flappy bird 为例子来讲
看完这个我好像脑子里有个程序了 :
https://www.zhihu.com/question/26408259
小鸟飞例子-建模关键点:
增强学习有三个要素:状态S,动作A,奖惩R的策略Q
S:
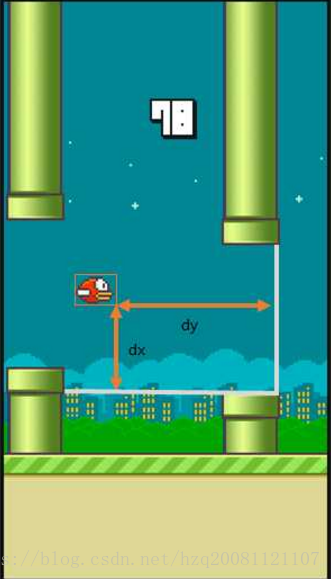
d(x,y)表示小鸟离下一根柱子的距离和高度差
A:
飞一下 或者 不飞,两种可选动作
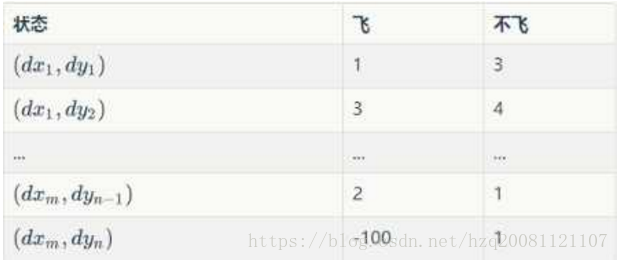
Q(S+A->R):
为一个策略表,也称之为Q,其实就是我们最终想学到的东西。就是在某状态S下采用不同动作A 可以得到的奖惩R。
如何训练:
Initialize Q arbitrarily //随机初始化Q值 (撞地上或者柱子上初始化为负值)
Repeat (for each episode): //每一次游戏,从小鸟出生到死亡是一个episode
Initialize S //小鸟刚开始飞,S为初始位置的状态
Repeat (for each step of episode):
。。。根据当前Q和位置S,使用一种策略,得到动作A //这个策略可以是ε-greedy等
做了动作A,小鸟到达新的位置S',并获得奖励R //奖励可以是1,50或者-1000
Q(S,A) ← (1-α)*Q(S,A) + α*[R + γ*maxQ(S',a)] //在Q中更新S
S ← S'
until S is terminal //即到 小鸟死亡为止
关键的这一步怎么理解呢?
Q(S,A) ← (1-α)*Q(S,A) + α*[R + γ*maxQ(S',a)]
1 当处于S状态采取A策略后,根据S'我们可以得到R, 那么这个R应该跟新到Q(S,A)中,我们可能会这样做:
Q(S,A) ← (1-α)*Q(S,A) + α*R
其中α是0~1之间的一个数,我们称之为学习率。
2 上面的公式太短视,我们更新Q(S,A) 时是不是要考虑一下,通过步骤A走到下一个状态S'的收益呢?
Q(S,A) ← (1-α)*Q(S,A) + α*[R + γ*Q(S',?)]
其中γ是一个0~1的小数,表示我们关注长期(下一步)收益的程度,代表对历史经验的重视程度。
3 Q(S',?)表示状态S'的收益,Q(S',?)有飞和不飞2个值,我们既然知道奖惩,肯定是采用Q(S',?)中最大的那一种操作于是我们得到
Q(S,A) ← (1-α)*Q(S,A) + α*[R + γ*maxQ(S',a)]
根据以上信息就可以写代码啦!
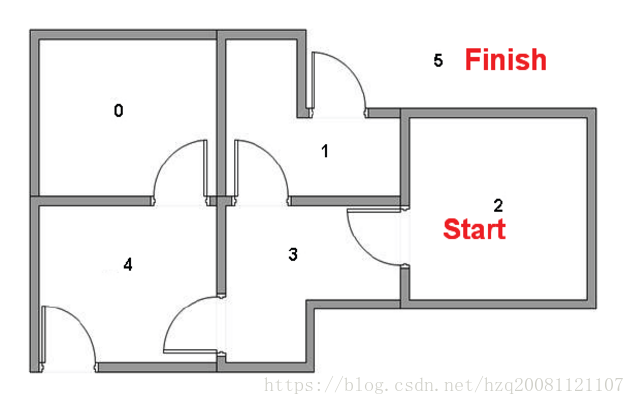
现在用走房子的例子来写一个程序:
题目参考:http://blog.csdn.net/itplus/article/details/9361915#0-qzone-1-29435-d020d2d2a4e8d1a374a433f596ad1440
我们需要尽快从当前房子走到目的房子:
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
#define N 6
int pass[N][N];
float Q[N][N];
int dest;
void input()
{
int n,m,a,b,i,j;
//srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for (i=0; i<N; i++)
{
for (j=0; j<N; j++){
pass[i][j] = 0;
Q[i][j] = 0;//(rand()%100)/100.0;//0;
}
}
cin>>n;//一共有n扇门
printf("%d doorsn",n);
while(n--){
cin>>a>>b;//房间a和b之间有互通
pass[a][b] = pass[b][a] = 1;
Q[a][b] = (rand()%100)/1000.0;//0;
Q[b][a] = (rand()%100)/1000.0;//0;
}
printf("input donen");
//输入目标房间
cin>>m;//m为目的房间号
Q[m][m] = 1;//目标房间号的收益是最高的,为1
dest = m;
}
void displayQ(){
printf("n");
int i,j;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++){
for (j = 0; j < N; j++){
printf("%.3f ",Q[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}
}
//从pqm中随机选出一个元素
int select_rand_ele(map <int, float> pqm){
int n = rand()%(pqm.size());
map<int, float>::iterator it = pqm.begin();
while(n--){
it ++;
}
return it->first;
}
//从一个矩阵的第pos行找出最大值,返回其位置
int find_max_Q(int pos, float &chosen_q){
int i;
int chosen_p = -1;
for (i=0; i<N; i++){
if (pass[pos][i] != 0){
if (chosen_p == -1 || Q[pos][i] > chosen_q)
{
chosen_q = Q[pos][i];
chosen_p = i;
}
}
}
return chosen_p;
}
//起始位置在序号为pos的房间,以0.3的概率走随机门
void train(int pos, float rr = 0.3){
printf("%d ", pos);
int i,j,k;
if (pos == dest){
return;
}
//action choice,开门换房
map <int, float> pqm;
float chosen_q;
int chosen_p = -1;
for (i=0; i<N; i++){
if (pass[pos][i] != 0){
pqm[i] = Q[pos][i];
if (chosen_p == -1 || Q[pos][i] > chosen_q)
{
chosen_q = Q[pos][i];
chosen_p = i;
}
}
}
if (chosen_p == -1){//这是一个没有门的房间
return;
}
//以一定概率走随机门
if ((rand()%100)/100.0 < rr){
chosen_p = select_rand_ele(pqm);
chosen_q = pqm[chosen_p];
}
// 更新Q
float lr = 0.5;// 学习率
float next_q_max_value = 0;
find_max_Q(chosen_p, next_q_max_value);
Q[pos][chosen_p] = lr * Q[pos][chosen_p] + (1-lr) *(next_q_max_value - 0.1);//走一扇门的代价是-0.1
//下一个位置
train(chosen_p, 0.3);
}
/*
输入
6
4 5
4 3
3 2
1 3
0 4
1 5
5
6
4 5
4 3
3 2
1 3
0 4
1 5
2
*/
int main()
{
input();
displayQ();
int n = 1000;
while(n--){
train(rand()%N, 0.5);//从随机的一个房间开始走
displayQ();
}
system("pause");
}
最后
以上就是过时心情最近收集整理的关于强化学习入门例子的全部内容,更多相关强化学习入门例子内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复