利用spring框架实现对象的创建及IOC案例
本文是基于Windows 10系统环境,利用spring框架实现实现对象的创建及IOC案例
- Windows 10
- IntelliJ
一、基于xml方式的构建过程
(1) 打开IntelliJ,创建一个新项目
(2) 选择“maven”工程,然后点击“next”
(3) 填写公司ID等信息,然后点击“next”
(4) 目录结构
(5) 点击“pom.xml”文件,然后填写各种依赖的坐标
- pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.inspur</groupId>
<artifactId>spring_day01_eesy_03spring</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
(6) 创建一个IAccountDao接口类,以及相应的实现类
- IAccountDao接口类
package com.inspur.dao;
/**
* 账户的持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 模拟保存账户
*/
public void saveAccount();
}
- AccountDaoImpl实现类
package com.inspur.dao.impl;
import com.inspur.dao.IAccountDao;
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存了账户");
}
}
(7) 创建一个IAccountService接口类,以及相应的实现类
- IAccountService接口类
package com.inspur.service;
/**
* 账户业务层接口
*/
public interface IAccountService {
/**
* 模拟保存账户
*/
public void saveAccount();
}
- AccountServiceImpl实现类
package com.inspur.service.impl;
import com.inspur.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.inspur.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.inspur.service.IAccountService;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IAccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl();
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
(8) 创建一个bean.xml配置文件
- bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 把对象的创建交给spring来管理 -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.inspur.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.inspur.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
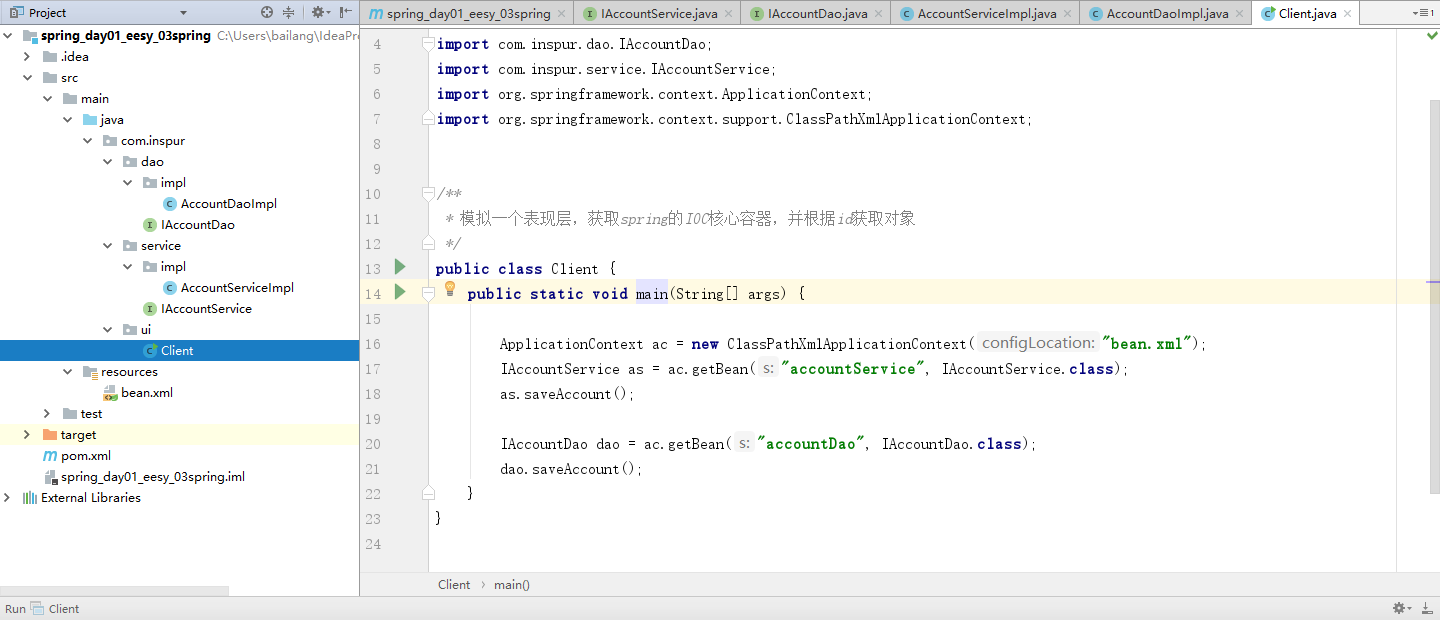
(9) 创建一个表现层的Client类用于测试
- Client.java
package com.inspur.ui;
import com.inspur.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.inspur.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 模拟一个表现层,获取spring的IOC核心容器,并根据id获取对象
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
as.saveAccount();
IAccountDao dao = ac.getBean("accountDao", IAccountDao.class);
dao.saveAccount();
}
}
二、三种创建bean对象的方式
(1) 第一种方式:使用默认构造函数创建
<!-- 第一种方式:使用默认构造函数创建。在spring的配置文件中使用bean标签,配以id和class属性之后,
且没有其他属性和标签时。采用的就是默认构造函数创建bean对象,此时如果类中没有默认构造函数,
则对象无法创建。-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
(2) 第二种方式:使用普通工厂中的方法创建对象
<!-- 第二种方式: 使用普通工厂中的方法创建对象(使用某个类中的方法创建对象,并存入spring容器)-->
<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.itheima.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
(3) 第三种方式:使用工厂中的静态方法创建对象
<!-- 第三种方式:使用工厂中的静态方法创建对象(使用某个类中的静态方法创建对象,并存入spring容器)-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
三、三种注入bean对象的方式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- spring中的依赖注入
依赖注入:
Dependency Injection
IOC的作用:
降低程序间的耦合(依赖关系)
依赖关系的管理:
以后都交给spring来维护
在当前类需要用到其他类的对象,由spring为我们提供,我们只需要在配置文件中说明
依赖关系的维护:
就称之为依赖注入。
依赖注入:
能注入的数据:有三类
基本类型和String
其他bean类型(在配置文件中或者注解配置过的bean)
复杂类型/集合类型
注入的方式:有三种
第一种:使用构造函数提供
第二种:使用set方法提供
第三种:使用注解提供(明天的内容)
-->
<!--构造函数注入:
使用的标签:constructor-arg
标签出现的位置:bean标签的内部
标签中的属性
type:用于指定要注入的数据的数据类型,该数据类型也是构造函数中某个或某些参数的类型
index:用于指定要注入的数据给构造函数中指定索引位置的参数赋值。索引的位置是从0开始
name:用于指定给构造函数中指定名称的参数赋值 常用的
=============以上三个用于指定给构造函数中哪个参数赋值===============================
value:用于提供基本类型和String类型的数据
ref:用于指定其他的bean类型数据。它指的就是在spring的Ioc核心容器中出现过的bean对象
优势:
在获取bean对象时,注入数据是必须的操作,否则对象无法创建成功。
弊端:
改变了bean对象的实例化方式,使我们在创建对象时,如果用不到这些数据,也必须提供。
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="泰斯特"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="birthday" ref="now"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 配置一个日期对象 -->
<bean id="now" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<!-- set方法注入 更常用的方式
涉及的标签:property
出现的位置:bean标签的内部
标签的属性
name:用于指定注入时所调用的set方法名称
value:用于提供基本类型和String类型的数据
ref:用于指定其他的bean类型数据。它指的就是在spring的Ioc核心容器中出现过的bean对象
优势:
创建对象时没有明确的限制,可以直接使用默认构造函数
弊端:
如果有某个成员必须有值,则获取对象是有可能set方法没有执行。
-->
<bean id="accountService2" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl2">
<property name="name" value="TEST" ></property>
<property name="age" value="21"></property>
<property name="birthday" ref="now"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 复杂类型的注入/集合类型的注入
用于给List结构集合注入的标签:
list array set
用于个Map结构集合注入的标签:
map props
结构相同,标签可以互换
-->
<bean id="accountService3" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl3">
<property name="myStrs">
<set>
<value>AAA</value>
<value>BBB</value>
<value>CCC</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="myList">
<array>
<value>AAA</value>
<value>BBB</value>
<value>CCC</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="mySet">
<list>
<value>AAA</value>
<value>BBB</value>
<value>CCC</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="myMap">
<props>
<prop key="testC">ccc</prop>
<prop key="testD">ddd</prop>
</props>
</property>
<property name="myProps">
<map>
<entry key="testA" value="aaa"></entry>
<entry key="testB">
<value>BBB</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
四、基于注解方式的构建过程
(1) 创建一个bean.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--告知spring在创建容器时要扫描的包,配置所需要的标签不是在beans的约束中,而是一个名称为
context名称空间和约束中-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
(2) 创建一个实现类
package com.itheima.service.impl;
import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*
* 曾经XML的配置:
* <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"
* scope="" init-method="" destroy-method="">
* <property name="" value="" | ref=""></property>
* </bean>
*
* 用于创建对象的
* 他们的作用就和在XML配置文件中编写一个<bean>标签实现的功能是一样的
* Component:
* 作用:用于把当前类对象存入spring容器中
* 属性:
* value:用于指定bean的id。当我们不写时,它的默认值是当前类名,且首字母改小写。
* Controller:一般用在表现层
* Service:一般用在业务层
* Repository:一般用在持久层
* 以上三个注解他们的作用和属性与Component是一模一样。
* 他们三个是spring框架为我们提供明确的三层使用的注解,使我们的三层对象更加清晰
*
*
* 用于注入数据的
* 他们的作用就和在xml配置文件中的bean标签中写一个<property>标签的作用是一样的
* Autowired:
* 作用:自动按照类型注入。只要容器中有唯一的一个bean对象类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,就可以注入成功
* 如果ioc容器中没有任何bean的类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,则报错。
* 如果Ioc容器中有多个类型匹配时:
* 出现位置:
* 可以是变量上,也可以是方法上
* 细节:
* 在使用注解注入时,set方法就不是必须的了。
* Qualifier:
* 作用:在按照类中注入的基础之上再按照名称注入。它在给类成员注入时不能单独使用。但是在给方法参数注入时可以(稍后我们讲)
* 属性:
* value:用于指定注入bean的id。
* Resource
* 作用:直接按照bean的id注入。它可以独立使用
* 属性:
* name:用于指定bean的id。
* 以上三个注入都只能注入其他bean类型的数据,而基本类型和String类型无法使用上述注解实现。
* 另外,集合类型的注入只能通过XML来实现。
*
* Value
* 作用:用于注入基本类型和String类型的数据
* 属性:
* value:用于指定数据的值。它可以使用spring中SpEL(也就是spring的el表达式)
* SpEL的写法:${表达式}
*
* 用于改变作用范围的
* 他们的作用就和在bean标签中使用scope属性实现的功能是一样的
* Scope
* 作用:用于指定bean的作用范围
* 属性:
* value:指定范围的取值。常用取值:singleton prototype
*
* 和生命周期相关 了解
* 他们的作用就和在bean标签中使用init-method和destroy-methode的作用是一样的
* PreDestroy
* 作用:用于指定销毁方法
* PostConstruct
* 作用:用于指定初始化方法
*/
@Service("accountService")
//@Scope("prototype")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
// @Autowired
// @Qualifier("accountDao1")
@Resource(name = "accountDao2")
private IAccountDao accountDao = null;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("初始化方法执行了");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("销毁方法执行了");
}
public void saveAccount(){
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
五、基于xml方式的IOC案例
(1) 文件目录结构,以及pom依赖
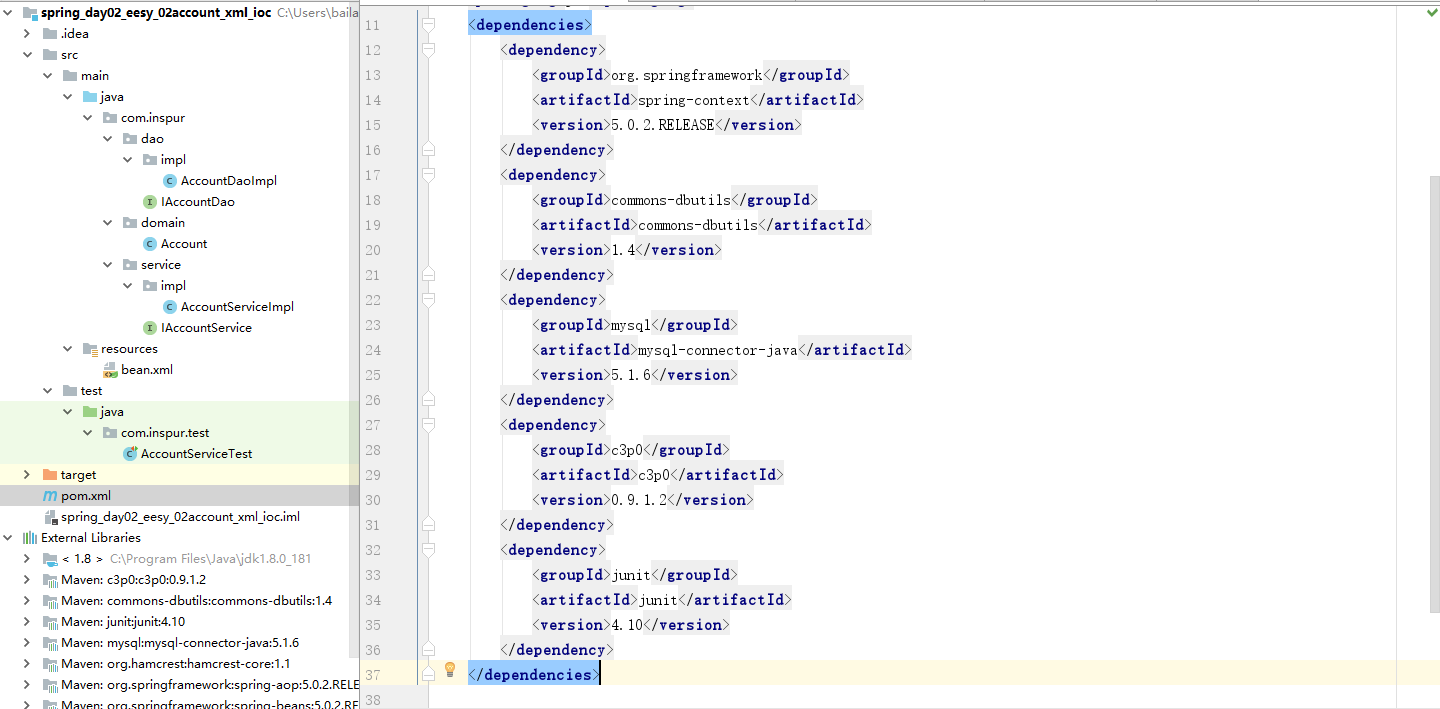
- pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="accountService" class="com.inspur.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.inspur.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="runner" ref="runner"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype">
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://172.30.12.59:3306/eesy"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
(2) 创建一个Account类
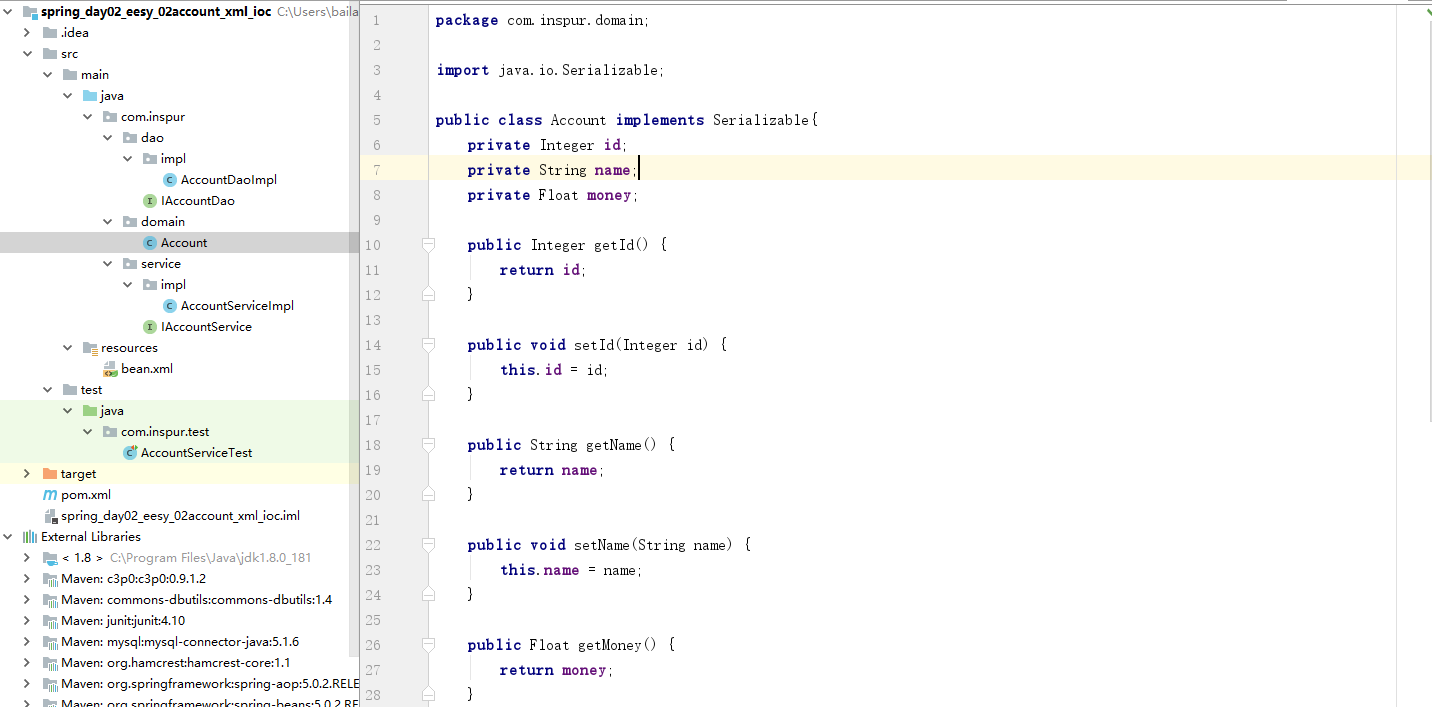
- Account.java
package com.inspur.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Account implements Serializable{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Float money;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Float money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + ''' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
(3) 创建一个IAccountDao接口类
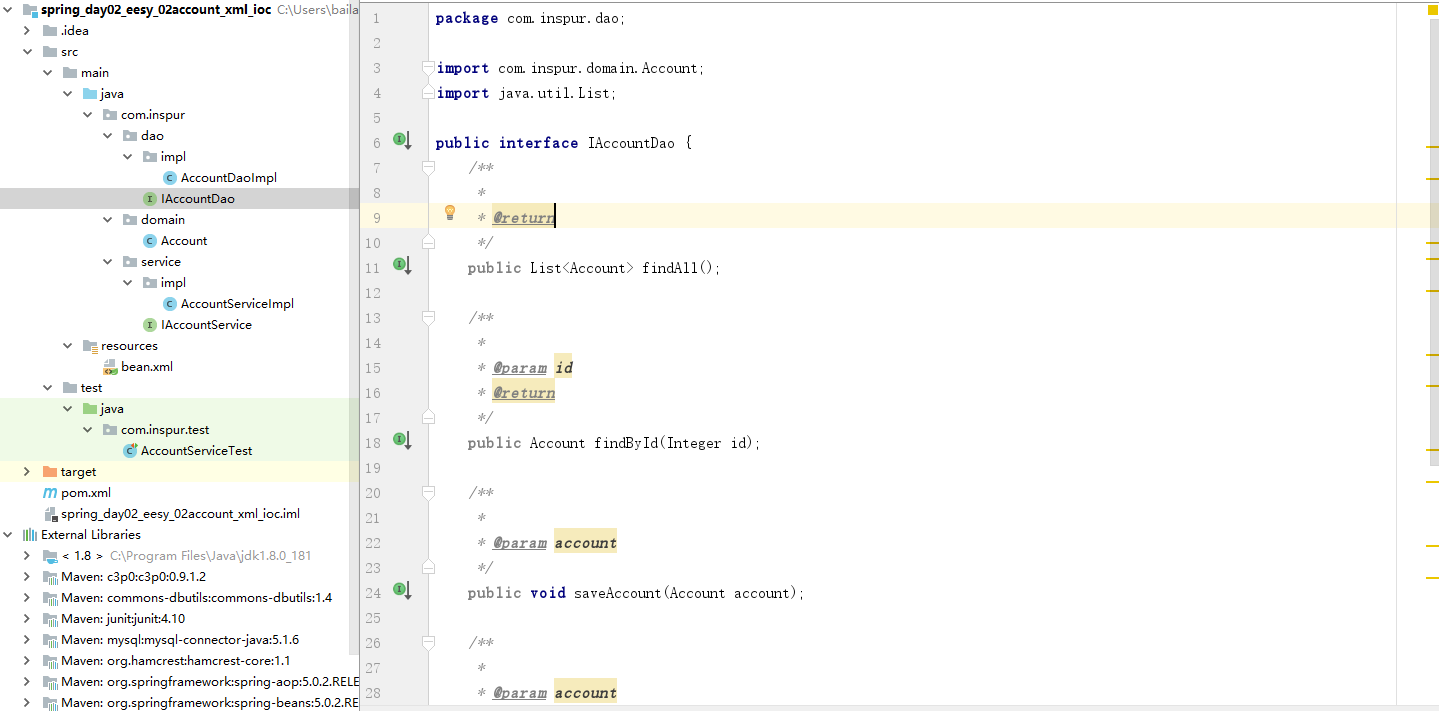
- IAccountDao.java
package com.inspur.dao;
import com.inspur.domain.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
*
* @return
*/
public List<Account> findAll();
/**
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
public Account findById(Integer id);
/**
*
* @param account
*/
public void saveAccount(Account account);
/**
*
* @param account
*/
public void updateAccount(Account account);
/**
*
* @param id
*/
public void deleteAccount(Integer id);
}
(4) 创建一个AccountDaoImpl实现类
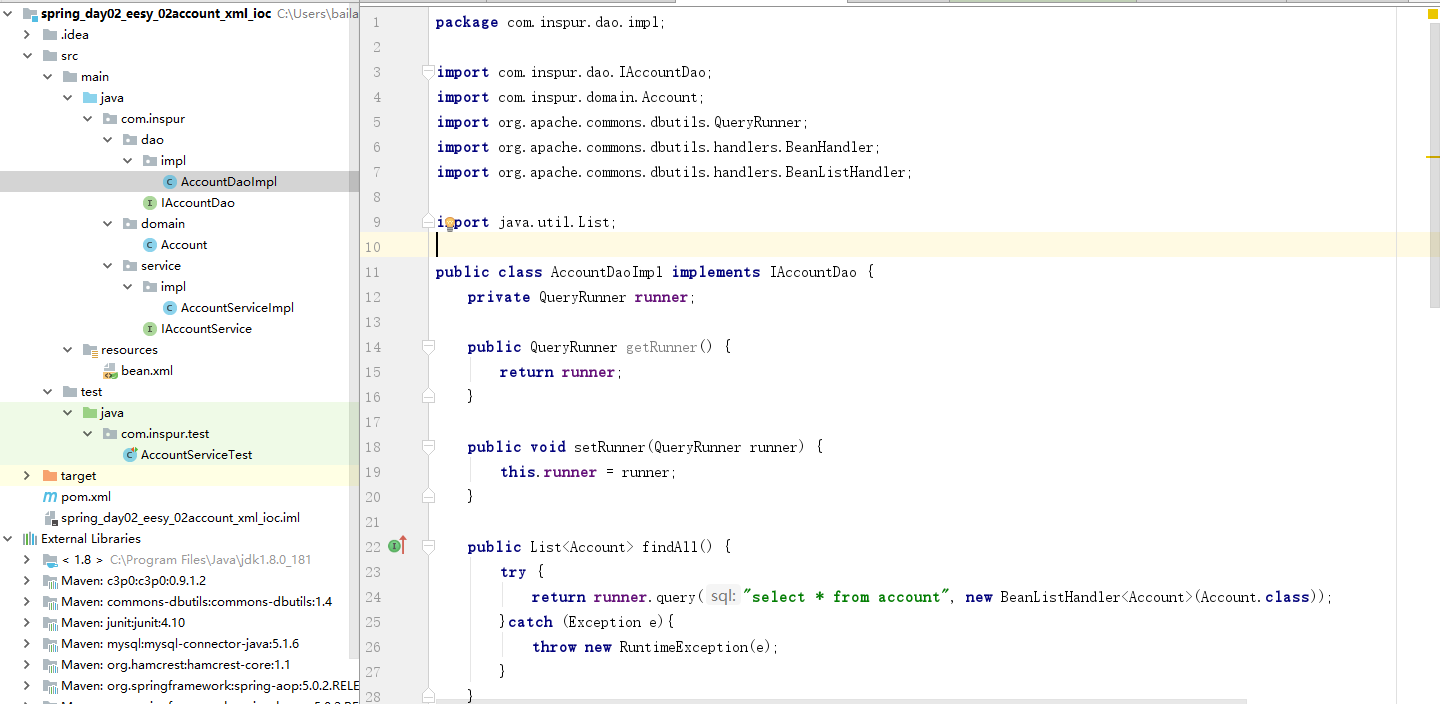
- AccountDaoImpl.java
package com.inspur.dao.impl;
import com.inspur.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.inspur.domain.Account;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import java.util.List;
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private QueryRunner runner;
public QueryRunner getRunner() {
return runner;
}
public void setRunner(QueryRunner runner) {
this.runner = runner;
}
public List<Account> findAll() {
try {
return runner.query("select * from account", new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class));
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Account findById(Integer id) {
try {
return runner.query("select * from account where id=?", new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class), id);
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
try {
runner.update("insert into account(name,money) values(?,?)", account.getName(), account.getMoney());
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
runner.update("update account set name=?, money=? where id=?", account.getName(), account.getMoney(), account.getId());
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void deleteAccount(Integer id) {
try {
runner.update("delete from account where id=?", id);
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
(5) 创建一个IAccountService类
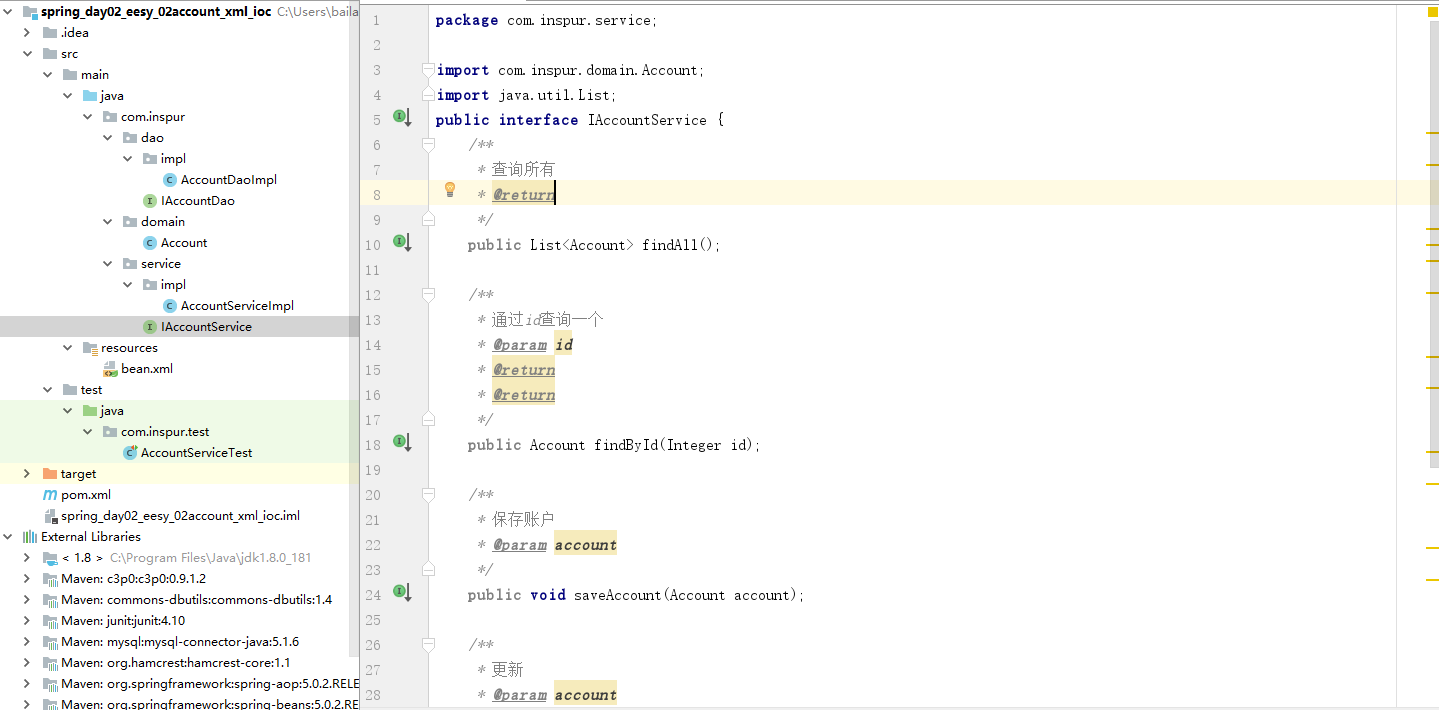
- IAccountService.java
package com.inspur.service;
import com.inspur.domain.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface IAccountService {
/**
* 查询所有
* @return
*/
public List<Account> findAll();
/**
* 通过id查询一个
* @param id
* @return
* @return
*/
public Account findById(Integer id);
/**
* 保存账户
* @param account
*/
public void saveAccount(Account account);
/**
* 更新
* @param account
*/
public void updateAccount(Account account);
/**
* 删除
* @param id
*/
public void deleteAccount(Integer id);
}
(6) 创建一个AccountServiceImpl实现类
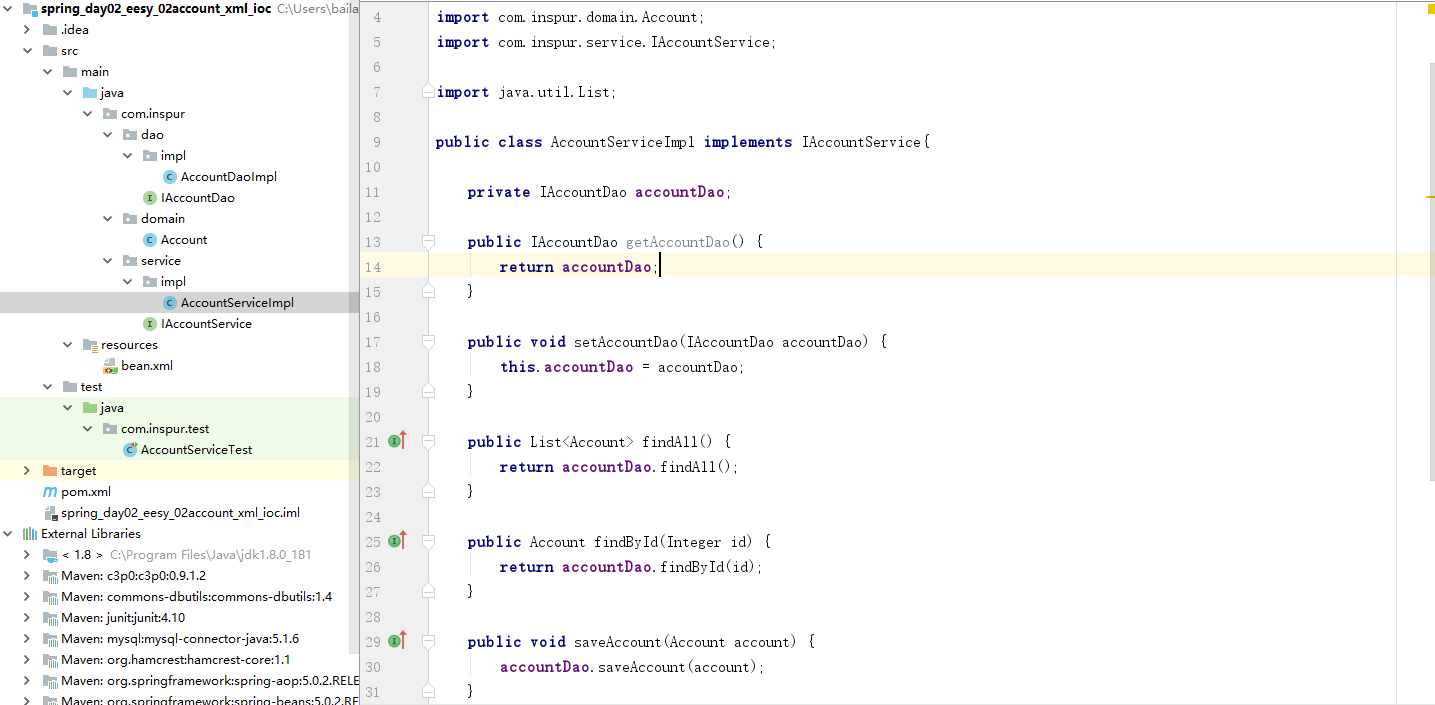
- AccountServiceImpl.java
package com.inspur.service.impl;
import com.inspur.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.inspur.domain.Account;
import com.inspur.service.IAccountService;
import java.util.List;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService{
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public IAccountDao getAccountDao() {
return accountDao;
}
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public List<Account> findAll() {
return accountDao.findAll();
}
public Account findById(Integer id) {
return accountDao.findById(id);
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
accountDao.saveAccount(account);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
}
public void deleteAccount(Integer id) {
accountDao.deleteAccount(id);
}
}
(7) 创建一个配置文件bean.xml
- bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="accountService" class="com.inspur.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.inspur.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="runner" ref="runner"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype">
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://172.30.12.59:3306/eesy"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
(8) 创建一个测试类
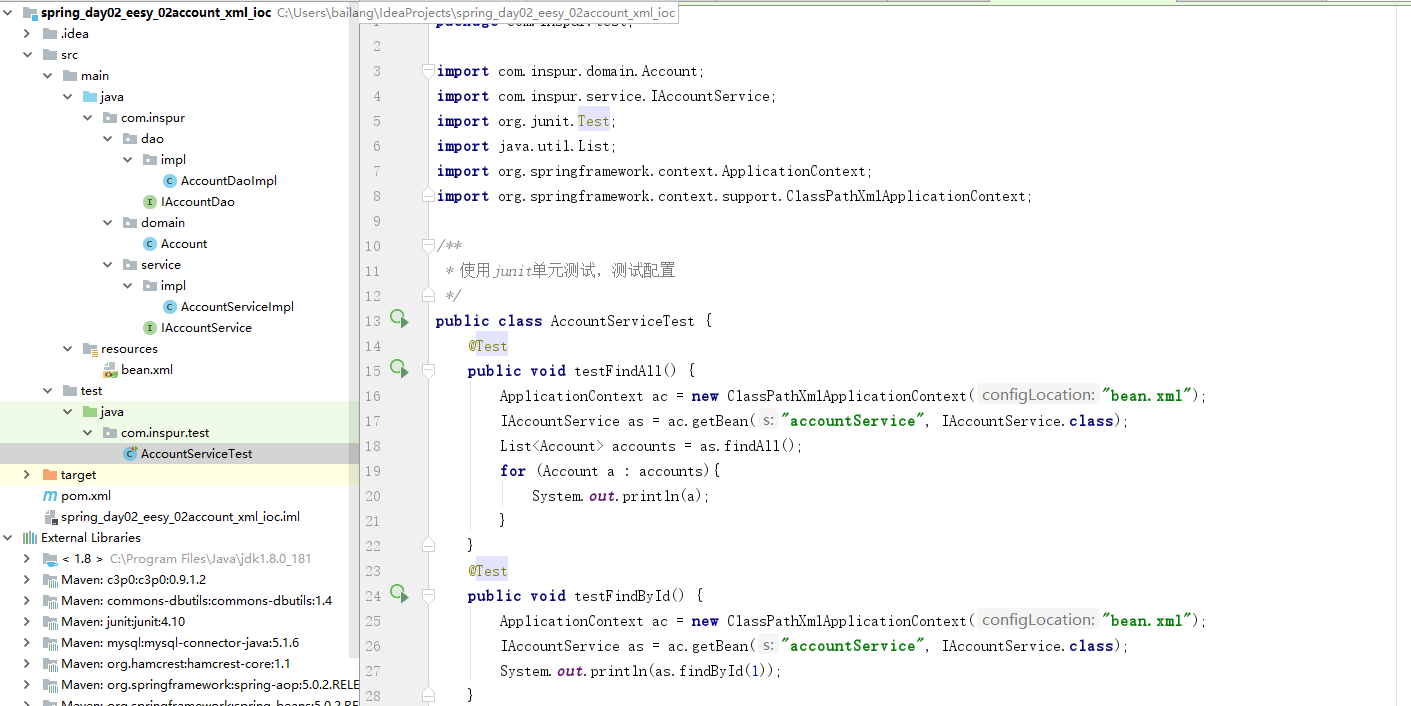
- AccountServiceTest.java
package com.inspur.test;
import com.inspur.domain.Account;
import com.inspur.service.IAccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 使用Junit单元测试,测试配置
*/
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Test
public void testFindAll() {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
List<Account> accounts = as.findAll();
for (Account a : accounts){
System.out.println(a);
}
}
@Test
public void testFindById() {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
System.out.println(as.findById(1));
}
@Test
public void testSaveAccount() {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
Account a = new Account();
a.setName("xuzheng");
a.setMoney(new Float(100000000.0));
as.saveAccount(a);
testFindAll();
}
@Test
public void testUpdateAccount() {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
Account a = new Account();
a.setId(2);
a.setName("bbb");
a.setMoney(new Float(2000.0));
as.updateAccount(a);
testFindAll();
}@Test
public void testDeleteAccount() {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
as.deleteAccount(3);
testFindAll();
}
}
最后
以上就是洁净篮球最近收集整理的关于利用spring框架实现对象的创建及IOC案例利用spring框架实现对象的创建及IOC案例的全部内容,更多相关利用spring框架实现对象内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复