadBalance方法做负载均衡,最终选出一个可以调用的Invoker。这个Invoker在调用之前又会进入一个过滤器链,这个过滤器链通常是处理上下文、限流、计数等。
接着,会使用Client做数据传输。传输之前肯定要做一些私有协议的构造,此时就会用到Codec接口。构造完成之后,就对数据包做序列化(Serialization),然后传输到服务提供者端。服务提供者接收到数据包,也会使用Codec处理协议头及一些半包、粘包等。处理完成之后再对完整的数据报文做反序列化处理。
随后,这个Request会被分配到线程池(ThreadPool)中进行处理。Server会处理这些Request,
根据请求查找对应的Exporter(它内部持有了Invoker)。Invoker是被用装饰器模式一层一层套了很多Filter的,因此在调用最终的实现类之前,又会经过一个服务提供者端的过滤器链。
最终,我们得到了具体接口的真实实现并调用,在原路把结果返回。
以上就是Dubbo调用过程的基本概述,参考了:《深入理解Apache Dubbo与实战》一书。
接下来本篇文章会从源码角度分析一下Dubbo调用过程中的几个关键链路。
源码
消费端的调用
调用的起始——代理
假设有一个userService服务,是远程的Dubbo服务,当我们通过本地调用其getNameById方法时,会如何调用呢?
@Override
public String getNameById(String id) {
return userService.getNameById(id);
}
如果你Debug一下,你会发现,调用到了代理里面。在Dubbo服务的引用一节,我们知道,Dubbo服务实际上是将远程的服务包装成了一个代理,因此,这里也就不难理解了。
private static class ReferenceBeanInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final ReferenceBean referenceBean;
private Object bean;
private ReferenceBeanInvocationHandler(ReferenceBean referenceBean) {
this.referenceBean = referenceBean;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return method.invoke(bean, args);
}
private void init() {
this.bean = referenceBean.get();
}
}
此类的 init 方法即为 服务引用的入口,最终会将内部对象 bean设置为对应的代理引用,bean的实际类型为 com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.InvokerInvocationHandler。调用该类的 invoke 方法如下:
public class InvokerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Invoker<?> invoker;
public InvokerInvocationHandler(Invoker<?> handler) {
this.invoker = handler;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.toString();
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate();
}
}
InvokerInvocationHandler 内部的 invoker 为 MockClusterInvoker ,它是服务引用的时候包装的。
Cluster层的调用
MockClusterInvoker 主要功能是对Dubbo Mock特性的支持。Dubbo服务在调用到此处的时候发挥了作用。
如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result result = null;
// $-- 从url里面获取mock配置
String value = directory.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.MOCK_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString()).trim();
if (value.length() == 0 || value.equalsIgnoreCase("false")) {
// $-- 无mock场景,直接调用
//no mock
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
} else if (value.startsWith("force")) {
// $-- 强制mock场景
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.info("force-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " force-mock enabled , url : " + directory.getUrl());
}
//force:direct mock
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, null);
} else {
// $-- 失败进入mock场景
//fail-mock
try {
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) {
throw e;
} else {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("fail-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " fail-mock enabled , url : " + directory.getUrl(), e);
}
// $-- 发生异常,进入mock
// $-- mock
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, e);
}
}
}
return result;
}
如果我们没有配置mock的话,就会继续往下调用。这里调用的 invoker 类型是 FailoverClusterInvoker 。
@Override
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
// $-- 校验节点是否销毁
checkWhetherDestroyed();
LoadBalance loadbalance = null;
// $-- 将attachments绑定到invocation中
// binding attachments into invocation.
Map<String, String> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachments();
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
((RpcInvocation) invocation).addAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
// $-- 获取invoker列表
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
if (invokers != null && !invokers.isEmpty()) {
// $-- 获取第一个服务提供者的invoker的负载均衡策略,默认为 random
loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(invokers.get(0).getUrl()
.getMethodParameter(RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation), Constants.LOADBALANCE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE));
}
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
}
在这个方法里面,我们需要关注一下 invoker 的获取。
事实上,Dubbo关于 invoker 的获取,有一套集群容错的策略。一般来说,流程如下:
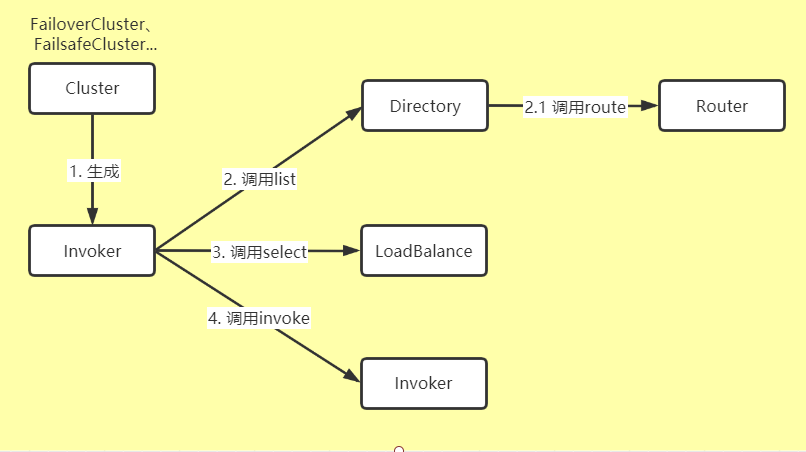
Cluster的总体工作流程可以分为以下几步:
1. 生成invoker对象
2. 获得可调用的服务列表
3. 做负载均衡
4. 做RPC调用
在这个方法里面,我们主要完成了前两步,并且获取到了相应的负载均衡策略。
invoker 的获取逻辑(list方法)如下:
protected List<Invoker<T>> list(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = directory.list(invocation);
return invokers;
}
list方法里,将 invoker 的获取逻辑又委派给了 Directory ,实现逻辑在方法com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.directory.AbstractDirectory#list 中
@Override
public List<Invoker<T>> list(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
if (destroyed) {
throw new RpcException("Directory already destroyed .url: " + getUrl());
}
// $-- 调用子类的doList方法获取invokers列表
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = doList(invocation);
List<Router> localRouters = this.routers; // local reference
if (localRouters != null && !localRouters.isEmpty()) {
// $-- 遍历所有的router,进行invoker的过滤
for (Router router : localRouters) {
try {
if (router.getUrl() == null || router.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.RUNTIME_KEY, false)) {
invokers = router.route(invokers, getConsumerUrl(), invocation);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Failed to execute router: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
}
return invokers;
}
doList 方法是由其子类 RegistryDirectory 来实现的,其中的 invoker列表 是在 notify 的时候更新的。
@Override
public List<Invoker<T>> doList(Invocation invocation) {
if (forbidden) {
// 1. No service provider 2. Service providers are disabled
throw new RpcException(RpcException.FORBIDDEN_EXCEPTION,
"No provider available from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " for service " + getConsumerUrl().getServiceKey() + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please check status of providers(disabled, not registered or in blacklist).");
}
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = null;
// $-- 这里的methodInvokerMap是在notify的时候更新的
Map<String, List<Invoker<T>>> localMethodInvokerMap = this.methodInvokerMap; // local reference
if (localMethodInvokerMap != null && localMethodInvokerMap.size() > 0) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
Object[] args = RpcUtils.getArguments(invocation);
if (args != null && args.length > 0 && args[0] != null
&& (args[0] instanceof String || args[0].getClass().isEnum())) {
// $-- 根据方法名和首参匹配invoker。有点奇怪。。。
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName + "." + args[0]); // The routing can be enumerated according to the first parameter
}
if (invokers == null) {
// $-- 根据方法名匹配invoker
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName);
}
if (invokers == null) {
// $-- 根据*匹配invoker
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(Constants.ANY_VALUE);
}
if (invokers == null) {
// $-- 遍历映射结果集,取第一个invoker
Iterator<List<Invoker<T>>> iterator = localMethodInvokerMap.values().iterator();
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
invokers = iterator.next();
}
}
}
return invokers == null ? new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(0) : invokers;
}
对于获取到的 invoker列表 ,还要进行route过滤。这里使用的 router列表 ,是根据Dubbo 的SPI机制获取的,并且额外还增加了一个 MockInvokerSeleter 类,用于Mock特性的实现。
route 的具体逻辑我们就不细看了,我们接着回到 invoke 方法中。
带着获取到的 invoker列表 和通过Dubbo SPI获取到的 负载均衡器,Dubbo会调用 FailoverClusterInvoker 的 doInvoke 方法。
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
List<Invoker<T>> copyinvokers = invokers;
// $-- invoker空校验
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
// $-- 获取retries重试次数,默认一次
int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.RETRIES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1;
if (len <= 0) {
len = 1;
}
// retry loop.
// $-- 记录最后一次异常
RpcException le = null; // last exception.
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyinvokers.size()); // invoked invokers.
Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
//Reselect before retry to avoid a change of candidate `invokers`.
//NOTE: if `invokers` changed, then `invoked` also lose accuracy.
if (i > 0) {
// $-- 有过一次失败之后,需要重新校验节点节点是否被销毁、invokers是否为空
checkWhetherDestroyed();
copyinvokers = list(invocation);
// check again
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
}
// $-- 重新负载均衡
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyinvokers, invoked);
invoked.add(invoker);
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked);
try {
// $-- 进行远程调用
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Although retry the method " + invocation.getMethodName()
+ " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ " was successful by the provider " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress()
+ ", but there have been failed providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ le.getMessage(), le);
}
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) { // biz exception.
throw e;
}
le = e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
}
throw new RpcException(le != null ? le.getCode() : 0, "Failed to invoke the method "
+ invocation.getMethodName() + " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ ". Tried " + len + " times of the providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version "
+ Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ (le != null ? le.getMessage() : ""), le != null && le.getCause() != null ? le.getCause() : le);
}
failover是Dubbo默认的容错机制。出现失败后,会重试其他服务器。通过retries参数进行重试次数配置
FailoverClusterInvoker 中,先是对 invoker列表 做了 负载均衡,选出要调用的 invoker,然后再进行 invoker 的调用。当然,其中有大量的代码,是为了其集群容错的机制的实现而写的,这里暂不关注。
我们先看看其负载均衡的调用,在 select 方法中
protected Invoker<T> select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty())
return null;
String methodName = invocation == null ? "" : invocation.getMethodName();
// $-- 粘性调用(粘滞连接)参数获取。如果设置为true,则使用同一个provider进行调用
boolean sticky = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.CLUSTER_STICKY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_STICKY);
{
//ignore overloaded method
if (stickyInvoker != null && !invokers.contains(stickyInvoker)) {
// $-- 如果能获取到上次调用的invoker,但是不在此次的invokers列表中,则将缓存的粘滞连接invoker置空
stickyInvoker = null;
}
//ignore concurrency problem
if (sticky && stickyInvoker != null && (selected == null || !selected.contains(stickyInvoker))) {
if (availablecheck && stickyInvoker.isAvailable()) {
// $-- 缓存的粘滞连接invoker满足条件,直接返回
return stickyInvoker;
}
}
}
Invoker<T> invoker = doSelect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
if (sticky) {
// $-- 配置了粘性调用,则保存invoker,方便下次调用直接获取
stickyInvoker = invoker;
}
return invoker;
}
可以看到,select 方法并不是集群容错的具体实现。这个方法其实做的是“粘性调用”的特性的支持。
有时候我们发现一系列的Dubbo请求总是调用到同一台机器中,就是与粘性调用相关了。
真正负载均衡相关的操作,在其 doSelect 方法中
private Invoker<T> doSelect(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty())
return null;
if (invokers.size() == 1)
return invokers.get(0);
if (loadbalance == null) {
// $-- 获取负载均衡扩展实现,默认 random
loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE);
}
// $-- 负载均衡节点选择
Invoker<T> invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, getUrl(), invocation);
//If the `invoker` is in the `selected` or invoker is unavailable && availablecheck is true, reselect.
// $-- 如果(invoker在已选择列表中) 或 (invoker不可用,但是配置了可用性检测),则需要重新负载均衡进行选择(reselect)
if ((selected != null && selected.contains(invoker))
|| (!invoker.isAvailable() && getUrl() != null && availablecheck)) {
try {
Invoker<T> rinvoker = reselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected, availablecheck);
if (rinvoker != null) {
invoker = rinvoker;
} else {
//Check the index of current selected invoker, if it's not the last one, choose the one at index+1.
// $-- 如果reselect获取不到invoker,则将select获取的invoker,序列号+1从invoker列表中获取invoker
// $-- 如果select获取invoker已经是invoker列表中的最后一个,那么就只能返回此invoker了
int index = invokers.indexOf(invoker);
try {
//Avoid collision
invoker = index < invokers.size() - 1 ? invokers.get(index + 1) : invokers.get(0);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(e.getMessage() + " may because invokers list dynamic change, ignore.", e);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("cluster reselect fail reason is :" + t.getMessage() + " if can not solve, you can set cluster.availablecheck=false in url", t);
}
}
return invoker;
}
loadbalance.select方法是具体负载均衡的实现,Dubbo中涉及到3中不同的策略。具体的策略这里就不再细述了。
负载均衡之后,我们终于选出来了一个invoker,进行调用了。但是真的就这么简单吗?其实并不是。
Protocol层的调用
接下来的调用,就涉及到Protocol层了。
负载均衡选出来的 invoker对象 ,实际上是 com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.InvokerWrapper类。正如它的名字一样,它其实也是一个包装类,其内部包装的invoker是 ProtocolFilterWrapper 类。
private static <T> Invoker<T> buildInvokerChain(final Invoker<T> invoker, String key, String group) {
Invoker<T> last = invoker;
// $-- 根据key和group获取自动激活的Filter
List<Filter> filters = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Filter.class).getActivateExtension(invoker.getUrl(), key, group);
if (!filters.isEmpty()) {
// $-- 这里是倒排遍历,因为只有倒排,最外层的Invoker才能使第一个过滤器
for (int i = filters.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final Filter filter = filters.get(i);
// $-- 会把真实的Invoker(服务对象ref)放到拦截器的末尾
final Invoker<T> next = last;
// $-- 为每一个filter生成一个exporter,依次串起来
last = new Invoker<T>() {
@Override
public Class<T> getInterface() {
return invoker.getInterface();
}
@Override
public URL getUrl() {
return invoker.getUrl();
}
@Override
public boolean isAvailable() {
return invoker.isAvailable();
}
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
// $-- 每次调用都会传递给下一个拦截器
return filter.invoke(next, invocation);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
invoker.destroy();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return invoker.toString();
}
};
}
}
return last;
}
如果你看过Dubbo的服务引用过程,就会知道,invoker在包装的时候,是会经过 filter链 和 listener链 的包装的。
这里的 invoker 是 ProtocolFilterWrapper类,其会调用配置的 filter链。默认来说,会调用 以下几个filter:
- ConsumerContextFilter
- FutureFilter
- MonitorFilter
filter链 调用完之后,会调用内部的 listener链。listener链 的 invoke 调用结束之后,会调用到 AbstractInvoker 的 invoke 方法。
public Result invoke(Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
// if invoker is destroyed due to address refresh from registry, let's allow the current invoke to proceed
if (destroyed.get()) {
logger.warn("Invoker for service " + this + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " is destroyed, "
+ ", dubbo version is " + Version.getVersion() + ", this invoker should not be used any longer");
}
RpcInvocation invocation = (RpcInvocation) inv;
invocation.setInvoker(this);
if (attachment != null && attachment.size() > 0) {
invocation.addAttachmentsIfAbsent(attachment);
}
Map<String, String> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachments();
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
/**
* invocation.addAttachmentsIfAbsent(context){@link RpcInvocation#addAttachmentsIfAbsent(Map)}should not be used here,
* because the {@link RpcContext#setAttachment(String, String)} is passed in the Filter when the call is triggered
* by the built-in retry mechanism of the Dubbo. The attachment to update RpcContext will no longer work, which is
* a mistake in most cases (for example, through Filter to RpcContext output traceId and spanId and other information).
*/
invocation.addAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
if (getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.ASYNC_KEY, false)) {
invocation.setAttachment(Constants.ASYNC_KEY, Boolean.TRUE.toString());
}
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
try {
return doInvoke(invocation);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) { // biz exception
Throwable te = e.getTargetException();
if (te == null) {
return new RpcResult(e);
} else {
if (te instanceof RpcException) {
((RpcException) te).setCode(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION);
}
return new RpcResult(te);
}
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) {
return new RpcResult(e);
} else {
throw e;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
return new RpcResult(e);
}
}
这个方法里,doInvoke 调用的,是 DubboInvoker类的 doInvoke 方法。
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
inv.setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath());
inv.setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, version);
ExchangeClient currentClient;
if (clients.length == 1) {
currentClient = clients[0];
} else {
currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length];
}
try {
boolean isAsync = RpcUtils.isAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);
int timeout = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
if (isOneway) {
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
return new RpcResult();
} else if (isAsync) {
ResponseFuture future = currentClient.request(inv, timeout);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(new FutureAdapter<Object>(future));
return new RpcResult();
} else {
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
return (Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get();
}
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION, "Invoke remote method timeout. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, "Failed to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
DubboInvoker 的 doInvoke 方法,里面涉及到具体Dubbo协议相关部分的处理逻辑,包括请求的构建、传输。其下层就是Exchange层的内容了。
Exchange层、Transport层的调用
Dubbo服务调用到这里,就已经基本不涉及到业务部分了。Dubbo的Exchange层和Transport层,主要是和网络传输、协议相关的内容。对于想要了解Dubbo协议、Dubbo请求响应模型、线程模型的同学,可以再细看。这里我们就不赘述了。
服务提供端的响应
Exchange层、Transport层的调用
服务提供端接收到消费端的调用请求后,一般情况下会经由以下调用链路
- ChannelEventRunnable.run
- DecodeHandler.received
- HeaderExchangeHandler.received
- HeaderExchangeHandler.handleRequest
这一部分链路,主要还是处理网络传输、协议、编解码相关的内容,解析出上游的请求报文。
Protocol层的调用
随后就会进行Dubbo协议的处理了。
- DubboProtocol.reply
@Override
public Object reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
if (message instanceof Invocation) {
Invocation inv = (Invocation) message;
// $-- 查找关联的invoker
Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv);
// need to consider backward-compatibility if it's a callback
if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equals(inv.getAttachments().get(IS_CALLBACK_SERVICE_INVOKE))) {
String methodsStr = invoker.getUrl().getParameters().get("methods");
boolean hasMethod = false;
if (methodsStr == null || methodsStr.indexOf(",") == -1) {
hasMethod = inv.getMethodName().equals(methodsStr);
} else {
String[] methods = methodsStr.split(",");
for (String method : methods) {
if (inv.getMethodName().equals(method)) {
hasMethod = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (!hasMethod) {
logger.warn(new IllegalStateException("The methodName " + inv.getMethodName()
+ " not found in callback service interface ,invoke will be ignored."
+ " please update the api interface. url is:"
+ invoker.getUrl()) + " ,invocation is :" + inv);
return null;
}
}
RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(channel.getRemoteAddress());
// $-- 继续进行invoke调用
return invoker.invoke(inv);
}
throw new RemotingException(channel, "Unsupported request: "
+ (message == null ? null : (message.getClass().getName() + ": " + message))
+ ", channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress());
}
这里的reply是匿名内部类的方法。其关键是invoker.invoke(inv);这一句调用。这里的invoker是 ProtocolFilterWrapper 类。
ProtocolFilterWrapper在构建的时候,就已经包装好了一些列的filter链和listener链,此处的调用会触发一系列的filter链和listener链的调用,如 EchoFilter、ClassLoaderFilter、GenericFilter…ExceptionFilter。
我们以 ExceptionFilter 为例,看一下其内部如何处理。
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
try {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
// $-- 不会处理GenericService类型invoker的异常
if (result.hasException() && GenericService.class != invoker.getInterface()) {
try {
Throwable exception = result.getException();
// directly throw if it's checked exception
// $-- check Exception直接抛出
if (!(exception instanceof RuntimeException) && (exception instanceof Exception)) {
return result;
}
// directly throw if the exception appears in the signature
// $-- 如果异常已经在被调用方法中声明了,那么也直接抛出
try {
Method method = invoker.getInterface().getMethod(invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes());
Class<?>[] exceptionClassses = method.getExceptionTypes();
for (Class<?> exceptionClass : exceptionClassses) {
if (exception.getClass().equals(exceptionClass)) {
return result;
}
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
return result;
}
// for the exception not found in method's signature, print ERROR message in server's log.
logger.error("Got unchecked and undeclared exception which called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost()
+ ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName()
+ ", exception: " + exception.getClass().getName() + ": " + exception.getMessage(), exception);
// directly throw if exception class and interface class are in the same jar file.
// $-- 如果异常类和接口类在同一个jar包中,那么也直接抛出异常
String serviceFile = ReflectUtils.getCodeBase(invoker.getInterface());
String exceptionFile = ReflectUtils.getCodeBase(exception.getClass());
if (serviceFile == null || exceptionFile == null || serviceFile.equals(exceptionFile)) {
return result;
}
// directly throw if it's JDK exception
// $-- JDK异常也直接抛出
String className = exception.getClass().getName();
if (className.startsWith("java.") || className.startsWith("javax.")) {
return result;
}
// directly throw if it's dubbo exception
// $-- Dubbo异常也直接抛出
if (exception instanceof RpcException) {
return result;
}
// otherwise, wrap with RuntimeException and throw back to the client
// $-- 其他类型的异常(一般是消费者端不存在的自定义异常),将异常转换为字符串,并包装成一个RuntimeException返回
return new RpcResult(new RuntimeException(StringUtils.toString(exception)));
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Fail to ExceptionFilter when called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost()
+ ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName()
+ ", exception: " + e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
return result;
}
}
return result;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
logger.error("Got unchecked and undeclared exception which called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost()
+ ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName()
+ ", exception: " + e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
throw e;
}
}
ExceptionFilter 中主要处理异常相关的处理。其中对于真实方法的调用,其实也是一句 Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
这里的 invoker 其实也是 InvokerWrapper,它会依次调用如下方法:
- InvokerWrapper.invoke
- DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker.invoke
- AbstractProxyInvoker.invoke
在 AbstractProxyInvoker.invoke 中,会执行 doInvoke 方法,然后将其构造成一个 Result 类型的对象返回。
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
try {
return new RpcResult(doInvoke(proxy, invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes(), invocation.getArguments()));
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
return new RpcResult(e.getTargetException());
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to invoke remote proxy method " + invocation.getMethodName() + " to " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
我们注意到,当你再点击 doInvoke 方法,查看它的具体实现时,发现只有两个(默认情况下):
-
JavassistProxyFactory.doInvoke
-
JdkProxyFactory.doInvoke
这里的两个方法,其实都是去使用代理调用真正的方法。到底使用哪一个进行调用,要看你Dubbo SPI中配置的是哪一个了。
默认情况下,Dubbo使用 JavassistProxyFactory.doInvoke 方法进行调用。
调用的尾声——代理
JavassistProxyFactory.doInvoke其实是个匿名方法,它会依次调用如下方法:
- JavassistProxyFactory$1.doInvoke
- Wrapper1.invokeMethod(Wrapper1.java)
- UserServiceImpl.getNameById(真正的目标方法)
这里插一些题外话:这个doInvoke方法是什么时候构造的呢?
其实答案就在 JavassistProxyFactory 类中,它的getInvoker方法中,进行了Invoker实例的创建。
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
// TODO Wrapper cannot handle this scenario correctly: the classname contains '$'
// $-- Wrapper不能正确处理带$的类名
// $-- 对实现类进行包装,如果类名含有$,则使用接口类型
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf('$') < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type);
// $-- 创建Invoker实例并返回
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
}
};
}
这里其实也可以看到,doInvoke方法,实际上又调用了 wrapper的invokeMethod方法。而这个wrapper呢,是通过Wrapper.getWrapper来动态生成的代码。因此在实际调用运行时进行debug的话,你debug不到这些代码执行的。
public static Wrapper getWrapper(Class<?> c) {
while (ClassGenerator.isDynamicClass(c)) // can not wrapper on dynamic class.
c = c.getSuperclass();
// $-- Object类型处理
if (c == Object.class)
return OBJECT_WRAPPER;
// $-- 先去WRAPPER_MAP缓存中查找
Wrapper ret = WRAPPER_MAP.get(c);
if (ret == null) {
// $-- 缓存中没有,生成Wrapper类,并放入缓存
ret = makeWrapper(c);
WRAPPER_MAP.put(c, ret);
}
return ret;
}
上述代码中的 makeWrapper方法,就是动态生成代码的代码了。(太长了,这里就不展示了)
以本次调用的getNameById方法为例,实际动态生成的invokeMethod方法如下:
public Object invokeMethod(Object o, String n, Class[] p, Object[] v) throws java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException {
cn.hewie.hservice.facade.impl.UserServiceImpl w;
try {
w = ((cn.hewie.hservice.facade.impl.UserServiceImpl) $1);
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
}
try {
if ("getNameById".equals($2) && $3.length == 1) {
return ($w) w.getNameById((java.lang.String) $4[0]);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException(e);
}
throw new com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.NoSuchMethodException("Not found method "" + $2 + "" in class cn.hewie.hservice.facade.impl.UserServiceImpl.");
}
这里就能清楚的看到,它最终还是调用了我们的getNameById方法,不过在外部加了一些异常处理的逻辑。
到这里,整个从消费端到提供端的调用逻辑,就已经走通了。
总结
总结一下吧!在服务的引用过程中,Dubbo经过层层的包装,将Invoker做成了一个代理,提供给用户。使得用户仅仅只要像调用自己本地服务一样调用即可。
在Dubbo服务调用的过程中,其实正是这一过程的“逆过程”。Dubbo将代理的Invoker层层剥开,放出里面一个又一个“套娃”,每个套娃完成自己特定的功能和效用,最终协调一致,完成了整个服务的调用。
Dubbo说简单点,就是远程服务的调用。但是为了其各种各样的特性,因此多了很多处理逻辑。如 集群容错、路由、负载均衡、Mock。。。在体会Dubbo调用过程中,这些细节可以暂时放一放,不要太纠结,这样才能更快更好的理解Dubbo服务调用的过程实质。
最后
以上就是感动衬衫最近收集整理的关于Dubbo服务调用的过程的全部内容,更多相关Dubbo服务调用内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复