Spring Bean的创建包含几个阶段,与对象的创建阶段是相对应的。
阶段1:对象实例化
阶段2:对象属性赋值
阶段3:对象初始化方法调用
本文基于Spring 5.2.9 通过流程图的方式梳理了对象属性赋值的操作,其中@Autowired的注入会通过AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessProperties()进行处理,@Resource 会通过commonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessProperties()进行处理。
下面是图片,此处会持续完善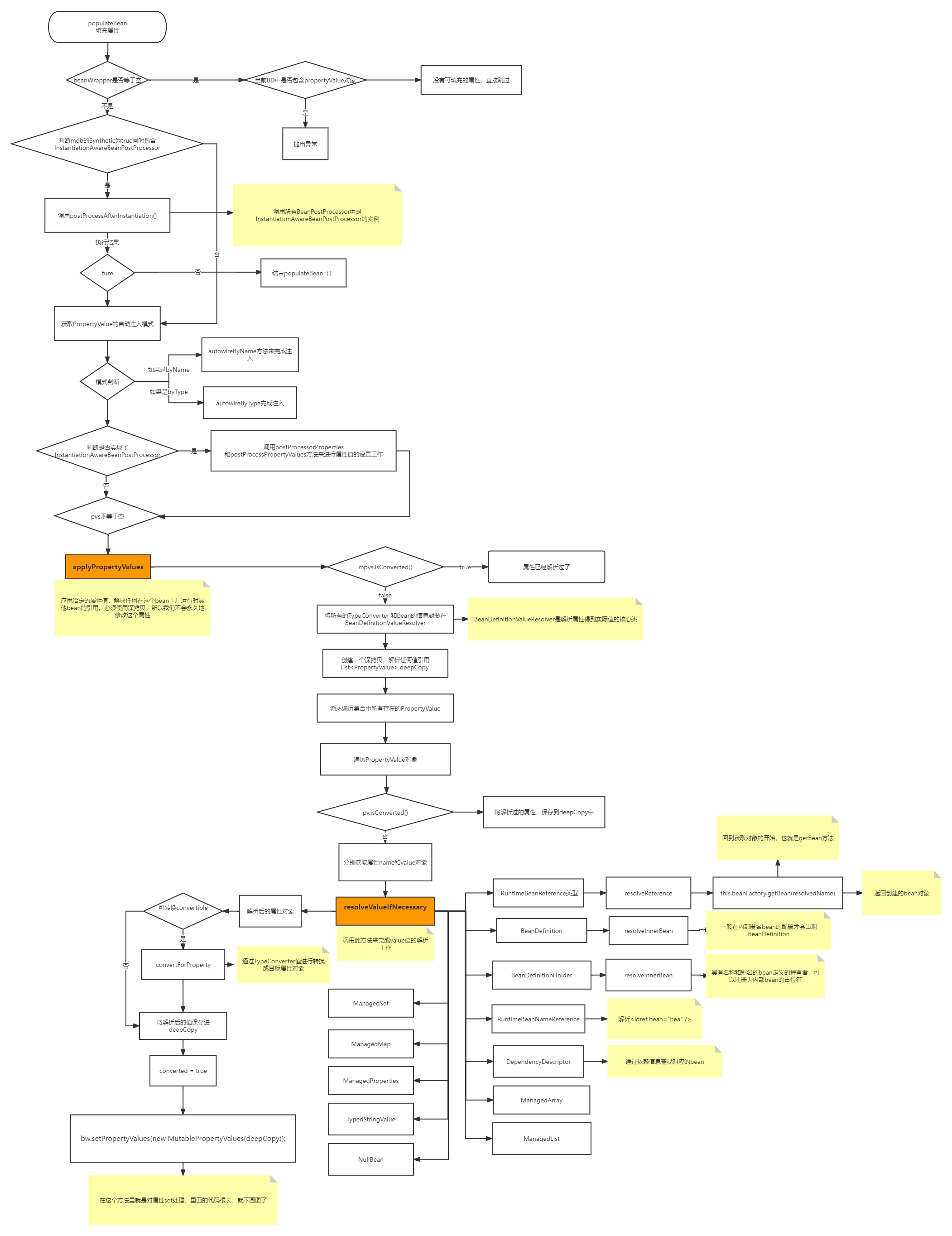
下面是加了注释的填充属性核心类代码,但是可能不够全面,我放在下面是因为提示我的文章字数不够,我又不想写。
/*
* Copyright 2002-2020 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.beans.factory.support;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.security.AccessController;
import java.security.PrivilegedAction;
import java.security.PrivilegedActionException;
import java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapper;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapperImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyAccessorUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.TypeConverter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.Aware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InjectionPoint;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowiredPropertyMarker;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConstructorArgumentValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DependencyDescriptor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.TypedStringValue;
import org.springframework.core.DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.core.NamedThreadLocal;
import org.springframework.core.ParameterNameDiscoverer;
import org.springframework.core.PriorityOrdered;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* 综合abstractBeanFactory并对接口AutowireCapableBeanFcatory进行实现
*
* Abstract bean factory superclass that implements default bean creation,
* with the full capabilities specified by the {@link RootBeanDefinition} class.
* Implements the {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory}
* interface in addition to AbstractBeanFactory's {@link #createBean} method.
*
* <p>Provides bean creation (with constructor resolution), property population,
* wiring (including autowiring), and initialization. Handles runtime bean
* references, resolves managed collections, calls initialization methods, etc.
* Supports autowiring constructors, properties by name, and properties by type.
*
* <p>The main template method to be implemented by subclasses is
* {@link #resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor, String, Set, TypeConverter)},
* used for autowiring by type. In case of a factory which is capable of searching
* its bean definitions, matching beans will typically be implemented through such
* a search. For other factory styles, simplified matching algorithms can be implemented.
*
* <p>Note that this class does <i>not</i> assume or implement bean definition
* registry capabilities. See {@link DefaultListableBeanFactory} for an implementation
* of the {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory} and
* {@link BeanDefinitionRegistry} interfaces, which represent the API and SPI
* view of such a factory, respectively.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @author Mark Fisher
* @author Costin Leau
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Sam Brannen
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 13.02.2004
* @see RootBeanDefinition
* @see DefaultListableBeanFactory
* @see BeanDefinitionRegistry
*/
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory
implements AutowireCapableBeanFactory {
/**
* bean的生成策略,默认是cglib
* Strategy for creating bean instances. */
private InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy = new CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy();
/**
* 解析策略的方法参数
* Resolver strategy for method parameter names. */
@Nullable
private ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer = new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer();
/**
* 尝试解析循环引用
* Whether to automatically try to resolve circular references between beans. */
private boolean allowCircularReferences = true;
/**
* 在循环引用的而情况下,是否需要注入一个原始的bean实例
*
* Whether to resort to injecting a raw bean instance in case of circular reference,
* even if the injected bean eventually got wrapped.
*/
private boolean allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping = false;
/**
* 依赖项检查和自动装配时忽略的依赖项类型
*
* Dependency types to ignore on dependency check and autowire, as Set of
* Class objects: for example, String. Default is none.
*/
private final Set<Class<?>> ignoredDependencyTypes = new HashSet<>();
/**
* 依赖项检查和自动装配时忽略的依赖项接口
*
* Dependency interfaces to ignore on dependency check and autowire, as Set of
* Class objects. By default, only the BeanFactory interface is ignored.
*/
private final Set<Class<?>> ignoredDependencyInterfaces = new HashSet<>();
/**
* 当前正在创建的bean
*
* The name of the currently created bean, for implicit dependency registration
* on getBean etc invocations triggered from a user-specified Supplier callback.
*/
private final NamedThreadLocal<String> currentlyCreatedBean = new NamedThreadLocal<>("Currently created bean");
/**
* beanName和FactoryBean的映射
*
* Cache of unfinished FactoryBean instances: FactoryBean name to BeanWrapper. */
private final ConcurrentMap<String, BeanWrapper> factoryBeanInstanceCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 类和候选方法的映射
*
* Cache of candidate factory methods per factory class. */
private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, Method[]> factoryMethodCandidateCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 类和propertyDescriptor的映射
*
* Cache of filtered PropertyDescriptors: bean Class to PropertyDescriptor array. */
private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, PropertyDescriptor[]> filteredPropertyDescriptorsCache =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 构造方法,忽略BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware,BeanClassLoaderAware的依赖
*
* Create a new AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.
*/
public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory() {
super();
// 忽略要依赖的接口
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanNameAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanFactoryAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanClassLoaderAware.class);
}
/**
* Create a new AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory with the given parent.
* @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory, or {@code null} if none
*/
public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory(@Nullable BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) {
this();
setParentBeanFactory(parentBeanFactory);
}
/**
* 实例化生成策略的设置和获取
*
* Set the instantiation strategy to use for creating bean instances.
* Default is CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy.
* @see CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy
*/
public void setInstantiationStrategy(InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy) {
this.instantiationStrategy = instantiationStrategy;
}
/**
* Return the instantiation strategy to use for creating bean instances.
*/
protected InstantiationStrategy getInstantiationStrategy() {
return this.instantiationStrategy;
}
/**
* 解析策略的方法参数的设置和获取
*
* Set the ParameterNameDiscoverer to use for resolving method parameter
* names if needed (e.g. for constructor names).
* <p>Default is a {@link DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer}.
*/
public void setParameterNameDiscoverer(@Nullable ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer) {
this.parameterNameDiscoverer = parameterNameDiscoverer;
}
/**
* Return the ParameterNameDiscoverer to use for resolving method parameter
* names if needed.
*/
@Nullable
protected ParameterNameDiscoverer getParameterNameDiscoverer() {
return this.parameterNameDiscoverer;
}
/**
* 尝试解决循环依赖的值设置
*
* Set whether to allow circular references between beans - and automatically
* try to resolve them.
* <p>Note that circular reference resolution means that one of the involved beans
* will receive a reference to another bean that is not fully initialized yet.
* This can lead to subtle and not-so-subtle side effects on initialization;
* it does work fine for many scenarios, though.
* <p>Default is "true". Turn this off to throw an exception when encountering
* a circular reference, disallowing them completely.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> It is generally recommended to not rely on circular references
* between your beans. Refactor your application logic to have the two beans
* involved delegate to a third bean that encapsulates their common logic.
*/
public void setAllowCircularReferences(boolean allowCircularReferences) {
this.allowCircularReferences = allowCircularReferences;
}
/**
* 在循环引用的情况下,是否需要注入一个原视的bean实例
*
* Set whether to allow the raw injection of a bean instance into some other
* bean's property, despite the injected bean eventually getting wrapped
* (for example, through AOP auto-proxying).
* <p>This will only be used as a last resort in case of a circular reference
* that cannot be resolved otherwise: essentially, preferring a raw instance
* getting injected over a failure of the entire bean wiring process.
* <p>Default is "false", as of Spring 2.0. Turn this on to allow for non-wrapped
* raw beans injected into some of your references, which was Spring 1.2's
* (arguably unclean) default behavior.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> It is generally recommended to not rely on circular references
* between your beans, in particular with auto-proxying involved.
* @see #setAllowCircularReferences
*/
public void setAllowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping(boolean allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping) {
this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping = allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping;
}
/**
* 依赖项检查和自动装配时忽略的依赖项类型
*
* Ignore the given dependency type for autowiring:
* for example, String. Default is none.
*/
public void ignoreDependencyType(Class<?> type) {
this.ignoredDependencyTypes.add(type);
}
/**
* 依赖项检查和自动装配时忽略的依赖项接口
*
* Ignore the given dependency interface for autowiring.
* <p>This will typically be used by application contexts to register
* dependencies that are resolved in other ways, like BeanFactory through
* BeanFactoryAware or ApplicationContext through ApplicationContextAware.
* <p>By default, only the BeanFactoryAware interface is ignored.
* For further types to ignore, invoke this method for each type.
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware
* see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware
*/
public void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc) {
this.ignoredDependencyInterfaces.add(ifc);
}
/**
* 复制父类的几种配置
* @param otherFactory
*/
@Override
public void copyConfigurationFrom(ConfigurableBeanFactory otherFactory) {
super.copyConfigurationFrom(otherFactory);
if (otherFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory otherAutowireFactory =
(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) otherFactory;
this.instantiationStrategy = otherAutowireFactory.instantiationStrategy;
this.allowCircularReferences = otherAutowireFactory.allowCircularReferences;
this.ignoredDependencyTypes.addAll(otherAutowireFactory.ignoredDependencyTypes);
this.ignoredDependencyInterfaces.addAll(otherAutowireFactory.ignoredDependencyInterfaces);
}
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Typical methods for creating and populating external bean instances
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 创建bean
* @param beanClass the class of the bean to create
* @param <T>
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T createBean(Class<T> beanClass) throws BeansException {
// Use prototype bean definition, to avoid registering bean as dependent bean.
// 封装RootBeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition bd = new RootBeanDefinition(beanClass);
// 设置bean的作用域
bd.setScope(SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);
// 是否允许被缓存
bd.allowCaching = ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(beanClass, getBeanClassLoader());
return (T) createBean(beanClass.getName(), bd, null);
}
@Override
public void autowireBean(Object existingBean) {
// Use non-singleton bean definition, to avoid registering bean as dependent bean.
// 使用非单例的beanDefinition,防止注册bean为bean的依赖
RootBeanDefinition bd = new RootBeanDefinition(ClassUtils.getUserClass(existingBean));
// 设置作用域
bd.setScope(SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);
// 是否允许被缓存
bd.allowCaching = ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(bd.getBeanClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(existingBean);
// 初始化beanWrapper
initBeanWrapper(bw);
// 给bean的属性赋值
populateBean(bd.getBeanClass().getName(), bd, bw);
}
@Override
public Object configureBean(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 如果已经创建了bean,那么bean的定义要清除
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
// 重新设置bean的定义
BeanDefinition mbd = getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName);
RootBeanDefinition bd = null;
if (mbd instanceof RootBeanDefinition) {
RootBeanDefinition rbd = (RootBeanDefinition) mbd;
bd = (rbd.isPrototype() ? rbd : rbd.cloneBeanDefinition());
}
if (bd == null) {
bd = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
}
if (!bd.isPrototype()) {
bd.setScope(SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);
bd.allowCaching = ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(ClassUtils.getUserClass(existingBean), getBeanClassLoader());
}
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(existingBean);
// 初始化BeanWrapper
initBeanWrapper(bw);
// 给bean的属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, bd, bw);
// 调用init方法,完成初始化
return initializeBean(beanName, existingBean, bd);
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Specialized methods for fine-grained control over the bean lifecycle
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public Object createBean(Class<?> beanClass, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck) throws BeansException {
// Use non-singleton bean definition, to avoid registering bean as dependent bean.
RootBeanDefinition bd = new RootBeanDefinition(beanClass, autowireMode, dependencyCheck);
bd.setScope(SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);
return createBean(beanClass.getName(), bd, null);
}
@Override
public Object autowire(Class<?> beanClass, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck) throws BeansException {
// Use non-singleton bean definition, to avoid registering bean as dependent bean.
RootBeanDefinition bd = new RootBeanDefinition(beanClass, autowireMode, dependencyCheck);
bd.setScope(SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);
// 如果是构造器注入
if (bd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR) {
return autowireConstructor(beanClass.getName(), bd, null, null).getWrappedInstance();
}
else {
Object bean;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
bean = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(bd, null, this),
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 生成bean
bean = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(bd, null, this);
}
// 给bean的属性赋值
populateBean(beanClass.getName(), bd, new BeanWrapperImpl(bean));
return bean;
}
}
@Override
public void autowireBeanProperties(Object existingBean, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck)
throws BeansException {
// 如果注入类型是构造器注入,直接抛出异常
if (autowireMode == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR not supported for existing bean instance");
}
// Use non-singleton bean definition, to avoid registering bean as dependent bean.
RootBeanDefinition bd =
new RootBeanDefinition(ClassUtils.getUserClass(existingBean), autowireMode, dependencyCheck);
bd.setScope(SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(existingBean);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
populateBean(bd.getBeanClass().getName(), bd, bw);
}
@Override
public void applyBeanPropertyValues(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
BeanDefinition bd = getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName);
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(existingBean);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
applyPropertyValues(beanName, bd, bw, bd.getPropertyValues());
}
@Override
public Object initializeBean(Object existingBean, String beanName) {
return initializeBean(beanName, existingBean, null);
}
/**
* 初始化之前调用的方法
* @param existingBean the existing bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean, to be passed to it if necessary
* (only passed to {@link BeanPostProcessor BeanPostProcessors};
* can follow the {@link #ORIGINAL_INSTANCE_SUFFIX} convention in order to
* enforce the given instance to be returned, i.e. no proxies etc)
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
//初始化返回结果为existingBean
Object result = existingBean;
//遍历 该工厂创建的bean的BeanPostProcessors列表
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// postProcessBeforeInitialization:在任何Bean初始化回调之前(如初始化Bean的afterPropertiesSet或自定义的init方法)
// 将此BeanPostProcessor 应用到给定的新Bean实例。Bean已经填充了属性值。返回的Bean实例可能时原始Bean的包装器。
// 默认实现按原样返回给定的 Bean
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
// 如果 current为null
if (current == null) {
//直接返回result,中断其后续的BeanPostProcessor处理
return result;
}
//让result引用processor的返回结果,使其经过所有BeanPostProcess对象的后置处理的层层包装
result = current;
}
//返回经过所有BeanPostProcess对象的后置处理的层层包装后的result
return result;
}
/**
* 对existingBean进行初始化后的后处理:
* @param existingBean the existing bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean, to be passed to it if necessary
* (only passed to {@link BeanPostProcessor BeanPostProcessors};
* can follow the {@link #ORIGINAL_INSTANCE_SUFFIX} convention in order to
* enforce the given instance to be returned, i.e. no proxies etc)
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
//初始化结果对象为result,默认引用existingBean
Object result = existingBean;
//遍历该工厂创建的bean的BeanPostProcessors列表
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
//回调BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization来对现有的bean实例进行包装
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
//一般processor对不感兴趣的bean会回调直接返回result,使其能继续回调后续的BeanPostProcessor;
// 但有些processor会返回null来中断其后续的BeanPostProcessor
// 如果current为null
if (current == null) {
//直接返回result,中断其后续的BeanPostProcessor处理
return result;
}
//让result引用processor的返回结果,使其经过所有BeanPostProcess对象的后置处理的层层包装
result = current;
}
//返回经过所有BeanPostProcess对象的后置处理的层层包装后的result
return result;
}
@Override
public void destroyBean(Object existingBean) {
new DisposableBeanAdapter(existingBean, getBeanPostProcessors(), getAccessControlContext()).destroy();
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Delegate methods for resolving injection points
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public Object resolveBeanByName(String name, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
// 获取bean
return getBean(name, descriptor.getDependencyType());
}
finally {
// 为目标工厂方法提供依赖描述符
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) throws BeansException {
return resolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, null, null);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of relevant AbstractBeanFactory template methods
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Central method of this class: creates a bean instance,
* populates the bean instance, applies post-processors, etc.
* @see #doCreateBean
*/
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
// 锁定class,根据设置的class属性或者根据className来解析class
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
// 进行条件筛选,重新赋值RootBeanDefinition,并设置BeanClass属性
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
// 重新创建一个RootBeanDefinition对象
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
// 设置BeanClass属性值
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
// 验证及准备覆盖的方法,lookup-method replace-method,当需要创建的bean对象中包含了lookup-method和replace-method标签的时候,会产生覆盖操作
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
// 给BeanPostProcessors一个机会来返回代理来替代真正的实例,应用实例化前的前置处理器,用户自定义动态代理的方式,针对于当前的被代理类需要经过标准的代理流程来创建对象
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
// 实际创建bean的调用
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
/**
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
* at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.
* <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a new instance of the bean
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
* @see #instantiateBean
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
*/
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
// 这个beanWrapper是用来持有创建出来的bean对象的
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
// 获取factoryBean实例缓存
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 如果是单例对象,从factorybean实例缓存中移除当前bean定义信息
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
// 没有就创建实例,会在此处进行实例化
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 根据执行bean使用对应的策略创建新的实例,如,工厂方法,构造函数主动注入、简单初始化
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 从包装类中获取原始bean,
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
// 获取具体的bean对象的Class属性
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
// 如果不等于NullBean类型,那么修改目标类型
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
// 允许beanPostProcessor去修改合并的beanDefinition
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
// MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor后置处理器修改合并bean的定义,其中有一个非常重要的实现类 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
// 判断当前bean是否需要提前曝光:单例&允许循环依赖&当前bean正在创建中,检测循环依赖
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
// 为避免后期循环依赖,可以在bean初始化完成前将创建实例的ObjectFactory加入工厂,加入三级缓存
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
// ======================== 测试代码 start, 测试假如只有二级缓存======================
//只保留二级缓存,不向三级缓存中存放对象
// earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName,bean);
// registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
// ======================== 测试代码 end======================
// synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
// //实例化后的对象先添加到三级缓存中,三级缓存对应beanName的是一个lambda表达式(能够触发创建代理对象的机制)
// this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
// this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
// }
// }
// ======================== 测试代码 end======================
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
// 初始化bean实例
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 对bean的属性进行填充,将各个属性值注入,其中,可能存在依赖于其他bean的属性,则会递归初始化依赖的bean
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 执行初始化逻辑
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
// 从缓存中获取具体的对象
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
// earlySingletonReference只有在检测到有循环依赖的情况下才会不为空
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
// 如果exposedObject没有在初始化方法中被改变,也就是没有被增强
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
// 返回false说明依赖还没实例化好
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
// 因为bean创建后所依赖的bean一定是已经创建的
// actualDependentBeans不为空则表示当前bean创建后其依赖的bean却没有全部创建完,也就是说存在循环依赖
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
// 注册bean对象,方便后续在容器销毁的时候销毁对象
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
@Override
@Nullable
protected Class<?> predictBeanType(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?>... typesToMatch) {
// 确定给定bean定义的目标类型
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd, typesToMatch);
// Apply SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors to predict the
// eventual type after a before-instantiation shortcut.
// 通过SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor获取实际类型
if (targetType != null && !mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
boolean matchingOnlyFactoryBean = typesToMatch.length == 1 && typesToMatch[0] == FactoryBean.class;
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
Class<?> predicted = ibp.predictBeanType(targetType, beanName);
if (predicted != null &&
(!matchingOnlyFactoryBean || FactoryBean.class.isAssignableFrom(predicted))) {
return predicted;
}
}
}
}
return targetType;
}
/**
* Determine the target type for the given bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean (for error handling purposes)
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param typesToMatch the types to match in case of internal type matching purposes
* (also signals that the returned {@code Class} will never be exposed to application code)
* @return the type for the bean if determinable, or {@code null} otherwise
*/
@Nullable
protected Class<?> determineTargetType(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?>... typesToMatch) {
Class<?> targetType = mbd.getTargetType();
if (targetType == null) {
targetType = (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null ?
getTypeForFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, typesToMatch) :
resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName, typesToMatch));
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(typesToMatch) || getTempClassLoader() == null) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = targetType;
}
}
return targetType;
}
/**
* 工厂方法确定给定bean定义的目标类型。仅在尚未为目标bean注册单例实例时调用
*
* Determine the target type for the given bean definition which is based on
* a factory method. Only called if there is no singleton instance registered
* for the target bean already.
* <p>This implementation determines the type matching {@link #createBean}'s
* different creation strategies. As far as possible, we'll perform static
* type checking to avoid creation of the target bean.
* @param beanName the name of the bean (for error handling purposes)
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param typesToMatch the types to match in case of internal type matching purposes
* (also signals that the returned {@code Class} will never be exposed to application code)
* @return the type for the bean if determinable, or {@code null} otherwise
* @see #createBean
*/
@Nullable
protected Class<?> getTypeForFactoryMethod(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?>... typesToMatch) {
// 尝试获取bean的合并bean定义中的缓存工厂方法返回类型
ResolvableType cachedReturnType = mbd.factoryMethodReturnType;
// 如果成功获取到了bean的合并bean定义中的缓存工厂方法返回类型
if (cachedReturnType != null) {
// ResolvableType.resolve:将ResolvableType对象解析为Class,如果无法解析,则返回null
return cachedReturnType.resolve();
}
// 通用的返回类型,经过比较 AutowireUtils#resolveReturnTypeForFactoryMethod方法的返回结果
// 和Method#getReturnType方法的返回结果所得到共同父类。
Class<?> commonType = null;
// 尝试获取bean的合并bean定义中的缓存用于自省的唯一工厂方法对象
Method uniqueCandidate = mbd.factoryMethodToIntrospect;
// 如果成功获取到了bean的合并bean定义中的缓存用于自省的唯一工厂方法对象
if (uniqueCandidate == null) {
Class<?> factoryClass;
boolean isStatic = true;
// 获取bean的合并bean定义的工厂bean名
String factoryBeanName = mbd.getFactoryBeanName();
// 如果成功获取到bean的合并bean定义的工厂bean名
if (factoryBeanName != null) {
// 如果工厂bean名与生成该bean的bean名相等
if (factoryBeanName.equals(beanName)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"factory-bean reference points back to the same bean definition");
}
// Check declared factory method return type on factory class.
// 检查工厂类上声明的工厂方法返回类型
// 获取factoryBeanName对应的工厂类
factoryClass = getType(factoryBeanName);
isStatic = false;
}
else {
// Check declared factory method return type on bean class.
// 检查bean类上声明的工厂方法返回类型
// 为mbd解析bean类,将bean类名解析为Class引用(如果需要),并将解析后的Class存储在
// mbd中以备将来使用。
factoryClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName, typesToMatch);
}
// 如果mbd指定的工厂类获取失败
if (factoryClass == null) {
return null;
}
// 如果factoryClass是CGLIB生成的子类,则返回factoryClass的父类,否则直接返回factoryClass
factoryClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(factoryClass);
// If all factory methods have the same return type, return that type.
// Can't clearly figure out exact method due to type converting / autowiring!
// 如果所有工厂方法都具有相同的返回类型,则返回该类型。
// 由于类型转换/自动装配,无法明确找出确切的方法。
// 如果mbd有配置构造函数参数值,就获取该构造函数参数值的数量,否则为0
int minNrOfArgs =
(mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() ? mbd.getConstructorArgumentValues().getArgumentCount() : 0);
// 在子类和所有超类上获取一组唯一的已声明方法,即被重写非协变返回类型的方法
// 首先包含子类方法和然后遍历父类层次结构任何方法,将过滤出所有与已包含的方法匹配的签名方法。
Method[] candidates = this.factoryMethodCandidateCache.computeIfAbsent(factoryClass,
clazz -> ReflectionUtils.getUniqueDeclaredMethods(clazz, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS));
// 遍历候选方法
for (Method candidate : candidates) {
// 如果candidate是否静态的判断结果与isStatic一致且candidate有资格作为工厂方法且candidate的方法参数数量>=minNrOfArgs
if (Modifier.isStatic(candidate.getModifiers()) == isStatic && mbd.isFactoryMethod(candidate) &&
candidate.getParameterCount() >= minNrOfArgs) {
// Declared type variables to inspect?
// 声明要检查的类型变量?
// 如果candidate的参数数量>0
if (candidate.getTypeParameters().length > 0) {
try {
// Fully resolve parameter names and argument values.
// 完全解析参数名称和参数值
// 获取candidate的参数类型数组
Class<?>[] paramTypes = candidate.getParameterTypes();
// 参数名数组
String[] paramNames = null;
// 获取参数名发现器
ParameterNameDiscoverer pnd = getParameterNameDiscoverer();
// 如果pnd不为null
if (pnd != null) {
// 使用pnd获取candidate的参数名
paramNames = pnd.getParameterNames(candidate);
}
// 获取mbd的构造函数参数值
ConstructorArgumentValues cav = mbd.getConstructorArgumentValues();
// HashSet:HashSet简单的理解就是HashSet对象中不能存储相同的数据,存储数据时是无序的。
// 但是HashSet存储元素的顺序并不是按照存入时的顺序(和List显然不同) 是按照哈希值来存的所以取数据也是按照哈希值取得。
// 定义一个存储构造函数参数值ValueHolder对象的HashSet
Set<ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder> usedValueHolders = new HashSet<>(paramTypes.length);
// 定义一个用于存储参数值的数组
Object[] args = new Object[paramTypes.length];
// 遍历参数值
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
// 获取第i个构造函数参数值ValueHolder对象
// 尽可能的提供位置,参数类型,参数名以最精准的方式获取获取第i个构造函数参数值ValueHolder对象,传入
// usedValueHolder来提示cav#getArgumentValue方法不应再次返回该usedValueHolder所出现的ValueHolder对象
// (如果有 多个类型的通用参数值,则允许返回下一个通用参数匹配项)
ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder valueHolder = cav.getArgumentValue(
i, paramTypes[i], (paramNames != null ? paramNames[i] : null), usedValueHolders);
// 如果valueHolder获取失败
if (valueHolder == null) {
// 使用不匹配类型,不匹配参数名的方式获取除userValueHolders以外的下一个参数值valueHolder对象
valueHolder = cav.getGenericArgumentValue(null, null, usedValueHolders);
}
// 如果valueHolder获取成功
if (valueHolder != null) {
// 从valueHolder中获取值保存到第i个args元素中
args[i] = valueHolder.getValue();
// 将valueHolder添加到usedValueHolders缓存中,表示该valueHolder已经使用过
usedValueHolders.add(valueHolder);
}
}
// 获取candidate的最终返回类型,该方法支持泛型情况下的目标类型获取
Class<?> returnType = AutowireUtils.resolveReturnTypeForFactoryMethod(
candidate, args, getBeanClassLoader());
// 如果commonType为null且returnType等于candidate直接获取的返回类型,唯一候选方法就是candidate,否则为null
uniqueCandidate = (commonType == null && returnType == candidate.getReturnType() ?
candidate : null);
// 获取returnType与commonType的共同父类,将该父类重新赋值给commonType
commonType = ClassUtils.determineCommonAncestor(returnType, commonType);
// 如果commonType为null
if (commonType == null) {
// Ambiguous return types found: return null to indicate "not determinable".
// 找到不明确的返回类型:返回null表示'不可确定'
return null;
}
}
// 捕捉获取commonType的所有异常
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to resolve generic return type for factory method: " + ex);
}
}
}
// 如果candidate无需参数
else {
// 如果还没有找到commonType,candidate就为唯一的候选方法
uniqueCandidate = (commonType == null ? candidate : null);
// 获取candidate返回类型与commonType的共同父类,将该父类重新赋值给commonType
commonType = ClassUtils.determineCommonAncestor(candidate.getReturnType(), commonType);
// 如果commonType为null
if (commonType == null) {
// Ambiguous return types found: return null to indicate "not determinable".
// 找到不明确的返回类型:返回null表示'不可确定'
return null;
}
}
}
}
// 缓存uniqueCandidate到mbd的factoryMethodToIntrospect
mbd.factoryMethodToIntrospect = uniqueCandidate;
// 如果commonType为null,加上这个判断能保证下面的步骤commonType肯定有值
if (commonType == null) {
// 找到不明确的返回类型:返回null表示'不可确定'
return null;
}
}
// Common return type found: all factory methods return same type. For a non-parameterized
// unique candidate, cache the full type declaration context of the target factory method.
// 找到常见的返回类型:所有工厂方法都返回相同的类型。对象非参数化的唯一候选者,缓存目标工厂方法的
// 完整类型声明上下文
// 如果获取到了uniqueCandidate就获取uniqueCandidate的返回类型,否则就用commonType作为返回类型
cachedReturnType = (uniqueCandidate != null ?
ResolvableType.forMethodReturnType(uniqueCandidate) : ResolvableType.forClass(commonType));
// 缓存cachedReturnType到mdb的factoryMethodReturnType
mbd.factoryMethodReturnType = cachedReturnType;
// 返回cachedReturnType封装的Class对象
return cachedReturnType.resolve();
}
/**
* This implementation attempts to query the FactoryBean's generic parameter metadata
* if present to determine the object type. If not present, i.e. the FactoryBean is
* declared as a raw type, checks the FactoryBean's {@code getObjectType} method
* on a plain instance of the FactoryBean, without bean properties applied yet.
* If this doesn't return a type yet, and {@code allowInit} is {@code true} a
* full creation of the FactoryBean is used as fallback (through delegation to the
* superclass's implementation).
* <p>The shortcut check for a FactoryBean is only applied in case of a singleton
* FactoryBean. If the FactoryBean instance itself is not kept as singleton,
* it will be fully created to check the type of its exposed object.
*/
@Override
protected ResolvableType getTypeForFactoryBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, boolean allowInit) {
// Check if the bean definition itself has defined the type with an attribute
ResolvableType result = getTypeForFactoryBeanFromAttributes(mbd);
if (result != ResolvableType.NONE) {
return result;
}
ResolvableType beanType =
(mbd.hasBeanClass() ? ResolvableType.forClass(mbd.getBeanClass()) : ResolvableType.NONE);
// For instance supplied beans try the target type and bean class
if (mbd.getInstanceSupplier() != null) {
result = getFactoryBeanGeneric(mbd.targetType);
if (result.resolve() != null) {
return result;
}
result = getFactoryBeanGeneric(beanType);
if (result.resolve() != null) {
return result;
}
}
// Consider factory methods
String factoryBeanName = mbd.getFactoryBeanName();
String factoryMethodName = mbd.getFactoryMethodName();
// Scan the factory bean methods
if (factoryBeanName != null) {
if (factoryMethodName != null) {
// Try to obtain the FactoryBean's object type from its factory method
// declaration without instantiating the containing bean at all.
BeanDefinition factoryBeanDefinition = getBeanDefinition(factoryBeanName);
Class<?> factoryBeanClass;
if (factoryBeanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition &&
((AbstractBeanDefinition) factoryBeanDefinition).hasBeanClass()) {
factoryBeanClass = ((AbstractBeanDefinition) factoryBeanDefinition).getBeanClass();
}
else {
RootBeanDefinition fbmbd = getMergedBeanDefinition(factoryBeanName, factoryBeanDefinition);
factoryBeanClass = determineTargetType(factoryBeanName, fbmbd);
}
if (factoryBeanClass != null) {
result = getTypeForFactoryBeanFromMethod(factoryBeanClass, factoryMethodName);
if (result.resolve() != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
// If not resolvable above and the referenced factory bean doesn't exist yet,
// exit here - we don't want to force the creation of another bean just to
// obtain a FactoryBean's object type...
if (!isBeanEligibleForMetadataCaching(factoryBeanName)) {
return ResolvableType.NONE;
}
}
// If we're allowed, we can create the factory bean and call getObjectType() early
if (allowInit) {
FactoryBean<?> factoryBean = (mbd.isSingleton() ?
getSingletonFactoryBeanForTypeCheck(beanName, mbd) :
getNonSingletonFactoryBeanForTypeCheck(beanName, mbd));
if (factoryBean != null) {
// Try to obtain the FactoryBean's object type from this early stage of the instance.
Class<?> type = getTypeForFactoryBean(factoryBean);
if (type != null) {
return ResolvableType.forClass(type);
}
// No type found for shortcut FactoryBean instance:
// fall back to full creation of the FactoryBean instance.
return super.getTypeForFactoryBean(beanName, mbd, true);
}
}
if (factoryBeanName == null && mbd.hasBeanClass() && factoryMethodName != null) {
// No early bean instantiation possible: determine FactoryBean's type from
// static factory method signature or from class inheritance hierarchy...
return getTypeForFactoryBeanFromMethod(mbd.getBeanClass(), factoryMethodName);
}
result = getFactoryBeanGeneric(beanType);
if (result.resolve() != null) {
return result;
}
return ResolvableType.NONE;
}
private ResolvableType getFactoryBeanGeneric(@Nullable ResolvableType type) {
if (type == null) {
return ResolvableType.NONE;
}
return type.as(FactoryBean.class).getGeneric();
}
/**
* Introspect the factory method signatures on the given bean class,
* trying to find a common {@code FactoryBean} object type declared there.
* @param beanClass the bean class to find the factory method on
* @param factoryMethodName the name of the factory method
* @return the common {@code FactoryBean} object type, or {@code null} if none
*/
private ResolvableType getTypeForFactoryBeanFromMethod(Class<?> beanClass, String factoryMethodName) {
// CGLIB subclass methods hide generic parameters; look at the original user class.
Class<?> factoryBeanClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(beanClass);
FactoryBeanMethodTypeFinder finder = new FactoryBeanMethodTypeFinder(factoryMethodName);
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(factoryBeanClass, finder, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
return finder.getResult();
}
/**
* This implementation attempts to query the FactoryBean's generic parameter metadata
* if present to determine the object type. If not present, i.e. the FactoryBean is
* declared as a raw type, checks the FactoryBean's {@code getObjectType} method
* on a plain instance of the FactoryBean, without bean properties applied yet.
* If this doesn't return a type yet, a full creation of the FactoryBean is
* used as fallback (through delegation to the superclass's implementation).
* <p>The shortcut check for a FactoryBean is only applied in case of a singleton
* FactoryBean. If the FactoryBean instance itself is not kept as singleton,
* it will be fully created to check the type of its exposed object.
*/
@Override
@Deprecated
@Nullable
protected Class<?> getTypeForFactoryBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
return getTypeForFactoryBean(beanName, mbd, true).resolve();
}
/**
* 获取对 指定Bean 的 早期访问引用,通常用于解决循环引用
*
* Obtain a reference for early access to the specified bean,
* typically for the purpose of resolving a circular reference.
* @param beanName the name of the bean (for error handling purposes)
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param bean the raw bean instance
* @return the object to expose as bean reference
*/
protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) {
// 默认最终公开的对象是bean,通过createBeanInstance创建出来的普通对象
Object exposedObject = bean;
// mbd的systhetic属性:设置此bean定义是否是"synthetic",一般是指只有AOP相关的pointCut配置或者Advice配置才会将 synthetic设置为true
// 如果mdb不是synthetic且此工厂拥有InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 遍历工厂内的所有后处理器
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 如果bp是SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor实例
if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 让exposedObject经过每个SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的包装
exposedObject = ibp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);
}
}
}
// 返回最终经过层次包装后的对象
return exposedObject;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation methods
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Obtain a "shortcut" singleton FactoryBean instance to use for a
* {@code getObjectType()} call, without full initialization of the FactoryBean.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @return the FactoryBean instance, or {@code null} to indicate
* that we couldn't obtain a shortcut FactoryBean instance
*/
@Nullable
private FactoryBean<?> getSingletonFactoryBeanForTypeCheck(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
synchronized (getSingletonMutex()) {
// 是否已经实例化
BeanWrapper bw = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.get(beanName);
if (bw != null) {
// 实例化直接返回
return (FactoryBean<?>) bw.getWrappedInstance();
}
// factoryBeanInstanceCache没有,看看是否已经创建
Object beanInstance = getSingleton(beanName, false);
// 创建好的单例时FactoryBean,直接返回
if (beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean) {
return (FactoryBean<?>) beanInstance;
}
// 创建好的单例不是FactoryBean,或者已经创建或者正在创建,返回空
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName) ||
(mbd.getFactoryBeanName() != null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(mbd.getFactoryBeanName()))) {
return null;
}
Object instance;
try {
// Mark this bean as currently in creation, even if just partially.
// 创建前检查
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
// 看看代理能不能返回一个实例
instance = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbd);
if (instance == null) {
// 代理没返回,就创建一个
bw = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, null);
instance = bw.getWrappedInstance();
}
}
catch (UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex) {
// Don't swallow, probably misconfiguration...
throw ex;
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
// Instantiation failure, maybe too early...
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean creation exception on singleton FactoryBean type check: " + ex);
}
onSuppressedException(ex);
return null;
}
finally {
// Finished partial creation of this bean.
// 创建后检查
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
// 获取到的实例转换为FactoryBean
FactoryBean<?> fb = getFactoryBean(beanName, instance);
if (bw != null) {
// 放入缓存
this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.put(beanName, bw);
}
return fb;
}
}
/**
* Obtain a "shortcut" non-singleton FactoryBean instance to use for a
* {@code getObjectType()} call, without full initialization of the FactoryBean.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @return the FactoryBean instance, or {@code null} to indicate
* that we couldn't obtain a shortcut FactoryBean instance
*/
@Nullable
private FactoryBean<?> getNonSingletonFactoryBeanForTypeCheck(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 当前线程有在创建
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
return null;
}
Object instance;
try {
// Mark this bean as currently in creation, even if just partially.
// 标记正在创建
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
// 看看代理能不能返回一个实例
instance = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbd);
if (instance == null) {
BeanWrapper bw = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, null);
instance = bw.getWrappedInstance();
}
}
catch (UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex) {
// Don't swallow, probably misconfiguration...
throw ex;
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
// Instantiation failure, maybe too early...
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean creation exception on non-singleton FactoryBean type check: " + ex);
}
onSuppressedException(ex);
return null;
}
finally {
// Finished partial creation of this bean.
// 标记创建结束
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
// 直接缓缓为factoryBean
return getFactoryBean(beanName, instance);
}
/**
* 应用MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors类型的beanPostProcessor到指定的beanDefinition中,
* 执行postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法
*
* Apply MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors to the specified bean definition,
* invoking their {@code postProcessMergedBeanDefinition} methods.
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param beanType the actual type of the managed bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @see MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
*/
protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp;
bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
}
}
/**
* 调用预实例化的postprocessor,处理是否有预实例化的快捷方式对于特殊的bean
*
* Apply before-instantiation post-processors, resolving whether there is a
* before-instantiation shortcut for the specified bean.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @return the shortcut-determined bean instance, or {@code null} if none
*/
@Nullable
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
// 如果beforeInstantiationResolved值为null或者true,那么表示尚未被处理,进行后续的处理
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
// 确认beanclass确实在此处进行处理
// 判断当前mbd是否是合成的,只有在实现aop的时候synthetic的值才为true,并且是否实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 获取类型
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
// 是否解析了
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
/**
* InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor类型的处理器处理,返回的是一个Object对象,也就是说此处可以做代理的事,如果发现有一个处理器返回
* 的不是null,就直接返回了
*
* Apply InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors to the specified bean definition
* (by class and name), invoking their {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} methods.
* <p>Any returned object will be used as the bean instead of actually instantiating
* the target bean. A {@code null} return value from the post-processor will
* result in the target bean being instantiated.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean to be instantiated
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean object to use instead of a default instance of the target bean, or {@code null}
* @see InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
*/
@Nullable
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Create a new instance for the specified bean, using an appropriate instantiation strategy:
* factory method, constructor autowiring, or simple instantiation.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
* @see #obtainFromSupplier
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
* @see #instantiateBean
*/
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
// 确认需要创建的bean实例的类可以实例化
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
// 确保class不为空,并且访问权限是public
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
// 判断当前beanDefinition中是否包含实例供应器,此处相当于一个回调方法,利用回调方法来创建bean
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
// 如果工厂方法不为空则使用工厂方法初始化策略
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 一个类可能有多个构造器,所以Spring得根据参数个数、类型确定需要调用的构造器
// 在使用构造器创建实例后,Spring会将解析过后确定下来的构造器或工厂方法保存在缓存中,避免再次创建相同bean时再次解析
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
// 标记下,防止重复创建同一个bean
boolean resolved = false;
// 是否需要自动装配
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
// 如果没有参数
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
// 因为一个类可能由多个构造函数,所以需要根据配置文件中配置的参数或传入的参数来确定最终调用的构造函数。
// 因为判断过程会比较,所以spring会将解析、确定好的构造函数缓存到BeanDefinition中的resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod字段中。
// 在下次创建相同时直接从RootBeanDefinition中的属性resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod缓存的值获取,避免再次解析
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
// 有构造参数的或者工厂方法
if (resolved) {
// 构造器有参数
if (autowireNecessary) {
// 构造函数自动注入
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
// 使用默认构造函数构造
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
// 从bean后置处理器中为自动装配寻找构造方法, 有且仅有一个有参构造或者有且仅有@Autowired注解构造
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
// 以下情况符合其一即可进入
// 1、存在可选构造方法
// 2、自动装配模型为构造函数自动装配
// 3、给BeanDefinition中设置了构造参数值
// 4、有参与构造函数参数列表的参数
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// Preferred constructors for default construction?
// 找出最合适的默认构造方法
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
// 构造函数自动注入
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
// 使用默认无参构造函数创建对象,如果没有无参构造且存在多个有参构造且没有@AutoWired注解构造,会报错
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
/**
* 从supplier获取bean
*
* Obtain a bean instance from the given supplier.
* @param instanceSupplier the configured supplier
* @param beanName the corresponding bean name
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
* @since 5.0
* @see #getObjectForBeanInstance
*/
protected BeanWrapper obtainFromSupplier(Supplier<?> instanceSupplier, String beanName) {
Object instance;
// 获取原先创建的beanName
String outerBean = this.currentlyCreatedBean.get();
// 用当前作对做替换
this.currentlyCreatedBean.set(beanName);
try {
// 调用supplier的方法
instance = instanceSupplier.get();
}
finally {
if (outerBean != null) {
this.currentlyCreatedBean.set(outerBean);
}
else {
this.currentlyCreatedBean.remove();
}
}
// 如果没有创建对象,默认为NullBean
if (instance == null) {
instance = new NullBean();
}
// 初始化BeanWrapper并返回
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(instance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
/**
* Overridden in order to implicitly register the currently created bean as
* dependent on further beans getting programmatically retrieved during a
* {@link Supplier} callback.
* @since 5.0
* @see #obtainFromSupplier
*/
@Override
protected Object getObjectForBeanInstance(
Object beanInstance, String name, String beanName, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 注册当前创建的bean和给定的beanName的依赖
String currentlyCreatedBean = this.currentlyCreatedBean.get();
if (currentlyCreatedBean != null) {
registerDependentBean(beanName, currentlyCreatedBean);
}
// 返回一个bean
return super.getObjectForBeanInstance(beanInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
/**
* 确定用于给定bean的候选构造函数,使用bean的后置处理器机制
*
* Determine candidate constructors to use for the given bean, checking all registered
* {@link SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors}.
* @param beanClass the raw class of the bean
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the candidate constructors, or {@code null} if none specified
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#determineCandidateConstructors
*/
@Nullable
protected Constructor<?>[] determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(@Nullable Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (beanClass != null && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
// 从SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor判断
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
Constructor<?>[] ctors = ibp.determineCandidateConstructors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null) {
return ctors;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Instantiate the given bean using its default constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
*/
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, this),
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 获取实例化策略并且进行实例化操作
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, this);
}
// 包装成BeanWrapper
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
/**
* 通过工厂方法实例化,先获取构造器解析器,然后用工厂方法进行实例化
*
* Instantiate the bean using a named factory method. The method may be static, if the
* mbd parameter specifies a class, rather than a factoryBean, or an instance variable
* on a factory object itself configured using Dependency Injection.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param explicitArgs argument values passed in programmatically via the getBean method,
* or {@code null} if none (-> use constructor argument values from bean definition)
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
* @see #getBean(String, Object[])
*/
protected BeanWrapper instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(
String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
// 创建构造器处理器并使用factorymethod进行实例化操作
return new ConstructorResolver(this).instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, explicitArgs);
}
/**
* 自动装配的构造方法
*
* "autowire constructor" (with constructor arguments by type) behavior.
* Also applied if explicit constructor argument values are specified,
* matching all remaining arguments with beans from the bean factory.
* <p>This corresponds to constructor injection: In this mode, a Spring
* bean factory is able to host components that expect constructor-based
* dependency resolution.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param ctors the chosen candidate constructors
* @param explicitArgs argument values passed in programmatically via the getBean method,
* or {@code null} if none (-> use constructor argument values from bean definition)
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
*/
protected BeanWrapper autowireConstructor(
String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Constructor<?>[] ctors, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
return new ConstructorResolver(this).autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, explicitArgs);
}
/**
* 用来自 BeanDefinition的属性值填充给定的BeanWrapper中的bean实例
*
* Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values
* from the bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param bw the BeanWrapper with bean instance
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // for postProcessPropertyValues
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
// 如果beanWrapper为空
if (bw == null) {
// 如果mbd有需要设置的属性
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
// 抛出bean创建异常
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
// 没有可填充的属性,直接跳过
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
// 给任何实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors的子类机会去修改bean的状态再设置属性之前,可以被用来支持类型的字段注入
// 否是"synthetic"。一般是指只有AOP相关的pointCut配置或者Advice配置才会将 synthetic设置为true
// 如果mdb是不是'syntheic'且工厂拥有InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
//遍历工厂中的BeanPostProcessor对象
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
//如果 bp 是 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 实例
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// //postProcessAfterInstantiation:一般用于设置属性
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
}
//PropertyValues:包含以一个或多个PropertyValue对象的容器,通常包括针对特定目标Bean的一次更新
//如果mdb有PropertyValues就获取其PropertyValues
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
// 获取 mbd 的 自动装配模式
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
// 如果 自动装配模式 为 按名称自动装配bean属性 或者 按类型自动装配bean属性
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
//MutablePropertyValues:PropertyValues接口的默认实现。允许对属性进行简单操作,并提供构造函数来支持从映射 进行深度复制和构造
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
// 根据autotowire的名称(如适用)添加属性值
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
//通过bw的PropertyDescriptor属性名,查找出对应的Bean对象,将其添加到newPvs中
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
// 根据自动装配的类型(如果适用)添加属性值
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
//通过bw的PropertyDescriptor属性类型,查找出对应的Bean对象,将其添加到newPvs中
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
//让pvs重新引用newPvs,newPvs此时已经包含了pvs的属性值以及通过AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME,AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE自动装配所得到的属性值
pvs = newPvs;
}
//工厂是否拥有InstiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
//mbd.getDependencyCheck(),默认返回 DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE,表示 不检查
//是否需要依赖检查
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
//经过筛选的PropertyDesciptor数组,存放着排除忽略的依赖项或忽略项上的定义的属性
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
//如果工厂拥有InstiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,那么处理对应的流程,主要是对几个注解的赋值工作包含的两个关键子类是CommonAnnoationBeanPostProcessor,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
//如果pvs为null
if (pvs == null) {
//尝试获取mbd的PropertyValues
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
//遍历工厂内的所有后置处理器
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
//如果 bp 是 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的实例
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
//将bp 强转成 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 对象
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
//postProcessProperties:在工厂将给定的属性值应用到给定Bean之前,对它们进行后处理,不需要任何属性扫描符。该回调方法在未来的版本会被删掉。
// -- 取而代之的是 postProcessPropertyValues 回调方法。
// 让ibp对pvs增加对bw的Bean对象的propertyValue,或编辑pvs的proertyValue
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
//如果pvs为null
if (pvsToUse == null) {
//如果filteredPds为null
if (filteredPds == null) {
//mbd.allowCaching:是否允许缓存,默认时允许的。缓存除了可以提高效率以外,还可以保证在并发的情况下,返回的PropertyDesciptor[]永远都是同一份
//从bw提取一组经过筛选的PropertyDesciptor,排除忽略的依赖项或忽略项上的定义的属性
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
//postProcessPropertyValues:一般进行检查是否所有依赖项都满足,例如基于"Require"注释在 bean属性 setter,
// -- 替换要应用的属性值,通常是通过基于原始的PropertyValues创建一个新的MutablePropertyValue实例, 添加或删除特定的值
// -- 返回的PropertyValues 将应用于bw包装的bean实例 的实际属性值(添加PropertyValues实例到pvs 或者 设置为null以跳过属性填充)
//回到ipd的postProcessPropertyValues方法
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
//如果pvsToUse为null,将终止该方法精致,以跳过属性填充
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
//让pvs引用pvsToUse
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
//如果需要依赖检查
if (needsDepCheck) {
//如果filteredPds为null
if (filteredPds == null) {
//从bw提取一组经过筛选的PropertyDesciptor,排除忽略的依赖项或忽略项上的定义的属性
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
//检查依赖项:主要检查pd的setter方法需要赋值时,pvs中有没有满足其pd的需求的属性值可供其赋值
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
//如果pvs不为null
if (pvs != null) {
//应用给定的属性值,解决任何在这个bean工厂运行时其他bean的引用。必须使用深拷贝,所以我们 不会永久地修改这个属性
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
/**
* 通过bw的PropertyDescriptor属性名,查找出对应的Bean对象,将其添加到pvs中
*
* Fill in any missing property values with references to
* other beans in this factory if autowire is set to "byName".
* @param beanName the name of the bean we're wiring up.
* Useful for debugging messages; not used functionally.
* @param mbd bean definition to update through autowiring
* @param bw the BeanWrapper from which we can obtain information about the bean
* @param pvs the PropertyValues to register wired objects with
*/
protected void autowireByName(
String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
//获取bw中有setter方法 && 非简单类型属性 && mbd的PropertyValues中没有该pd的属性名的 PropertyDescriptor 属性名数组
String[] propertyNames = unsatisfiedNonSimpleProperties(mbd, bw);
//遍历属性名
for (String propertyName : propertyNames) {
//如果该bean工厂有propertyName的beanDefinition或外部注册的singleton实例
if (containsBean(propertyName)) {
//获取该工厂中propertyName的bean对象
Object bean = getBean(propertyName);
//将propertyName,bean添加到pvs中
pvs.add(propertyName, bean);
//注册propertyName与beanName的依赖关系
registerDependentBean(propertyName, beanName);
//打印跟踪日志
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Added autowiring by name from bean name '" + beanName +
"' via property '" + propertyName + "' to bean named '" + propertyName + "'");
}
}
else {
//打印跟踪日志
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Not autowiring property '" + propertyName + "' of bean '" + beanName +
"' by name: no matching bean found");
}
}
}
}
/**
* 定义 "按类型自动装配" (按类型bean属性)行为的抽象方法
*
* Abstract method defining "autowire by type" (bean properties by type) behavior.
* <p>This is like PicoContainer default, in which there must be exactly one bean
* of the property type in the bean factory. This makes bean factories simple to
* configure for small namespaces, but doesn't work as well as standard Spring
* behavior for bigger applications.
* @param beanName the name of the bean to autowire by type
* @param mbd the merged bean definition to update through autowiring
* @param bw the BeanWrapper from which we can obtain information about the bean
* @param pvs the PropertyValues to register wired objects with
*/
protected void autowireByType(
String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
//获取工厂的自定义类型转换器
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
//如果没有配置自定义类型转换器
if (converter == null) {
//使用bw作为类型转换器
converter = bw;
}
//存放所有候选Bean名的集合
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
//获取bw中有setter方法 && 非简单类型属性 && mbd的PropertyValues中没有该pd的属性名的 PropertyDescriptor 属性名数组
String[] propertyNames = unsatisfiedNonSimpleProperties(mbd, bw);
//遍历属性名数组
for (String propertyName : propertyNames) {
try {
//PropertyDescriptor:表示JavaBean类通过存储器导出一个属性
//从bw中获取propertyName对应的PropertyDescriptor
PropertyDescriptor pd = bw.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName);
// Don't try autowiring by type for type Object: never makes sense,
// even if it technically is a unsatisfied, non-simple property.
// 不要尝试按类型自动装配对象:永远是有意义的,即使它在技术上是一个不满意,复杂属性
//如果pd的属性值类型不是 Object
if (Object.class != pd.getPropertyType()) {
//获取pd属性的Setter方法的方法参数包装对象
MethodParameter methodParam = BeanUtils.getWriteMethodParameter(pd);
// Do not allow eager init for type matching in case of a prioritized post-processor.
//判断bean对象是否是PriorityOrder实例,如果不是就允许急于初始化来进行类型匹配。
//eager为true时会导致初始化lazy-init单例和由FactoryBeans(或带有"factory-bean"引用的工厂方法)创建 的对象以进行类型检查
boolean eager = !(bw.getWrappedInstance() instanceof PriorityOrdered);
//AutowireByTypeDependencyDescriptor:根据类型依赖自动注入的描述符,重写了 getDependencyName() 方法,使其永远返回null
//将 methodParam 封装包装成AutowireByTypeDependencyDescriptor对象
DependencyDescriptor desc = new AutowireByTypeDependencyDescriptor(methodParam, eager);
//根据据desc的依赖类型解析出与descriptor所包装的对象匹配的候选Bean对象
Object autowiredArgument = resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, converter);
//如果autowiredArgument不为null
if (autowiredArgument != null) {
//将proeprtyName.autowireArgument作为键值添加到pvs中
pvs.add(propertyName, autowiredArgument);
}
//遍历所有候选Bean名集合
for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {
//注册beanName与dependentBeanNamed的依赖关系
registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, beanName);
//打印跟踪日志
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Autowiring by type from bean name '" + beanName + "' via property '" +
propertyName + "' to bean named '" + autowiredBeanName + "'");
}
}
//将候选Bean名集合清空
autowiredBeanNames.clear();
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
//捕捉自动装配时抛出的Bean异常,重新抛出 不满足依赖异常
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, propertyName, ex);
}
}
}
/**
* 返回一个不满足要求的非简单bean属性数组。这些可能是对工厂中其他bean的不满意的引用。不包括简单属性,如原始或字符串
*
* 获取bw中有setter方法 && 非简单类型属性 && mbd的PropertyValues中没有该pd的属性名的 PropertyDescriptor 属性名数组
*
* Return an array of non-simple bean properties that are unsatisfied.
* These are probably unsatisfied references to other beans in the
* factory. Does not include simple properties like primitives or Strings.
* @param mbd the merged bean definition the bean was created with
* @param bw the BeanWrapper the bean was created with
* @return an array of bean property names
* @see org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils#isSimpleProperty
*/
protected String[] unsatisfiedNonSimpleProperties(AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
//TreeSet:TreeSet底层是二叉树,可以对对象元素进行排序,但是自定义类需要实现comparable接口,重写comparaTo()方法。
Set<String> result = new TreeSet<>();
//获取mdbd的所有属性值
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
//PropertyDescriptor:表示JavaBean类通过存储器导出一个属性,获取bw的所有属性描述对象
PropertyDescriptor[] pds = bw.getPropertyDescriptors();
//遍历属性描述对象
for (PropertyDescriptor pd : pds) {
//如果 pd有写入属性方法 && 该pd不是被排除在依赖项检查之外 && pvs没有该pd的属性名 && pd的属性类型不是"简单值类型"
if (pd.getWriteMethod() != null && !isExcludedFromDependencyCheck(pd) && !pvs.contains(pd.getName()) &&
!BeanUtils.isSimpleProperty(pd.getPropertyType())) {
//将pdd的属性名添加到result中
result.add(pd.getName());
}
}
//将result装换成数组
return StringUtils.toStringArray(result);
}
/**
* 过滤出需要依赖检查的属性
*
* Extract a filtered set of PropertyDescriptors from the given BeanWrapper,
* excluding ignored dependency types or properties defined on ignored dependency interfaces.
* @param bw the BeanWrapper the bean was created with
* @param cache whether to cache filtered PropertyDescriptors for the given bean Class
* @return the filtered PropertyDescriptors
* @see #isExcludedFromDependencyCheck
* @see #filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapper)
*/
protected PropertyDescriptor[] filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(BeanWrapper bw, boolean cache) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filtered = this.filteredPropertyDescriptorsCache.get(bw.getWrappedClass());
if (filtered == null) {
filtered = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw);
// 缓存
if (cache) {
PropertyDescriptor[] existing =
this.filteredPropertyDescriptorsCache.putIfAbsent(bw.getWrappedClass(), filtered);
if (existing != null) {
filtered = existing;
}
}
}
return filtered;
}
/**
* Extract a filtered set of PropertyDescriptors from the given BeanWrapper,
* excluding ignored dependency types or properties defined on ignored dependency interfaces.
* @param bw the BeanWrapper the bean was created with
* @return the filtered PropertyDescriptors
* @see #isExcludedFromDependencyCheck
*/
protected PropertyDescriptor[] filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(BeanWrapper bw) {
List<PropertyDescriptor> pds = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(bw.getPropertyDescriptors()));
pds.removeIf(this::isExcludedFromDependencyCheck);
return pds.toArray(new PropertyDescriptor[0]);
}
/**
* 确定给定bean属性是否被排除在依赖项检查之外
*
* Determine whether the given bean property is excluded from dependency checks.
* <p>This implementation excludes properties defined by CGLIB and
* properties whose type matches an ignored dependency type or which
* are defined by an ignored dependency interface.
* @param pd the PropertyDescriptor of the bean property
* @return whether the bean property is excluded
* @see #ignoreDependencyType(Class)
* @see #ignoreDependencyInterface(Class)
*/
protected boolean isExcludedFromDependencyCheck(PropertyDescriptor pd) {
//pd的属性是CGLIB定义的属性 || 该工厂的忽略依赖类型列表中包含该pd的属性类型 || pd的属性是ignoredDependencyInterfaces里面的接口定义的方法
return (AutowireUtils.isExcludedFromDependencyCheck(pd) ||
this.ignoredDependencyTypes.contains(pd.getPropertyType()) ||
AutowireUtils.isSetterDefinedInInterface(pd, this.ignoredDependencyInterfaces));
}
/**
* 执行依赖检查所有暴露的属性已经被设置
*
* Perform a dependency check that all properties exposed have been set,
* if desired. Dependency checks can be objects (collaborating beans),
* simple (primitives and String), or all (both).
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition the bean was created with
* @param pds the relevant property descriptors for the target bean
* @param pvs the property values to be applied to the bean
* @see #isExcludedFromDependencyCheck(java.beans.PropertyDescriptor)
*/
protected void checkDependencies(
String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs)
throws UnsatisfiedDependencyException {
int dependencyCheck = mbd.getDependencyCheck();
for (PropertyDescriptor pd : pds) {
if (pd.getWriteMethod() != null && (pvs == null || !pvs.contains(pd.getName()))) {
boolean isSimple = BeanUtils.isSimpleProperty(pd.getPropertyType());
boolean unsatisfied = (dependencyCheck == AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_ALL) ||
(isSimple && dependencyCheck == AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_SIMPLE) ||
(!isSimple && dependencyCheck == AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_OBJECTS);
if (unsatisfied) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, pd.getName(),
"Set this property value or disable dependency checking for this bean.");
}
}
}
}
/**
* 应用给定的属性值,解决任何在这个bean工厂运行时其他bean的引用。必须使用深拷贝,所以我们不会永久地修改这个属性
*
* Apply the given property values, resolving any runtime references
* to other beans in this bean factory. Must use deep copy, so we
* don't permanently modify this property.
* @param beanName the bean name passed for better exception information
* @param mbd the merged bean definition
* @param bw the BeanWrapper wrapping the target object
* @param pvs the new property values
*/
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {
// 如果pvs没有PropertyValue
if (pvs.isEmpty()) {
// 直接结束方法
return;
}
// 如果有安全管理器,且bw是BeanWrapperImpl的实例
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && bw instanceof BeanWrapperImpl) {
// 设置bw的安全上下文为工厂的访问控制上下文
((BeanWrapperImpl) bw).setSecurityContext(getAccessControlContext());
}
//MutablePropertyValues:PropertyValues接口的默认实现。允许对属性进行简单操作,并提供构造函数来支持从映射 进行深度复制和构造
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = null;
// 原始属性列表
List<PropertyValue> original;
// 如果pvs是MutablePropertyValues
if (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) {
// 类型强制转换
mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs;
//isConverted:返回该holder是否只包含转换后的值(true),或者是否仍然需要转换这些值
//如果mpvs只包含转换后的值
if (mpvs.isConverted()) {
// Shortcut: use the pre-converted values as-is.
try {
// 已完成,直接返回
bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs);
return;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
//捕捉Bean异常,重新抛出Bean创佳异常:错误设置属性值。
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
// 获取mpvs的PropertyValue列表
original = mpvs.getPropertyValueList();
}
else {
//获取pvs的PropertyValue对象数组,并将其转换成列表
original = Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues());
}
// 获取用户自定义类型转换器
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
// 如果转换器为空,则直接把包装类赋值给converter
if (converter == null) {
converter = bw;
}
//BeanDefinitionValueResolver:在bean工厂实现中使用Helper类,它将beanDefinition对象中包含的值解析为应用于 目标bean实例的实际值
BeanDefinitionValueResolver valueResolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this, beanName, mbd, converter);
// Create a deep copy, resolving any references for values.
// 创建一个深拷贝,解析任何值引用
List<PropertyValue> deepCopy = new ArrayList<>(original.size());
//是否还需要解析标记
boolean resolveNecessary = false;
// 遍历属性,递归处理将属性转换为对应类的对应属性的类型
for (PropertyValue pv : original) {
// 如果该属性已经解析过
if (pv.isConverted()) {
//将pv添加到deepCopy中
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
// 如果属性没有被解析过
else {
// 获取属性的名字
String propertyName = pv.getName();
// 获取未经类型转换的值
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
// AutowiredPropertyMarker.INSTANCE:自动生成标记的规范实例
if (originalValue == AutowiredPropertyMarker.INSTANCE) {
//获取propertyName在bw中的setter方法
Method writeMethod = bw.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName).getWriteMethod();
//如果setter方法为null
if (writeMethod == null) {
//抛出非法参数异常:自动装配标记属性没有写方法。
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Autowire marker for property without write method: " + pv);
}
//将writerMethod封装到DependencyDescriptor对象
originalValue = new DependencyDescriptor(new MethodParameter(writeMethod, 0), true);
}
//交由valueResolver根据pv解析出originalValue所封装的对象,此方法对属性进行 递归 解析处理
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);
//默认转换后的值是刚解析出来的值
Object convertedValue = resolvedValue;
//可转换标记: propertyName是否bw中的可写属性 && propertyName不是表示索引属性或嵌套属性(如果propertyName中有'.'||'['就认为是索引属性或嵌套属性)
boolean convertible = bw.isWritableProperty(propertyName) &&
!PropertyAccessorUtils.isNestedOrIndexedProperty(propertyName);
//如果可转换
if (convertible) {
//将resolvedValue转换为指定的目标属性对象
convertedValue = convertForProperty(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter);
}
// Possibly store converted value in merged bean definition,
// in order to avoid re-conversion for every created bean instance.
// 可以将转换后的值存储合并后BeanDefinition中,以避免对每个创建的Bean实例进行重新转换
//如果resolvedValue与originalValue是同一个对象
if (resolvedValue == originalValue) {
//如果可转换
if (convertible) {
//将convertedValue设置到pv中
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
}
//将pv添加到deepCopy中
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
//TypedStringValue:类型字符串的Holder,这个holder将只存储字符串值和目标类型。实际得转换将由Bean工厂执行
//如果可转换 && originalValue是TypedStringValue的实例 && orginalValue不是标记为动态【即不是一个表达式】&&
// convertedValue不是Collection对象 或 数组
else if (convertible && originalValue instanceof TypedStringValue &&
!((TypedStringValue) originalValue).isDynamic() &&
!(convertedValue instanceof Collection || ObjectUtils.isArray(convertedValue))) {
//将convertedValue设置到pv中
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
//将pv添加到deepCopy中
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
//标记还需要解析
resolveNecessary = true;
//根据pv,convertedValue构建PropertyValue对象,并添加到deepCopy中
deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue));
}
}
}
//mpvs不为null && 已经不需要解析
if (mpvs != null && !resolveNecessary) {
//将此holder标记为只包含转换后的值@
mpvs.setConverted();
}
// Set our (possibly massaged) deep copy.
try {
//按原样使用deepCopy构造一个新的MutablePropertyValues对象然后设置到bw中以对bw的属性值更新
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy));
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
/**
* 给定的值转换为指定的目标属性对象
*
* Convert the given value for the specified target property.
*/
@Nullable
private Object convertForProperty(
@Nullable Object value, String propertyName, BeanWrapper bw, TypeConverter converter) {
//如果coverter是BeanWrapperImpl实例
if (converter instanceof BeanWrapperImpl) {
return ((BeanWrapperImpl) converter).convertForProperty(value, propertyName);
}
else {
//获取 propertyName的属性描述符对象
PropertyDescriptor pd = bw.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName);
//获取pd的setter方法参数
MethodParameter methodParam = BeanUtils.getWriteMethodParameter(pd);
//将value转换为pd要求的属性类型对象
return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, pd.getPropertyType(), methodParam);
}
}
/**
* 初始化给定的bean实例,应用工厂回调以及init方法和BeanPostProcessors
*
* Initialize the given bean instance, applying factory callbacks
* as well as init methods and bean post processors.
* <p>Called from {@link #createBean} for traditionally defined beans,
* and from {@link #initializeBean} for existing bean instances.
* @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
* @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
* @param mbd the bean definition that the bean was created with
* (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance)
* @return the initialized bean instance (potentially wrapped)
* @see BeanNameAware
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware
* @see BeanFactoryAware
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
* @see #invokeInitMethods
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
*/
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 如果安全管理器不为空
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
// 以特权的方式执行回调bean中的Aware接口方法
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// Aware接口处理器,调用BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、beanFactoryAware
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
//如果mdb不为null || mbd不是"synthetic"。一般是指只有AOP相关的prointCut配置或者Advice配置才会将 synthetic设置为true
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 将BeanPostProcessors应用到给定的现有Bean实例,调用它们的postProcessBeforeInitialization初始化方法。
// 返回的Bean实例可能是原始Bean包装器
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//调用初始化方法,先调用bean的InitializingBean接口方法,后调用bean的自定义初始化方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
//捕捉调用初始化方法时抛出的异常,重新抛出Bean创建异常:调用初始化方法失败
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
//如果mbd为null || mbd不是"synthetic"
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 将BeanPostProcessors应用到给定的现有Bean实例,调用它们的postProcessAfterInitialization方法。
// 返回的Bean实例可能是原始Bean包装器
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
//返回包装后的Bean
return wrappedBean;
}
/**
* 回调 bean 中 Aware接口 方法
* @param beanName
* @param bean
*/
private void invokeAwareMethods(String beanName, Object bean) {
//如果 bean 是 Aware 实例
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
//如果bean是BeanNameAware实例
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
//调用 bean 的setBeanName方法
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
//如果bean是 BeanClassLoaderAware 实例
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
//获取此工厂的类加载器以加载Bean类(即使无法使用系统ClassLoader,也只能为null)
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
//调用 bean 的 setBeanClassLoader 方法
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
//如果bean是 BeanFactoryAware 实例
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
// //调用 bean 的 setBeanFactory 方法
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
/**
* 调用初始化方法,先调用bean的InitializingBean接口方法,后调用bean的自定义初始化方法
*
* Give a bean a chance to react now all its properties are set,
* and a chance to know about its owning bean factory (this object).
* This means checking whether the bean implements InitializingBean or defines
* a custom init method, and invoking the necessary callback(s) if it does.
* @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
* @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
* @param mbd the merged bean definition that the bean was created with
* (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance)
* @throws Throwable if thrown by init methods or by the invocation process
* @see #invokeCustomInitMethod
*/
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
// InitializingBean:当Bean的所有属性都被BeanFactory设置好后,Bean需要执行相应的接口:例如执行自定义初始化,或者仅仅是检查所有强制属性是否已经设置好。
// bean是InitializingBean实例标记
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
// isExternallyManagedInitMethod是否外部受管理的Init方法名
// 如果bean是InitializingBean实例&&(mdb为null||'afterPropertiesSet'不是外部受管理的Init方法名)
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
// 如果是日志级别为跟踪模式
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
// 如果安全管理器不为null
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
// 以特权方式调用 bean的 afterPropertiesSet 方法
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
// 调用bean的afterPropertiesSet方法
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
// 如果mbd不为null&&bean不是NullBean类
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
// 获取mbd指定的初始化方法名
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
// 如果initMethodName不为null&&(bean不是InitializingBean实例&&'afterPropertiesSet'是初始化方法名)
// &&initMethodName不是外部受管理的Init方法名
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
// 在bean上调用指定的自定义init方法
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
/**
* 获取bean的自定义初始化方法,如果自身或者父类是接口类型的话,就反射出接口方法来,最后调用
*
* Invoke the specified custom init method on the given bean.
* Called by invokeInitMethods.
* <p>Can be overridden in subclasses for custom resolution of init
* methods with arguments.
* @see #invokeInitMethods
*/
protected void invokeCustomInitMethod(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
// 获取初始化方法名称
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
Assert.state(initMethodName != null, "No init method set");
// 获取初始化方法
Method initMethod = (mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed() ?
BeanUtils.findMethod(bean.getClass(), initMethodName) :
ClassUtils.getMethodIfAvailable(bean.getClass(), initMethodName));
if (initMethod == null) {
if (mbd.isEnforceInitMethod()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionValidationException("Could not find an init method named '" +
initMethodName + "' on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No default init method named '" + initMethodName +
"' found on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
// Ignore non-existent default lifecycle methods.
return;
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking init method '" + initMethodName + "' on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
Method methodToInvoke = ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(initMethod);
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(methodToInvoke);
return null;
});
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>)
() -> methodToInvoke.invoke(bean), getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
InvocationTargetException ex = (InvocationTargetException) pae.getException();
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
else {
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(methodToInvoke);
// 反射执行
methodToInvoke.invoke(bean);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
/**
* 应用所有已注册BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitalization回调,使它们有机会对FactoryBeans获得的对象进行后处理(例如,自动代理它们)
*
* Applies the {@code postProcessAfterInitialization} callback of all
* registered BeanPostProcessors, giving them a chance to post-process the
* object obtained from FactoryBeans (for example, to auto-proxy them).
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
*/
@Override
protected Object postProcessObjectFromFactoryBean(Object object, String beanName) {
// 初始化后的后处理
return applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(object, beanName);
}
/**
* 移除单例,并且从factoryBeanInstanceCache中移除指定beanName
*
* Overridden to clear FactoryBean instance cache as well.
*/
@Override
protected void removeSingleton(String beanName) {
synchronized (getSingletonMutex()) {
super.removeSingleton(beanName);
this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
}
/**
* 清空单例
*
* Overridden to clear FactoryBean instance cache as well.
*/
@Override
protected void clearSingletonCache() {
synchronized (getSingletonMutex()) {
super.clearSingletonCache();
this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.clear();
}
}
/**
* Expose the logger to collaborating delegates.
* @since 5.0.7
*/
Log getLogger() {
return logger;
}
/**
* Special DependencyDescriptor variant for Spring's good old autowire="byType" mode.
* Always optional; never considering the parameter name for choosing a primary candidate.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
private static class AutowireByTypeDependencyDescriptor extends DependencyDescriptor {
public AutowireByTypeDependencyDescriptor(MethodParameter methodParameter, boolean eager) {
super(methodParameter, false, eager);
}
@Override
public String getDependencyName() {
return null;
}
}
/**
* {@link MethodCallback} used to find {@link FactoryBean} type information.
*/
private static class FactoryBeanMethodTypeFinder implements MethodCallback {
private final String factoryMethodName;
private ResolvableType result = ResolvableType.NONE;
FactoryBeanMethodTypeFinder(String factoryMethodName) {
this.factoryMethodName = factoryMethodName;
}
@Override
public void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (isFactoryBeanMethod(method)) {
ResolvableType returnType = ResolvableType.forMethodReturnType(method);
ResolvableType candidate = returnType.as(FactoryBean.class).getGeneric();
if (this.result == ResolvableType.NONE) {
this.result = candidate;
}
else {
Class<?> resolvedResult = this.result.resolve();
Class<?> commonAncestor = ClassUtils.determineCommonAncestor(candidate.resolve(), resolvedResult);
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(resolvedResult, commonAncestor)) {
this.result = ResolvableType.forClass(commonAncestor);
}
}
}
}
private boolean isFactoryBeanMethod(Method method) {
return (method.getName().equals(this.factoryMethodName) &&
FactoryBean.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getReturnType()));
}
ResolvableType getResult() {
Class<?> resolved = this.result.resolve();
boolean foundResult = resolved != null && resolved != Object.class;
return (foundResult ? this.result : ResolvableType.NONE);
}
}
}
最后
以上就是斯文金鱼最近收集整理的关于图解Spring Bean的属性注入过程的全部内容,更多相关图解Spring内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复