1. 框架概述
- Spring是轻量级的开源JavaEE框架
- Spring可以解决企业应用开发的复杂性,可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库(实际上Spring自身也提供了展现层的SpringMVC和持久层的SpringJDBC)
- Spring有两个核心部分:IOC和Aop
- IOC(Inversion of Control) 控制反转,把创建对象的过程交给spring进行管理
- AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming) 面向切面,不修改源代码进行功能增强
spring特点
方便解耦,简化开发
AOP编程支持
方便程序测试
方便和其他框架进行整合
方便进行事务操作
降低API开发难度
spring下载地址
2. IOC容器
2.1 IOC概念原理
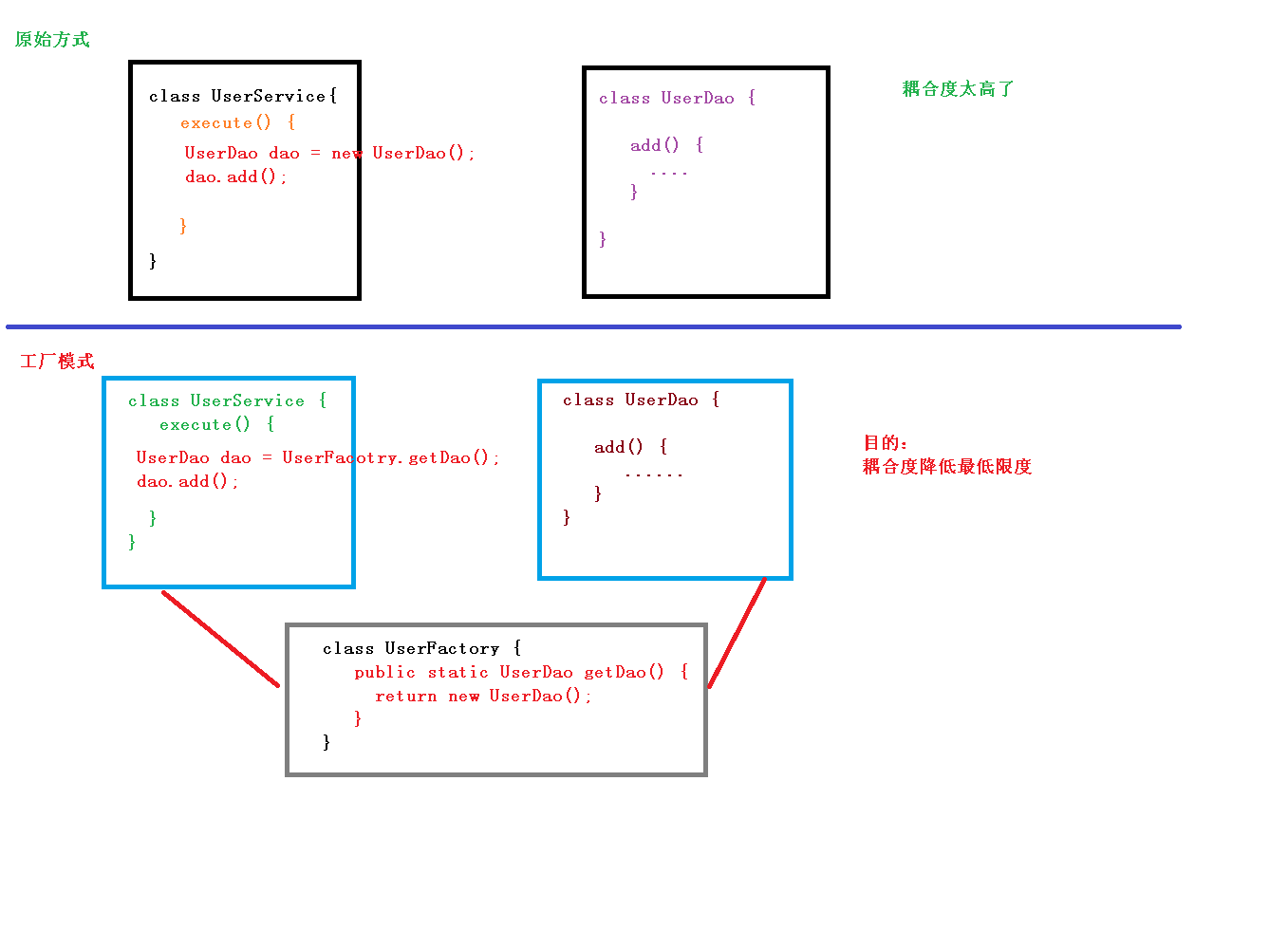
- 控制反转,把对象创建和对象之间的调用过程,交给Spring进行管理
- 使用IOC目的,为了耦合度降低
- 底层原理:xml解析、工厂模式、反射

2.2 IOC接口(BeeanFactory)
- IOC思想基于IOC容器完成,IOC容器底层就是对象工厂
- Spring提供IOC容器实现两种方式(两个接口)
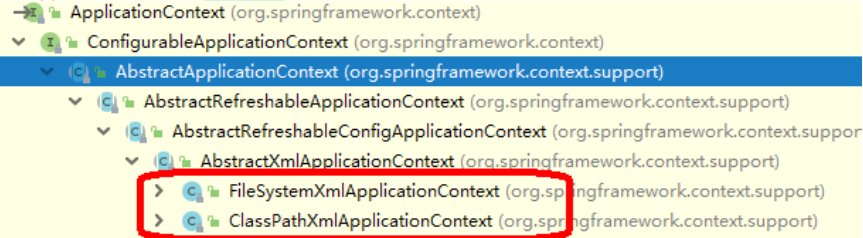
- BeanFactory:IOC容器基本实现,是Spring内部的使用接口,不提供开发人员进行使用,加载配置文件时,不会创建对象,获取(使用)对象时才会创建
- ApplicationContext:BeanFactory接口的子接口,提供更强大的功能,一般开发人员使用,加载配置文件时就会创建对象
- ApplicationContext主要实现类
2.3 IOC操作Bean管理(基于xml)
2.3.1 Bean管理
Bean管理指的就是两个操作
- Spring创建对象
- Spring注入属性
Bean管理有两种方式
- 基于xml配置文件方式
- 基于注解方式实现
2.3.2 基于xml方式创建对象
- 在spring配置文件中,使用bean标签,就可以实现对象创建
- id属性:唯一标识
- class属性:类全路径
- 创建对象时,默认执行无参数执行方法
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置User类对象创建-->
<bean id="user" class="com.spring5.User"></bean>
</beans>
2.3.3 基于xml方式注入属性
- DI:依赖注入,就是注入属性
- 1.set方法进行注入
<!--1.set方法注入属性-->
<bean id="book" class="com.spring5.Book">
<!--使用property完成属性注入-->
<property name="bName" value="0 to 1"></property>
</bean>
@Test
public void testBook1() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
Book book = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
System.out.println(book);
book.test();
}
- 2.使用有参构造进行注入
<!--2.有参构造器注入属性-->
<bean id="order" class="com.spring5.Order">
<constructor-arg name="oname" value="dj20210577731"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="Peking"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
@Test
public void testOrder() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
Order order = context.getBean("order", Order.class);
System.out.println(order);
order.test();
}
- 3.p名称空间注入,可以简化基于xml配置方式,使用不多
<bean id="book1" class="com.spring5.Book" p:bName="0000">
</bean>
xml注入其他类型属性
1.字面量
<!--向属性注入null值-->
<property name="address">
<null/>
</property>
<!--属性值中包含特殊符号 CDATA-->
<property name="address">
<value>
<![CDATA[<<<Shanghai>>>]]>
</value>
</property>
2.注入属性-外部bean
- 创建两个类service类和dao类
- 在service调用dao里的方法
- 在spring配置文件中进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--1.service和dao对象创建-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.spring5.service.UserService">
<!--注入userDao对象-->
<property name="userDao" ref="userDaoImpl"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="userDaoImpl" class="com.spring5.dao.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
public class TestBean {
@Test
public void test() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.add();
}
}
3.注入属性-内部bean和级联赋值
- 一对多关系:部门和员工
<!--内部bean-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.spring5.bean.Emp">
<property name="ename" value="gai"></property>
<property name="gender" value="男"></property>
<!--对象类型属性-->
<property name="dept">
<bean id="dept" class="com.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="经理部"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
4.注入属性-级联赋值
<!--级联赋值-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.spring5.bean.Emp">
<property name="ename" value="gai"></property>
<property name="gender" value="男"></property>
<!--级联赋值-->
<property name="dept" ref="dept"></property>
<property name="dept.dname" value="技术部"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="财务部"></property>
</bean>
xml注入属性集合
1.注入数组类型属性
2.注入List集合类型属性
3.注入Map集合类型属性
<bean id="stu" class="com.spring.collectiontype.Stu">
<!--数组类型属性注入-->
<property name="courses">
<array>
<value>语文</value>
<value>数学</value>
<value>英语</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--list类型属性注入-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>三三</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--map类型属性注入-->
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="语文" value="Yuwen"></entry>
<entry key="数学" value="Shuxue"></entry>
<entry key="英语" value="Yingyu"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--set类型属性注入-->
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>Mysql</value>
<value>redis</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
4.在集合里设置对象类型值
<bean class="com.spring.collectiontype.Course" id="course1">
<property name="cname" value="Java"/>
</bean>
<bean class="com.spring.collectiontype.Course" id="course2">
<property name="cname" value="Python"/>
</bean>
<property name="courseList">
<list>
<ref bean="course1"></ref>
<ref bean="course2"></ref>
</list>
</property>
5.把集合注入部分提取出来
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<!--提取list集合类型属性注入-->
<util:list id="bookList">
<value>Java</value>
<value>Python</value>
<value>C++</value>
</util:list>
<!--使用-->
<bean class="com.spring.collectiontype.Book" id="book">
<property name="list" ref="bookList"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
IOC操作Bean管理(FactoryBean)
- Spring有两种类型bean,一种普通bean,一种工厂bean
- 普通bean:定义什么类型返回什么类型
- 工厂bean:定义的类型和返回的类型可以不同
public class MyBean implements FactoryBean<Course> {
//定义返回bean
@Override
public Course getObject() throws Exception {
Course course = new Course();
course.setCname("yuwen");
return course;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
}
@Test
public void test3() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean12.xml");
Course course = context.getBean("myBean", Course.class);
System.out.println(course);
}
IOC操作Bean管理(bean作用域)
- 在spring里面,设置创建bean实例是单实例还是多实例
- 默认情况下,bean是单实例对象
- scope值singleton是单实例,加载spring配置文件就会创建单实例对象
- 是prototype时,不是在加载spring配置文件时创建对象,在调用getBean方法时创建多实例对象
<bean class="com.spring.collectiontype.Book" id="book" scope="prototype">
</bean>
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean11.xml");
Book book1 = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
Book book2 = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
System.out.println(book1);
System.out.println(book2);
}
bean生命周期
- 通过构造器创建bean实例(无参数构造)
- 为bean的属性设置值和对其他bean引用(调用set方法)
- 把bean实例传递给bean后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
- 调用bean的初始化方法(需要进行配置)
- 把bean实例传递给bean后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
- bean可以使用了(对象获取到了)
- 当容器关闭时,调用bean的销毁方法(需要进行配置)
public class Orders {
private String oname;
//无参构造
public Orders() {
System.out.println("第一步,无参构造");
}
public void setOname(String oname) {
this.oname = oname;
System.out.println("第二部,set方法");
}
//创建执行的初始化的方法
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("第三步,执行初始化方法");
}
//销毁的方法
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("第五步,销毁");
}
}
public class MyBeanPost implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("初始化前的方法");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("初始化后的方法");
return bean;
}
}
<bean class="com.spring.bean.Orders" id="orders" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<property name="oname" value="jd888"/>
</bean>
<!--配置后置处理器-->
<bean class="com.spring.bean.MyBeanPost" id="myBeanPost"></bean>
@Test
public void test4() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean13.xml");
Orders orders = context.getBean("orders", Orders.class);
System.out.println("第四步,获取创建bean实例");
System.out.println(orders);
//手动销毁实例
context.close();
}
xml自动装配
- 根据指定装配规则(属性名称byName或属性类型byType)spring自动将匹配的属性值进行注入
<!--自动装配-->
<bean class="com.spring.autowrite.Emp" name="emp" autowire="byName">
<!--<property name="dept" ref="dept"/>-->
</bean>
<bean class="com.spring.autowrite.Dept" name="dept"></bean>
引入外部属性文件
- 配置连接池
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<!--直接配置连接池-->
<bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" id="dataSource">
<property name="driverClassLoader" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/userDB"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<!--引入外部配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" id="dataSource1">
<property name="driverClassLoader" value="${prop.driverClass}"/>
<property name="url" value="${prop.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${prop.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${prop.password}"/>
</bean>
</beans>
2.4 IOC操作Bean管理(基于注解)
2.4.1 什么是注解
- 注解是代码特殊标记,格式:@注解名称(属性名称=属性值,属性名称=属性值)
- 使用注解,注解作用在类上面,方法上面,属性上面
- 使用注解的配置:简化xml配置
2.4.2 spring针对Bean管理中创建对象提供注解
- @Component
- @Service
- @Controller
- @Repository
上面四个注解功能是一样的,都可以用来创建bean实例
2.4.3 基于注解方式实现对象创建
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--第一步,开启组件扫描,指定扫描哪个包哪个类有注解-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spring.dao,com.spring.service">
</context:component-scan>
</beans>
//注解里value属性可以省略,默认是类名首字母小写
@Component(value = "userService")//<bean id="" class="">
public class UserService {
public void add(){
System.out.println("add method");
}
}
开启组件扫描细节配置
<!--use-default-filters不使用默认filter,自己配置filter-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spring" use-default-filters="false">
<!--设置扫描哪些内容-->
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spring">
<!--设置哪些内容不进行扫描-->
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
2.4.4 基于注解方式实现属性注入
- @Autowired:根据属性类型进行自动装配
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("dao add----");
}
}
@Service
public class UserService {
//定义dao类型属性
//不需要添加set方法
@Autowired //根据类型注入
private UserDao userDao;
public void add() {
System.out.println("add method");
userDao.add();
}
}
- @Qualifier:根据属性名称进行注入,和@Autowired一起使用
@Service
public class UserService {
//定义dao类型属性
//不需要添加set方法
@Autowired //根据类型注入
@Qualifier(value = "userDaoImpl1")
private UserDao userDao;
public void add() {
System.out.println("service add method");
userDao.add();
- @Resource:可以根据类型注入,也可以根据名称注入
// @Resource
@Resource(value="userDaoImpl")
private UserDao userDao;
- @Value:注入普通类型属性
@Value(value = "zhangsan")
private String name;
2.4.5 完全注解开发
//创建配置类,替代xml配置文件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.spring"})
public class SpringConfig {
}
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
userService.add();
}
3. AOP
3.1 AOP基本概念
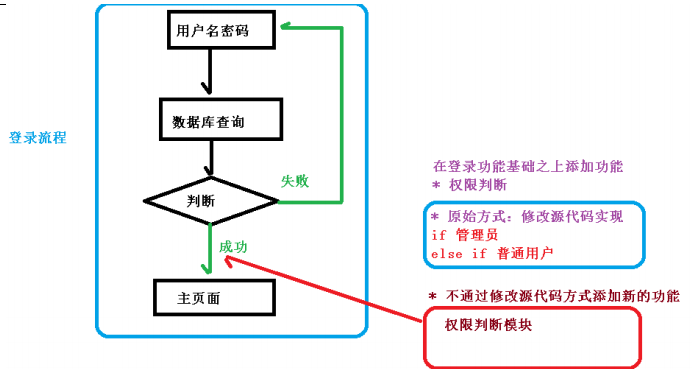
- 面向切面(方面)编程,利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高开发效率
- 不通过源代码的方式,在主干功能里添加新功能
- 使用登录例子说明AOP
3.2 底层原理
- AOP底层使用动态代理,有了两种情况动态代理
- 1.有接口情况,使用JDK动态代理,创建接口实现类代理对象,增强类的方法
- 2.没有接口情况,使用CGLIB动态代理,
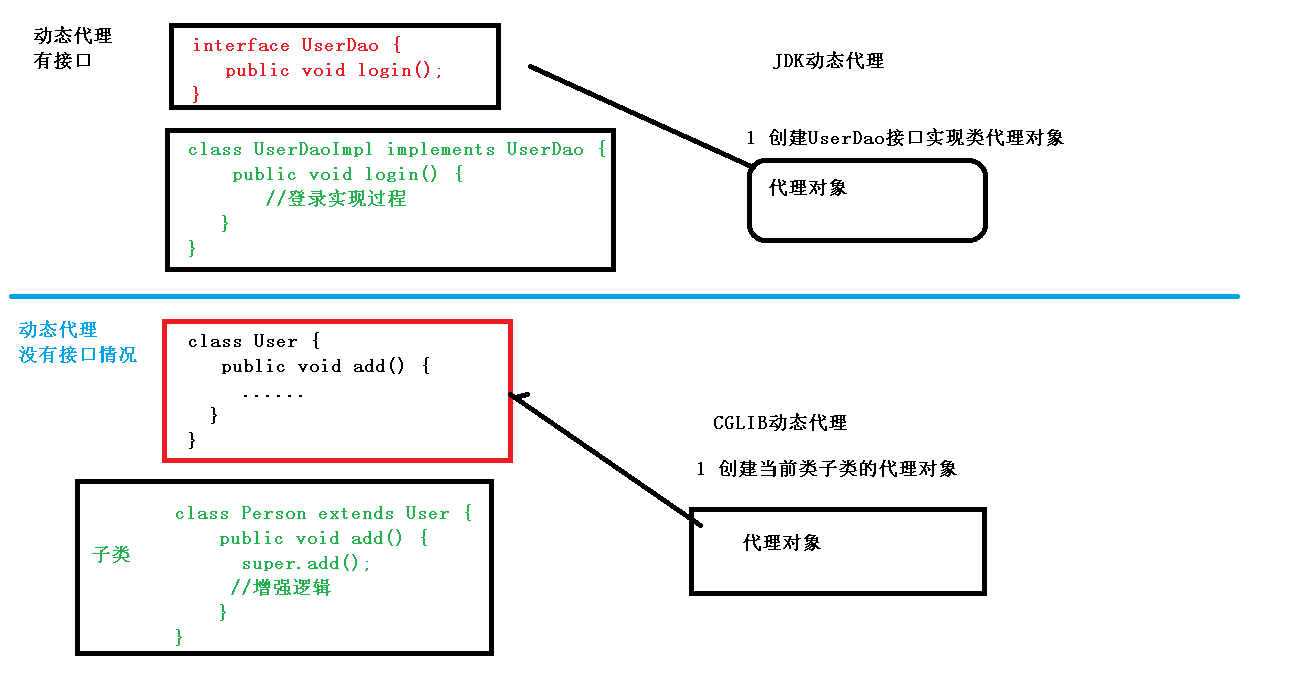
3.3 JDK动态代理
public interface UserDao {
public int add(int a, int b);
public String update(String id);
}
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("add方法");
return a + b;
}
@Override
public String update(String id) {
System.out.println("update方法");
return id;
}
}
public class JDKProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建接口实现类代理对象
Class[] interfaces = {UserDao.class};
UserDaoImpl userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
UserDao dao = (UserDao) Proxy.newProxyInstance(JDKProxy.class.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new UserDaoProxy(userDao));
System.out.println(dao.add(1, 2));
}
}
//创建代理对象代码
class UserDaoProxy implements InvocationHandler {
//有参构造传递
private Object obj;
public UserDaoProxy(Object obj) {
this.obj = obj;
}
//增强的逻辑
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//方法前
System.out.println("方法前执行" + method.getName() + ":传递的参数" + Arrays.toString(args));
//被增强的方法执行
Object res = method.invoke(obj, args);
//方法后
System.out.println("方法后执行" + obj);
return res;
}
}
3.4 相关术语
- 连接点
类里面哪些方法可以被增强,这些方法成为连接点
- 切入点
实际被真正增强的方法,称为切入点
- 通知(增强)
实际增强的逻辑部分称为通知(增强),通知有多种类型
- 前置通知
- 后置通知
- 环绕通知
- 异常通知
- 最终通知 finally
- 切面
是动作,把通知应用到切入点的过程
3.5 AOP准备操作
- Spring框架一般基于AspectJ实现AOP操作
- AspectJ不是Spring组成部分,独立AOP框架,一般把AspectJ和Spring框架一起使用,进行AOP操作
- 基于AspectJ实现AOP操作
- 基于xml配置文件实现,基于注解方式实现(多用)
3.5.1 切入点表达式
- 切入点表达式作用:知道对哪个类里面哪个方法进行增强
- 语法结构:execution([权限修饰符] [返回类型] [类全路径] [方法名称] ([参数列表]))
- 例如对com.dao.BookDao类的add()进行增强,execution(* com.dao.BookDao.add(…))
3.6 AspectJ注解AOP操作
//被增强类
@Component
public class User {
public void add() {
// int i = 12 / 0;
System.out.println("add-------");
}
}
//增强类
@Component
@Aspect //生成代理对象
@Order(3) //多个增强类的优先级,值越小越优先
public class UserProxy {
//相同切入点抽取
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void point() {
}
//前置通知
@Before(value = "execution(* aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("before");
}
//最终通知
@After(value = "execution(* aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("after");
}
//返回通知
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning");
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value = "point()")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing");
}
//环绕通知
@Around(value = "point()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕前");
//被增强的方法执行
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕后");
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">
<!--开启注解扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="aopanno"></context:component-scan>
<!--开启Aspect生成代理对象-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
或
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"aopanno"})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class ConfigAop {
}
3.7 AOP操作AspectJ配置文件AOP操作
public class Book {
public void buy() {
System.out.println("buy");
}
}
public class BookProxy {
public void before() {
System.out.println("before");
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">
<!--创建对象-->
<bean class="aopxml.Book" id="book"></bean>
<bean class="aopxml.BookProxy" id="bookProxy"></bean>
<!--配置aop增强-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="p" expression="execution(* aopxml.Book.buy(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect ref="bookProxy">
<!--增强作用在具体的方法上-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="p"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
4. JdbcTemplate
4.1 JdbcTemplate简介
- Spring框架对JDBC进行了封装,使用JdbcTemplate方便实现对数据库操作
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-contenxt.xsd
">
<!--组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="dao,service"></context:component-scan>
<!--数据库连接池-->
<bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" id="dataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///book"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
</bean>
<!--JdbcTemplate对象-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" id="jdbcTemplate">
<!--注入DataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
@Service
public class BookService {
//注入dao
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
}
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
//注入JdbcTemplate
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
}
4.2 JdbcTemplate 操作数据库-增删改查
public class Book {
private String userId;
private String username;
private String ustatus;
public String getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(String userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getUstatus() {
return ustatus;
}
public void setUstatus(String ustatus) {
this.ustatus = ustatus;
}
}
@Service
public class BookService {
//注入dao
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
//添加的方法
public void addBook(Book book) {
bookDao.add(book);
}
//修改方法
public void updateBook(Book book) {
bookDao.updaateBook(book);
}
//删除方法
public void deleteBook(String id) {
bookDao.delete(id);
}
//查询表记录数
public int findCount() {
return bookDao.selectCount();
}
//查询一个对象
public Book findOne(String id) {
return bookDao.findBookInfo(id);
}
//查询集合
public List<Book> findAll() {
return bookDao.findAllBook();
}
//批量添加
public void batchAdd(List<Object[]> batchArgs) {
bookDao.batchAddBook(batchArgs);
}
//批量修改
public void batchUpdate(List<Object[]> batchArgs){
bookDao.batchUpdateBook(batchArgs);
}
//批量删除
public void batchDelete(List<Object[]> batchArgs){
bookDao.batchDelete(batchArgs);
}
}
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
//注入JdbcTemplate
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//添加的方法
@Override
public void add(Book book) {
String sql = "insert into t_book values(?,?,?)";
Object[] args = {book.getUserId(), book.getUsername(), book.getUstatus()};
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
System.out.println(update);
}
@Override
public void updaateBook(Book book) {
String sql = "update t_book set username=?,ustatus=? where user_id=?";
Object[] args = {book.getUsername(), book.getUstatus(), book.getUserId()};
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
System.out.println(update);
}
@Override
public void delete(String id) {
String sql = "delete from t_book where user_id=?";
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, id);
System.out.println(update);
}
//查询记录数
@Override
public int selectCount() {
String sql = "select count(*) from t_book";
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
return count;
}
@Override
public Book findBookInfo(String id) {
String sql = "select * from t_book where user_id=?";
Book book = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Book>(Book.class), id);
return book;
}
@Override
public List<Book> findAllBook() {
String sql = "select * from t_book";
List<Book> list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Book>(Book.class));
return list;
}
@Override
public void batchAddBook(List<Object[]> batchArgs) {
String sql = "insert into t_book values(?,?,?)";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
@Override
public void batchUpdateBook(List<Object[]> batchArgs) {
String sql = "update t_book set username=?,ustatus=? where user_id=?";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
@Override
public void batchDelete(List<Object[]> batchArgs) {
String sql = "delete from t_book where user_id=?";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
}
public class TestBook {
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean1.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
Book book = new Book();
book.setUserId("1");
book.setUsername("Java");
book.setUstatus("A");
bookService.addBook(book);
}
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean1.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
Book book = new Book();
book.setUserId("1");
book.setUsername("python");
book.setUstatus("p");
bookService.updateBook(book);
}
@Test
public void test3() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean1.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
bookService.deleteBook("1");
}
@Test
public void test4() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean1.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
int count = bookService.findCount();
System.out.println(count);
}
@Test
public void test5() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean1.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
Book book = bookService.findOne("1");
System.out.println(book);
}
@Test
public void test6() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean1.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
List<Book> bookList = bookService.findAll();
System.out.println(bookList);
}
@Test
public void test7() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean1.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
Object[] o1 = {"10", "C", "C"};
Object[] o2 = {"11", "Go", "Go"};
Object[] o3 = {"12", "C++", "C++"};
batchArgs.add(o1);
batchArgs.add(o2);
batchArgs.add(o3);
bookService.batchAdd(batchArgs);
}
@Test
public void test8() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean1.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
Object[] o1 = {"C++", "C++", "10"};
Object[] o2 = {"GO", "GO", "11"};
Object[] o3 = {"C#", "C#", "12"};
batchArgs.add(o1);
batchArgs.add(o2);
batchArgs.add(o3);
bookService.batchUpdate(batchArgs);
}
@Test
public void test9() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resource/bean1.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
Object[] o1 = {"10"};
Object[] o2 = {"11"};
batchArgs.add(o1);
batchArgs.add(o2);
bookService.batchDelete(batchArgs);
}
}
5. 事务管理
5.1 事务的概念
- 事务时数据库操作最基本单元,要么都成功,如果有一个失败所有操作都失败
- 典型场景:银行转账
- A转账100给B,A少100,B多100
事务四个特性(ACID)
原子性
一致性
隔离性
持久性
5.2 Spring事务管理介绍
- 事务添加到JavaEE三层结构里Service层
- 在Spring进行事务管理操作,有两种方式:编程式事务管理和声明式事务管理(多使用)
- 声明式事务管理,有基于注解(多使用)和基于xml配置文件方式
- 在Spring进行声明式事务管理,底层使用AOP
- Spring提供一个接口,代表事务管理器,这个接口针对不同的框架提供不同的实现类
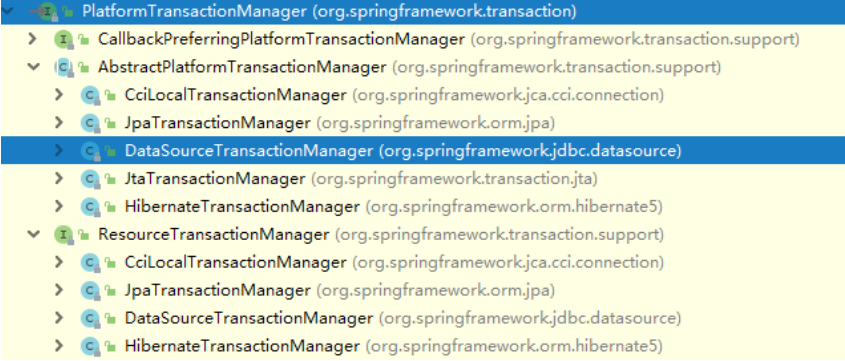
5.3 注解声明式事务管理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
">
<!--组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.dao,com.service"></context:component-scan>
<!--数据库连接池-->
<bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" id="dataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
</bean>
<!--JdbcTemplate对象-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" id="jdbcTemplate">
<!--注入DataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--创建事务管理器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="transactionManager">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--开启事务注解-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
</beans>
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void addMoney() {
String sql = "update t_account set money=money+? where username=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, 100, "Jack");
}
@Override
public void reduceMoney() {
String sql = "update t_account set money=money-? where username=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, 100, "Tom");
}
}
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
//注入dao
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
//转账方法
public void accountMoney() {
//少钱
userDao.reduceMoney();
int i = 12 / 0;
//多钱
userDao.addMoney();
}
}
5.3.1 参数配置
-
propagation事务传播行为:多事务方法直接进行调用,这个过程中事务是如何进行管理的
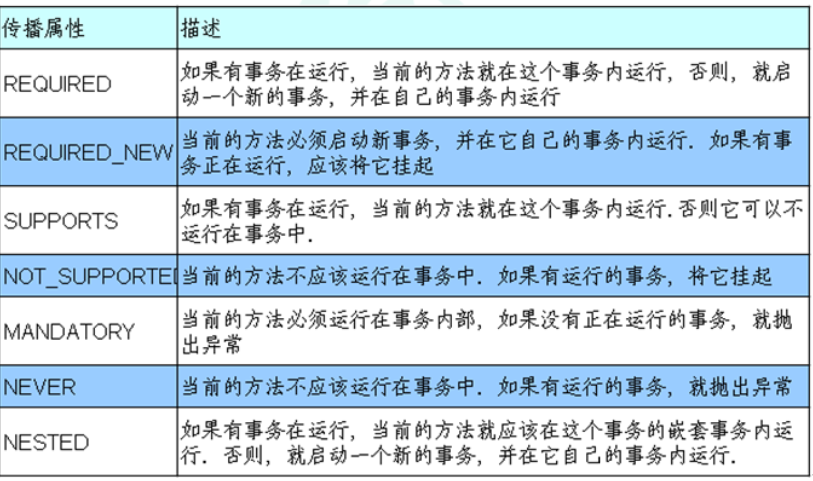
-
isolation事务隔离级别
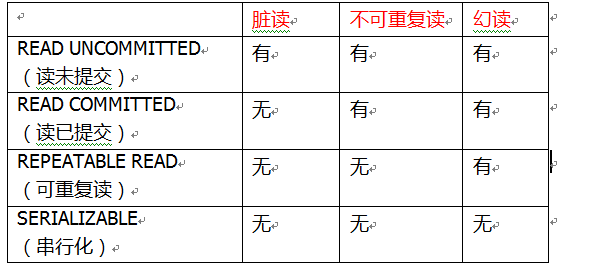
-
timeout超时时间:事务需要在一定时间内提交,否则回滚,默认-1
-
readOnly是否只读,默认false
-
rollbackFor/norollbackFor:设置出现哪些异常惊醒事务回滚/不回滚
5.3.2 完全注解配置Config类
- 配置类替代xml配置文件
@Configuration//配置类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com")//组件扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement//开启事务
public class TxConfig {
//创建数据库连接池
@Bean
public DruidDataSource getDuridDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///test");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
return dataSource;
}
//JdbcTemplate对象
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
//到ios容器中根据类型找到dataSOurce
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
//注入dataSource
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
//创建事务管理器
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
5.4 xml声明式事务管理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">
<!--组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.dao,com.service"></context:component-scan>
<!--数据库连接池-->
<bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" id="dataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
</bean>
<!--JdbcTemplate对象-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" id="jdbcTemplate">
<!--注入DataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--创建事务管理器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="transactionManager">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置通知-->
<tx:advice id="txadvice">
<!--配置事务相关参数-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--指定哪种规则的方法上面添加事务-->
<tx:method name="account*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--配置切入点和切面-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.service.UserService.*(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="pt"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
6. Spring5新特性
- 整个Spring5框架的代码基于Java8,运行时兼容JDK9,许多不建议使用的类和方法在代码库中删除
6.1 核心特性
6.1.1 Spring5自带了日志封装
- 移除了Log4jConfigListener,建议使用Log4j2
- log4j2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--日志级别以及优先级排序: OFF > FATAL > ERROR > WARN > INFO > DEBUG > TRACE > ALL -->
<!--Configuration后面的status用于设置log4j2自身内部的信息输出,可以不设置,当设置成trace时,可以看到log4j2内部各种详细输出-->
<configuration status="INFO">
<!--先定义所有的appender-->
<appenders>
<!--输出日志信息到控制台-->
<console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<!--控制日志输出的格式-->
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n"/>
</console>
</appenders>
<!--然后定义logger,只有定义了logger并引入的appender,appender才会生效-->
<!--root:用于指定项目的根日志,如果没有单独指定Logger,则会使用root作为默认的日志输出-->
<loggers>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="Console"/>
</root>
</loggers>
</configuration>
public class UserLog {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserLog.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("hello log4j2");
log.warn("hello");
}
}
6.2 核心容器
6.2.2 支持@Nullable注解
- 可以使用在方法、属性、参数上面,表示返回可以为空
@Nullable
String getId();
public <T> void registerBean(@Nullable String beanName, Class<T> beanClass, @Nullable Supplier<T> supplier, BeanDefinitionCustomizer... customizers) {
this.reader.registerBean(beanClass, beanName, supplier, customizers);
}
6.2.3 支持函数式风格GenericApplicationContext
//函数式风格创建对象,交给spring进行管理
@Test
public void test2() {
//1.创建GenericApplicationContext对象
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
//调用context的方法对象注册
context.refresh();
context.registerBean("user1", User.class, () -> new User());
//获取在spring注册的对象
// User user = (User) context.getBean("com.entity.User");
User user = (User) context.getBean("user1");
System.out.println(user);
}
6.2.4 支持整合JUnit5
JUnit4
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//单元测试框架
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:resource/bean1.xml")//加载配置文件
public class JTest4 {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void test1() {
userService.accountMoney();
}
}
JUnit5
//@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
//@ContextConfiguration("classpath:resource/bean1.xml")
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:resource/bean1.xml")
public class JTest5 {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void test2() {
userService.accountMoney();
}
}
6.3 Webflux
6.3.1 简介
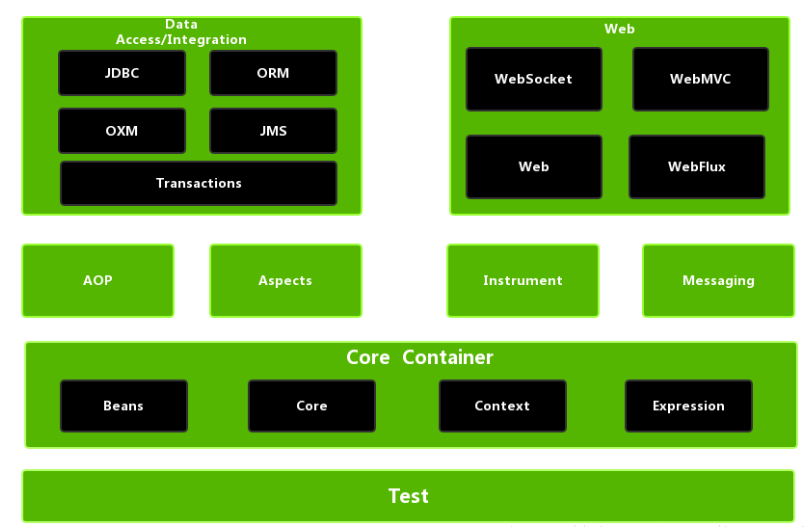
- 是Spring5添加新的模块,用于web开发的,功能与SpringMVC类似,Webflux使用当前一种比较流行的响应式编程出现的框架
- 使用传统web框架,比如SpringMVC,这些基于Servlet容器,Webflux是一种异步非阻塞的框架,异步非阻塞的框架在Servlet3.1以后才支持,核心是基于Reactor的相关API实现的
什么是异步非阻塞
异步和同步
阻塞和非阻塞
异步和同步针对调用者,调用者发送请求,如果等着对象回应后,才去做其他事情就是同步,不等着回应,就是异步
阻塞和非阻塞针对被调用者,被调用者收到请求后,做完请求任务后才给出反馈就是阻塞;收到请求后马上给出反馈再去做事就是非阻塞
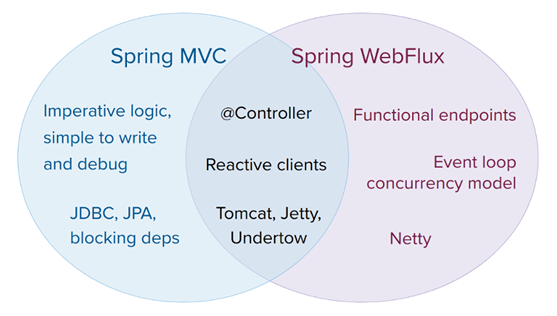
6.3.2 响应式编程
- 是一种面向数据流和变化传播的编程范式,电子表格就是响应式编程的例子,包含公式的单元格的值会依据其他单元格的值的变化而变化。
Java8及之前版本实现
- 提供的观察者模式两个类Observer和Observable
public class ObserverDemo extends Observable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObserverDemo observer = new ObserverDemo();
//添加观察者
observer.addObserver((o, arg) -> {
System.out.println("发生了变化");
});
observer.addObserver((o, arg) -> {
System.out.println("收到被观察者通知,准备改变");
});
observer.setChanged();//数据变化
observer.notifyObservers();//通知
}
}
Reactor实现
- 响应式编程操作中,Reactor满足Reactive规范框架
- Reactor有两个核心类,Mono和Flux,这两个类实现接口Publisher,提供丰富操作符。Flux对象实现发布者,返回N个元素;Mono实现发布者,返回0或1个元素
- Flux和Mono都是数据流的发布者,使用Flux和Mono都可以发出三种数据信号:元素值,错误信号,完成信号。错误、完成信号都是终止信号,不能共存
- 没有发送任何元素值,而是直接发送终止信号,表示是空数据流
- 没有终止信号,表示是无限数据流
public class TestReactor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//just方法直接声明
//just等方法只是声明了数据流,数据流并没有发出。只有订阅后才能触发数据流
Flux.just(1, 2, 3, 4).subscribe(System.out::println);
Mono.just(1).subscribe(System.out::println);
//其他方法
Integer[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4};
Flux.fromArray(array);
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(array);
Flux.fromIterable(list);
Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();
Flux.fromStream(stream);
}
}
- 操作符:对数据流进行一道道操作。比如工厂流水线
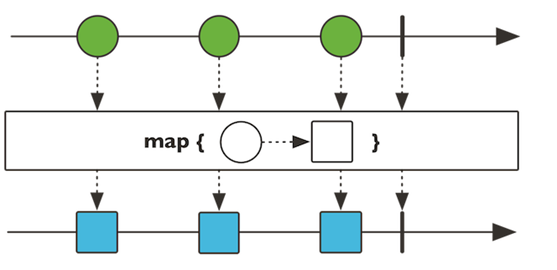
- map 元素映射为新元素
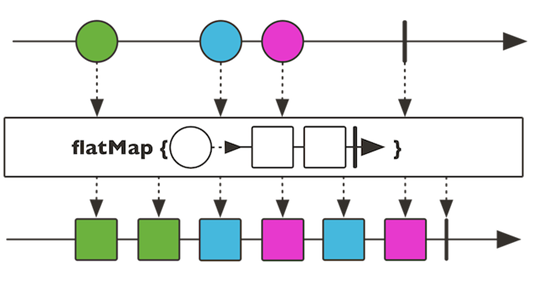
- flatMap 元素映射为流,把每个元素转换流,把转换之后多个流合并大的流
6.3.3 Webflux执行流程和核心API
- SpringWebflux基于Reactor,默认使用容器是Netty,Netty是高性能的NIO框架,异步非阻塞的框架
- BIO
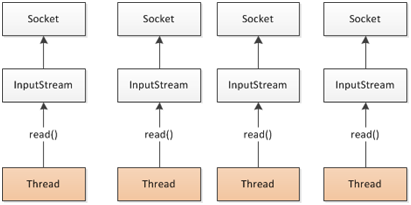
- NIO
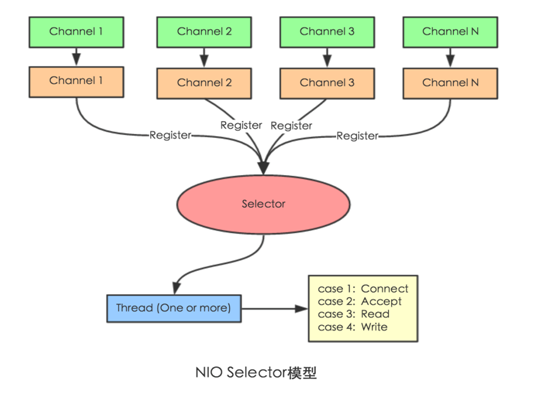
- SpringWebflux核心控制器DispatchHandler,实现接口WebHandler
- SpringWebflux里面DispatcherHandler负责请求的处理
- HandlerrMapping 请求查询到处理的方法
- HandlerAdapter 真正负责请求处理
- HandlerResultHandler 响应结果处理
- SpringWebflux实现函数式编程,两个接口:RouterFunction (路由处理)HandlerFunction (处理函数)
6.3.4 SpringWebflx(基于注解编程模型)
@Repository
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
//创建map集合存储数据
private final Map<Integer, User> users = new HashMap<>();
public UserServiceImpl() {
this.users.put(1, new User("zhang", "nan", 20));
this.users.put(2, new User("li", "nv", 34));
this.users.put(3, new User("wang", "nan", 70));
}
@Override
public Mono<User> getUserById(int id) {
return Mono.justOrEmpty(this.users.get(id));
}
//查询多个用户
@Override
public Flux<User> getAllUser() {
return Flux.fromIterable(this.users.values());
}
//添加用户
@Override
public Mono<Void> saveUserInfo(Mono<User> userMono) {
return userMono.doOnNext(person -> {
//向map集合里放值
int id = users.size() + 1;
users.put(id, person);
}).thenEmpty(Mono.empty());
}
}
@RestController
public class UserController {
//注入service
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
//id查询
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public Mono<User> getUserId(@PathVariable int id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
//查询所有
@GetMapping("/user")
public Flux<User> getUsers() {
return userService.getAllUser();
}
//添加
@PostMapping("/savauser")
public Mono<Void> saveUser(@RequestBody User user) {
Mono<User> userMono = Mono.just(user);
return userService.saveUserInfo(userMono);
}
}
- SpringMVC方式实现同步阻塞的方式,基于SpringMVC+Servlet+Tomcat
- SpringWebflux异步非阻塞方式,基于SpringWebflux+Reactor+Netty
6.3.5 SpringWebflx(基于函数式编程模型)
- 在使用函数式编程模型操作时,需要自己初始化服务器
- 基于函数式编程模型时,有两个核心接口:RouterFunction(实现路由功能,请求转发给对应的handler)和HandlerFunction(处理请求生成响应的函数)。核心任务定义两个函数式接口的实现并启动需要的服务器
- SpringWebflux请求和响应不再是ServletRequest和ServletResponse,而是ServerRequest和ServerResponse
public class UserHandler {
private final UserService userService;
public UserHandler(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
//根据 id 查询
public Mono<ServerResponse> getUserById(ServerRequest request) {
//获取 id 值
int userId = Integer.valueOf(request.pathVariable("id"));
//空值处理
Mono<ServerResponse> notFound = ServerResponse.notFound().build();
//调用 service 方法得到数据
Mono<User> userMono = this.userService.getUserById(userId);
//把 userMono 进行转换返回
//使用 Reactor 操作符 flatMap
return
userMono
.flatMap(person ->
ServerResponse.ok().contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.body(fromObject(person)))
.switchIfEmpty(notFound);
}
//查询所有
public Mono<ServerResponse> getAllUsers() {
//调用 service 得到结果
Flux<User> users = this.userService.getAllUser();
return
ServerResponse.ok().contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).body(users, User.cl
ass);
}
//添加
public Mono<ServerResponse> saveUser(ServerRequest request) {
//得到 user 对象
Mono<User> userMono = request.bodyToMono(User.class);
return
ServerResponse.ok().build(this.userService.saveUserInfo(userMono));
}
}
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Server server = new Server();
server.createReactorServer();
System.out.println("enter to exit");
System.in.read();
}
//1 创建 Router 路由
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> routingFunction() {
//创建 hanler 对象
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
UserHandler handler = new UserHandler(userService);
//设置路由
return RouterFunctions.route(
GET("/users/{id}").and(accept(APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::getUserById)
.andRoute(GET("/users").and(accept(APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::get
AllUsers);
}
//2 创建服务器完成适配
public void createReactorServer() {
//路由和 handler 适配
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route = routingFunction();
HttpHandler httpHandler = toHttpHandler(route);
ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter adapter = new
ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter(httpHandler);
//创建服务器
HttpServer httpServer = HttpServer.create();
httpServer.handle(adapter).bindNow();
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//调用服务器地址
WebClient webClient = WebClient.create("http://127.0.0.1:5794");
//根据 id 查询
String id = "1";
User userresult = webClient.get().uri("/users/{id}", id)
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).retrieve().bodyToMono(User
.class)
.block();
System.out.println(userresult.getName());
//查询所有
Flux<User> results = webClient.get().uri("/users")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).retrieve().bodyToFlux(User
.class);
results.map(stu -> stu.getName())
.buffer().doOnNext(System.out::println).blockFirst();
}
}
最后
以上就是碧蓝项链最近收集整理的关于Spring5框架-入门1. 框架概述2. IOC容器3. AOP3.6 AspectJ注解AOP操作3.7 AOP操作AspectJ配置文件AOP操作4. JdbcTemplate5. 事务管理6. Spring5新特性的全部内容,更多相关Spring5框架-入门1.内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复