一、概述
平时,经常会遇到权重随机算法,从不同权重的N个元素中随机选择一个,并使得总体选择结果是按照权重分布的。如广告投放、负载均衡等。
如有4个元素A、B、C、D,权重分别为1、2、3、4,随机结果中A:B:C:D的比例要为1:2:3:4。
总体思路:累加每个元素的权重A(1)-B(3)-C(6)-D(10),则4个元素的的权重管辖区间分别为[0,1)、[1,3)、[3,6)、[6,10)。然后随机出一个[0,10)之间的随机数。落在哪个区间,则该区间之后的元素即为按权重命中的元素。
实现方法:
利用TreeMap,则构造出的一个树为:
B(3)
/
/
A(1) D(10)
/
/
C(6)
然后,利用treemap.tailMap().firstKey()即可找到目标元素。
当然,也可以利用数组+二分查找来实现。
二、源码
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
|
这是我更改之后的,服务器不支持Pair类 (采用entrySet遍历key+value的效率要高于keySet,大数据时更明显,具体比较见https://blog.csdn.net/u013776390/article/details/83106606)
package app.sjgj.utils;
import com.google.common.base.Preconditions;
import java.util.*;
public class ServiceRandom<K,V extends Number> {
private TreeMap<Double, K> weightMap = new TreeMap<Double, K>();
public ServiceRandom(List<Map<K,V>> list) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(list, "list can NOT be null!");
//获取key和value
for (Map<K, V> map:list){
Iterator<Map.Entry<K, V>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry key = iterator.next();
double lastWeight = this.weightMap.size() == 0 ? 0 : this.weightMap.lastKey().doubleValue();//统一转为double
this.weightMap.put(Double.parseDouble(key.getValue().toString()) + lastWeight, (K)key.getKey());//权重累加
}
}
}
public K random() {
double randomWeight = this.weightMap.lastKey() * Math.random();
SortedMap<Double, K> tailMap = this.weightMap.tailMap(randomWeight, false);
return this.weightMap.get(tailMap.firstKey());
}
}
三、性能
4个元素A、B、C、D,其权重分别为1、2、3、4,运行1亿次,结果如下:
| 元素 | 命中次数 | 误差率 |
| A | 10004296 | 0.0430% |
| B | 19991132 | 0.0443% |
| C | 30000882 | 0.0029% |
| D | 40003690 | 0.0092% |
从结果,可以看出,准确率在99.95%以上。
四、另一种实现
利用B+树的原理。叶子结点存放元素,非叶子结点用于索引。非叶子结点有两个属性,分别保存左右子树的累加权重。如下图:
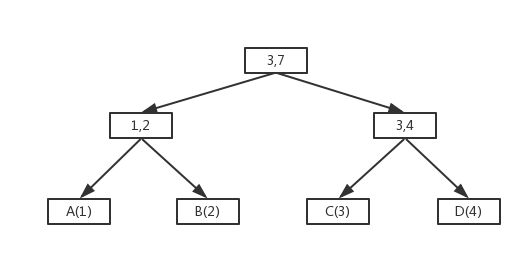
看到这个图,聪明的你应该知道怎么随机了吧。
此方法的优点是:更改一个元素,只须修改该元素到根结点那半部分的权值即可。
end
作者:水岩
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/waterystone/
本博客中未标明转载的文章归作者水岩和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
调用的时候我是这样写的
public
Object addserviceid(Integer cityid)
{
List<Pair<Integer, BigDecimal>> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<SjgjServicecity> list1 = sjgjServicecityMapper.selectByCity(cityid);
for (SjgjServicecity s:list1
) {
Pair<Integer, BigDecimal> pair = new Pair<Integer, BigDecimal>(s.getServiceid(),sysinstitutionMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(s.getServiceid()).getProportion());
list.add(pair);
}
WeightRandom weightRandom = new WeightRandom(list);
return weightRandom.random();
}备忘一下 菜鸟一枚
问题来了服务器是tomcat7 不支持pair 所以用自己的办法改了一下,在源码处新贴了自己的代码,下面是调用
List<Map<Integer, BigDecimal>> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<SjgjServicecity> list1 = sjgjServicecityMapper.selectByCity(171);
for (SjgjServicecity s:list1) {
Map<Integer, BigDecimal> map = new HashMap<Integer, BigDecimal>();
map.put(s.getServiceid(),sysinstitutionMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(s.getServiceid()).getProportion());
list2.add(map);
}
ServiceRandom serviceRandom = new ServiceRandom(list2);
Object o =
serviceRandom.random();
最后
以上就是感性发夹最近收集整理的关于权重随机算法的java实现 添加实现方法一、概述二、源码三、性能四、另一种实现的全部内容,更多相关权重随机算法的java实现内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复