1、C语言的位运算
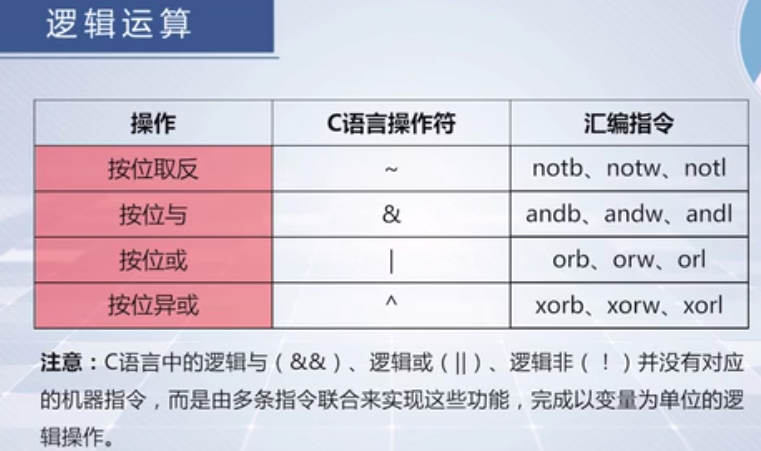
其中,l是长字(4字节),w是双字,b是一个字节。举个例子,建立bit.cpp:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int a = 5;
unsigned int b = 3;
short c = 5;
int d = 0;
a = ~a;
b = ~b;
c = ~c;
d = a&b;
d = a^b;
d = a|b;
return 0;
}
通过反汇编查看下指令:
g++ bit.cpp -g bit
objdump -Sd bit > tmp
00000000004006b6 <main>:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
4006b6: 55 push %rbp
4006b7: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
int a = 5;
4006ba: c7 45 f4 05 00 00 00 movl $0x5,-0xc(%rbp)
unsigned int b = 3;
4006c1: c7 45 f8 03 00 00 00 movl $0x3,-0x8(%rbp)
short c = 5;
4006c8: 66 c7 45 f2 05 00 movw $0x5,-0xe(%rbp)
int d = 0;
4006ce: c7 45 fc 00 00 00 00 movl $0x0,-0x4(%rbp)
a = ~a;
4006d5: f7 55 f4 notl -0xc(%rbp)
b = ~b;
4006d8: f7 55 f8 notl -0x8(%rbp)
c = ~c;
4006db: 66 f7 55 f2 notw -0xe(%rbp)
d = a&b;
4006df: 8b 45 f4 mov -0xc(%rbp),%eax
4006e2: 23 45 f8 and -0x8(%rbp),%eax
4006e5: 89 45 fc mov %eax,-0x4(%rbp)
d = a^b;
4006e8: 8b 45 f4 mov -0xc(%rbp),%eax
4006eb: 33 45 f8 xor -0x8(%rbp),%eax
4006ee: 89 45 fc mov %eax,-0x4(%rbp)
d = a|b;
4006f1: 8b 45 f4 mov -0xc(%rbp),%eax
4006f4: 0b 45 f8 or -0x8(%rbp),%eax
4006f7: 89 45 fc mov %eax,-0x4(%rbp)
return 0;
4006fa: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
}
4006ff: 5d pop %rbp
400700: c3 retq
2、C语言的逻辑运算
建立文件logicOper.cpp
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int a = 5;
unsigned int b = 3;
short c = 5;
int d = 0;
a = !a;
b = !b;
c = !c;
d = a&&b;
d = a||b;
return 0;
}
编译后反汇编;
g++ logicOper.cpp -g -o logicOper
objdump -Sd logicOper > tmp2
00000000004006b6 <main>:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
4006b6: 55 push %rbp
4006b7: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
int a = 5;
4006ba: c7 45 f4 05 00 00 00 movl $0x5,-0xc(%rbp)
unsigned int b = 3;
4006c1: c7 45 f8 03 00 00 00 movl $0x3,-0x8(%rbp)
short c = 5;
4006c8: 66 c7 45 f2 05 00 movw $0x5,-0xe(%rbp)
int d = 0;
4006ce: c7 45 fc 00 00 00 00 movl $0x0,-0x4(%rbp)
a = !a;
4006d5: 83 7d f4 00 cmpl $0x0,-0xc(%rbp)
4006d9: 0f 94 c0 sete %al
4006dc: 0f b6 c0 movzbl %al,%eax
4006df: 89 45 f4 mov %eax,-0xc(%rbp)
b = !b;
4006e2: 83 7d f8 00 cmpl $0x0,-0x8(%rbp)
4006e6: 0f 94 c0 sete %al
4006e9: 0f b6 c0 movzbl %al,%eax
4006ec: 89 45 f8 mov %eax,-0x8(%rbp)
c = !c;
4006ef: 66 83 7d f2 00 cmpw $0x0,-0xe(%rbp)
4006f4: 0f 94 c0 sete %al
4006f7: 0f b6 c0 movzbl %al,%eax
4006fa: 66 89 45 f2 mov %ax,-0xe(%rbp)
d = a&&b;
4006fe: 83 7d f4 00 cmpl $0x0,-0xc(%rbp)
400702: 74 0d je 400711 <main+0x5b>
400704: 83 7d f8 00 cmpl $0x0,-0x8(%rbp)
400708: 74 07 je 400711 <main+0x5b>
40070a: b8 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%eax
40070f: eb 05 jmp 400716 <main+0x60>
400711: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
400716: 0f b6 c0 movzbl %al,%eax
400719: 89 45 fc mov %eax,-0x4(%rbp)
d = a||b;
40071c: 83 7d f4 00 cmpl $0x0,-0xc(%rbp)
400720: 75 06 jne 400728 <main+0x72>
400722: 83 7d f8 00 cmpl $0x0,-0x8(%rbp)
400726: 74 07 je 40072f <main+0x79>
400728: b8 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%eax
40072d: eb 05 jmp 400734 <main+0x7e>
40072f: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
400734: 0f b6 c0 movzbl %al,%eax
400737: 89 45 fc mov %eax,-0x4(%rbp)
return 0;
40073a: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
}
40073f: 5d pop %rbp
400740: c3 retq
可以看出C语言中的逻辑操作并不是一条指令,而是多条指令。
3、C语言的移动操作
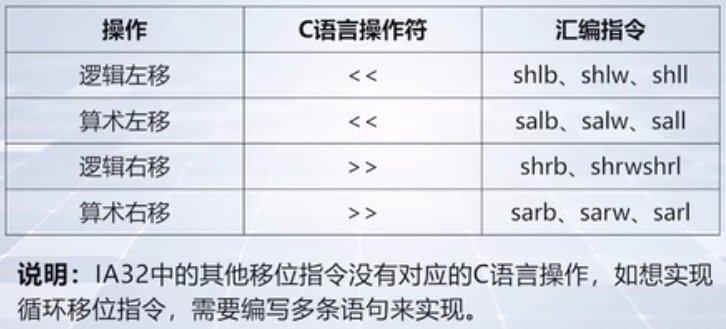
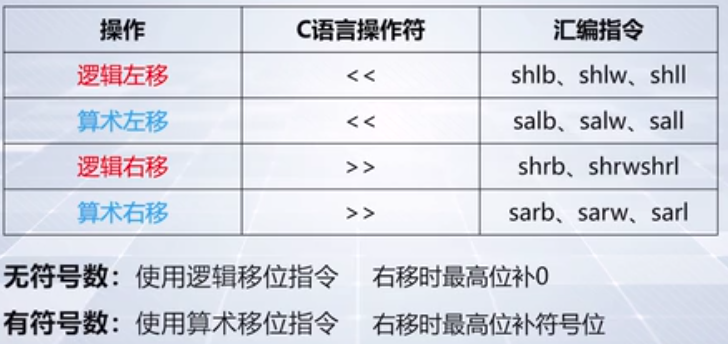
举个例子,建立shift.cpp
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int a = 0x80000000;
unsigned int b = 0x80000000;
short c = 0x8000;
unsigned short d = 0x8000;
a = a>>4;
b = b>>4;
a = c;
a = d;
b = c;
b = d;
return 0;
}
反汇编后看main函数
00000000004006b6 <main>:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
4006b6: 55 push %rbp
4006b7: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
int a = 0x80000000;
4006ba: c7 45 f8 00 00 00 80 movl $0x80000000,-0x8(%rbp)
unsigned int b = 0x80000000;
4006c1: c7 45 fc 00 00 00 80 movl $0x80000000,-0x4(%rbp)
short c = 0x8000;
4006c8: 66 c7 45 f4 00 80 movw $0x8000,-0xc(%rbp)
unsigned short d = 0x8000;
4006ce: 66 c7 45 f6 00 80 movw $0x8000,-0xa(%rbp)
a = a>>4;
4006d4: c1 7d f8 04 sarl $0x4,-0x8(%rbp)
b = b>>4;
4006d8: c1 6d fc 04 shrl $0x4,-0x4(%rbp)
a = c;
4006dc: 0f bf 45 f4 movswl -0xc(%rbp),%eax
4006e0: 89 45 f8 mov %eax,-0x8(%rbp)
a = d;
4006e3: 0f b7 45 f6 movzwl -0xa(%rbp),%eax
4006e7: 89 45 f8 mov %eax,-0x8(%rbp)
b = c;
4006ea: 0f bf 45 f4 movswl -0xc(%rbp),%eax
4006ee: 89 45 fc mov %eax,-0x4(%rbp)
b = d;
4006f1: 0f b7 45 f6 movzwl -0xa(%rbp),%eax
4006f5: 89 45 fc mov %eax,-0x4(%rbp)
return 0;
4006f8: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
}
4006fd: 5d pop %rbp
4006fe: c3 retq
可以看出,a右移的时候使用的是算数右移,b右移使用逻辑右移。并且,
a = c 使用的有符号扩展,
a = d 使用的是零扩展,
b = c使用的是符号扩展,
b = d使用的是零扩展。
这说明扩展完全是看等于号右边的类型是不是有符号类型,跟等号左边完全没有关系。
利用位运算还可以实现原位交换,例如

4.浮点数精度问题

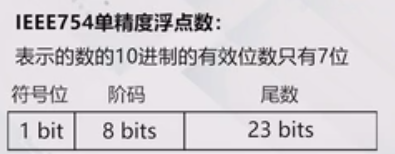

举个例子来说明精度问题:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
float tem[10];
float a = 123456789;
int* pTem;
int i;
pTem = (int*)tem;
tem[0] = 61.419996;
tem[1] = 61.419997;
tem[2] = 61.419998;
tem[3] = 61.419999;
tem[4] = 61.420000;
tem[5] = 61.420001;
tem[6] = 61.420002;
tem[7] = 61.420003;
tem[8] = 61.420004;
tem[9] = 61.420005;
for (i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
printf("%.6f,0x%Xn", tem[i], *(pTem+i));
}
printf("%fn", a);
return 0;
}
运行后结果为:
61.419994,0x4275AE13
61.419998,0x4275AE14
61.419998,0x4275AE14
61.419998,0x4275AE14
61.419998,0x4275AE14
61.420002,0x4275AE15
61.420002,0x4275AE15
61.420002,0x4275AE15
61.420006,0x4275AE16
61.420006,0x4275AE16
123456792.000000

发现只有上面两个结果是对的,实际上数据会做就近阶段,看上面的机器数只有4种表现形式,所以上面两个正确的结果也只是运气好而已。记住一个结论:
单精度浮点数只能表示7位有效数字,第8位表示不准确。
4.浮点数累加操作的大数吃小数问题
比如说把400万个0.1相同,其结果并不是40万
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int count = 4000000;
float result = 0;
for (int i =0 ;i < count;i++) {
result += 0.1;
}
printf("%fn", result);
return 0;
}
运行后结果为:
384524.781250


再看一个例子:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
float sum = 0;
float a = 10.2;
float b = 9;
int i;
printf("10.2-9=%.10fn", a-b);
a= 100000.2;
printf("100000.2-9=%.10fn", a-b);
return 0;
}
运行后结果为:
10.2-9=1.1999998093
100000.2-9=99991.2031250000

发现第二种情况,也就是a的值更大的情况时,误差更大,原因呢?

那么怎么减小误差呢?有个算法
 了解一下就行了,知道有这个算法即可。这个算法会带来多次加法。
了解一下就行了,知道有这个算法即可。这个算法会带来多次加法。
5.cache友好代码
cache是个缓存,写代码的时候注意下可以是程序运行更快。

因为当程序想要访问一段内存中的数据的时候,会把内存中的数据拷贝到cache中,所以如果我们继续访问附近的数据,说不定这些数据就在cache中了,速度当然更快。
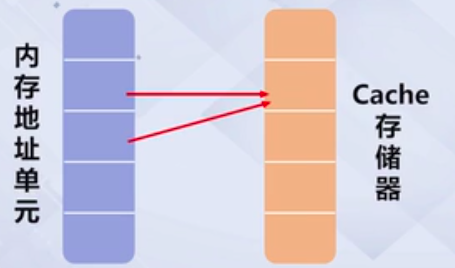
举个例子,矩阵相乘。

不同的循环顺序,结果非常不一样。
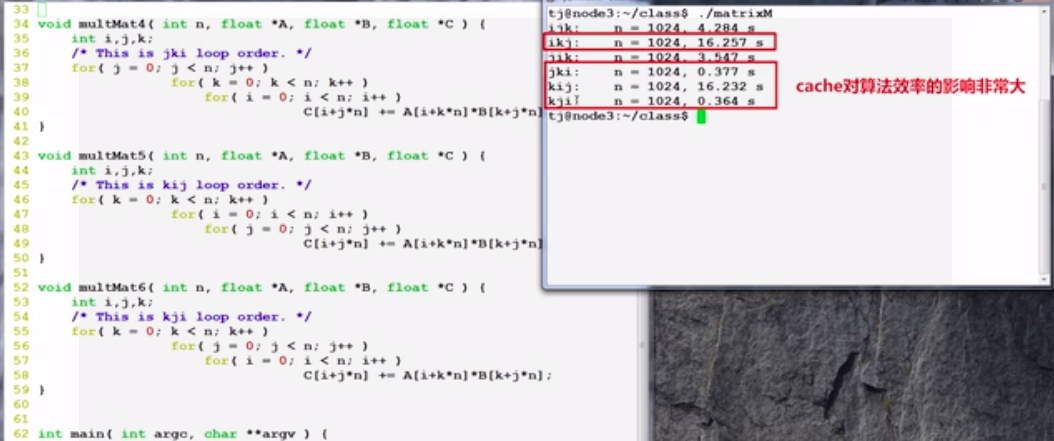
为什么会这样么,要看看矩阵是怎么存储的。
先看个相对比较慢的:

再看个最慢的:
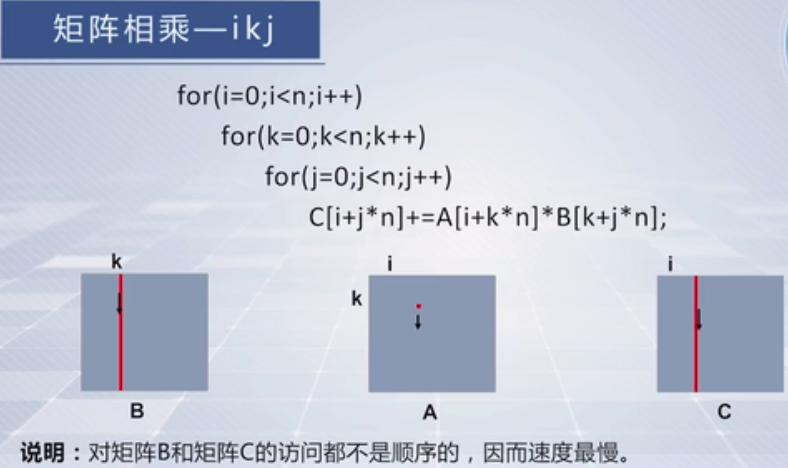
再看个最快的:

最后
以上就是端庄蜜粉最近收集整理的关于计算机系统基础第四篇-3 C语言常用操作的全部内容,更多相关计算机系统基础第四篇-3内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复