1.FileStream 读取文件
FileStream读取的文件为字节数组,与文件格式无关.(文件在内存中的真实状态为二进制保存)
FileStream fs = new FileStream(filePathAndName, FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read);
byte[] FileByte = new byte[fs.Length];
fs.Read(FileByte, 0, FileByte.Length);
fs.Close();
由于byte只表示数值(0-255),因此,只有指定了编码方式,才能将byte转化为一个可见的字符串。此外,你不能通过任何方式输出字符串:既没有类似C++中printf(%s)的用法,也不能直接byte[].toString()。
如果想转化为字符串,需要给定编码,并进行如下调用:
string str= Encoding.ASCII.GetString(FileByte);
由于ASCII编码的范围是0-127,因此,对于byte[]中大于127的值,在转换之后会直接变为字符’?’。
由于byte不能直接显示为字符,因此,byte并不是作为字符的存储格式,而是常用于存储数据流
将byte[]数组转换为char[]数组
char[] FileChar = new char[FileByte.Length];
Decoder d = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetDecoder();
d.GetChars(FileByte, 0, FileByte.Length, FileChar, 0);
Console.WriteLine(FileChar);
首先实例化编码器,并指定编码方式,将byte[]转换为char[]
2.FileStream写入文件
将char[] 使用FileStream 写入一个文件,首先要对char[]进行编码,将char[]转换为byte[]
char[] fileChar = "A Char Array".ToArray();
FileByte=new byte[FileChar.Length];
Encoder e = Encoding.UTF8.GetEncoder();
e.GetBytes(FileChar, 0, fileChar.Length, FileByte, 0, true);
FileStream fs2=new FileStream(loadFilePathAndName,FileMode.Create,FileAccess.Write);
fs2.Write(FileByte,0,FileByte.Length);
fs2.Close();
或者直接使用下面函数进行编码:
FileByte = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(FileChar,0,FileChar.Length);
3.StreamWriter
操作字节比较麻烦,fileStram首先要将字节按照指定的编码方式进行编码后(转为byte)才可以写入文件时,通常会创建一个StreamWriter 或者StreamReader,使用它们来处理文件
StreamWriter 可以将字符和字符串写入文件
由于一般直接使用File.Write()等方法,很少使用到StreamWriter,这里就直接贴资料中的代码:

使用StreamWriter写入文件
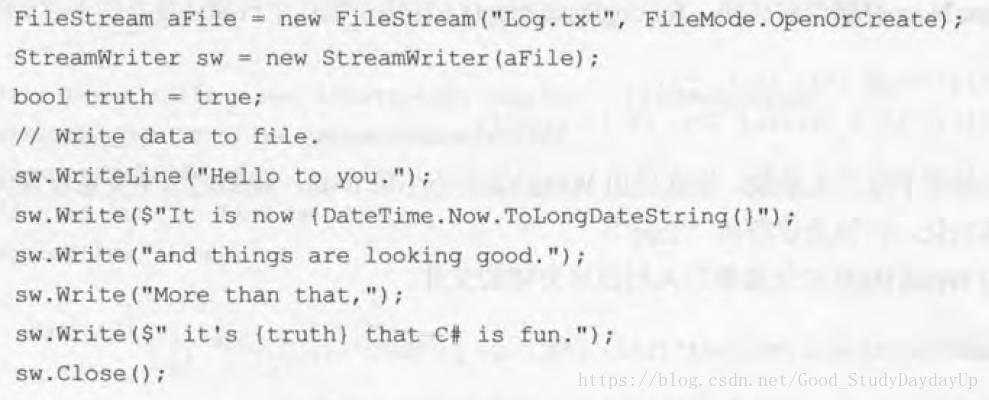
StreamReader与StreamWriter类似

总结:
FileStream Read到的数据流通常用来对文件进行存储,读到是文件真实的字节数组,所以便于传输.
将字节数组进行解码,按照指定的解码方式,会成为字节数组
StreamWriter 和StreamReader 可以直接操作字符和字符串,通常用来读取文件内容和向文件写入数据.
最后
以上就是饱满夏天最近收集整理的关于FileStream,StreamReader,StreamWiter的用法的全部内容,更多相关FileStream,StreamReader,StreamWiter内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复