2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
假设一个场景,需要连接两个很大的数据集,例如,用户日志和 OLTP 的用户数据。任何一个数据集都不是足够小到可以缓存在 map 作业的内存中。可以思考以下问题:如果在数据集的连接操作中,一个数据集中有的记录由于因为无法连接到另一个数据集的记录,将会被移除。这样还需要将整个数据集放到内存中吗?
在这个例子中,在用户日志中的用户仅仅是 OLTP 用户数据中的用户中的很小的一部分。那么就可以从 OLTP 用户数据中只取出存在于用户日志中的那部分用户的用户数据。然后就可以得到足够小到可以放在内存中的数据集。这种的解决方案就叫做半连接。
应用场景:
需要连接两个都很大的数据集,同时避免经过 shuffle 和 sort 阶段。解决方案:
在这个技术中,将会用到三个 MapReduce 作业来连接两个数据集,以此来减少 reduce 端连接的消耗。这个技术在这种场景下非常有用:连接两个很大的数据集,但是可以通过过滤与另一个数据集不匹配的记录来减少数据的大小,使得可以放入 task 的内存中。
下图说明了在半连接中将要执行的三个 MapReduce 作业(Job)。
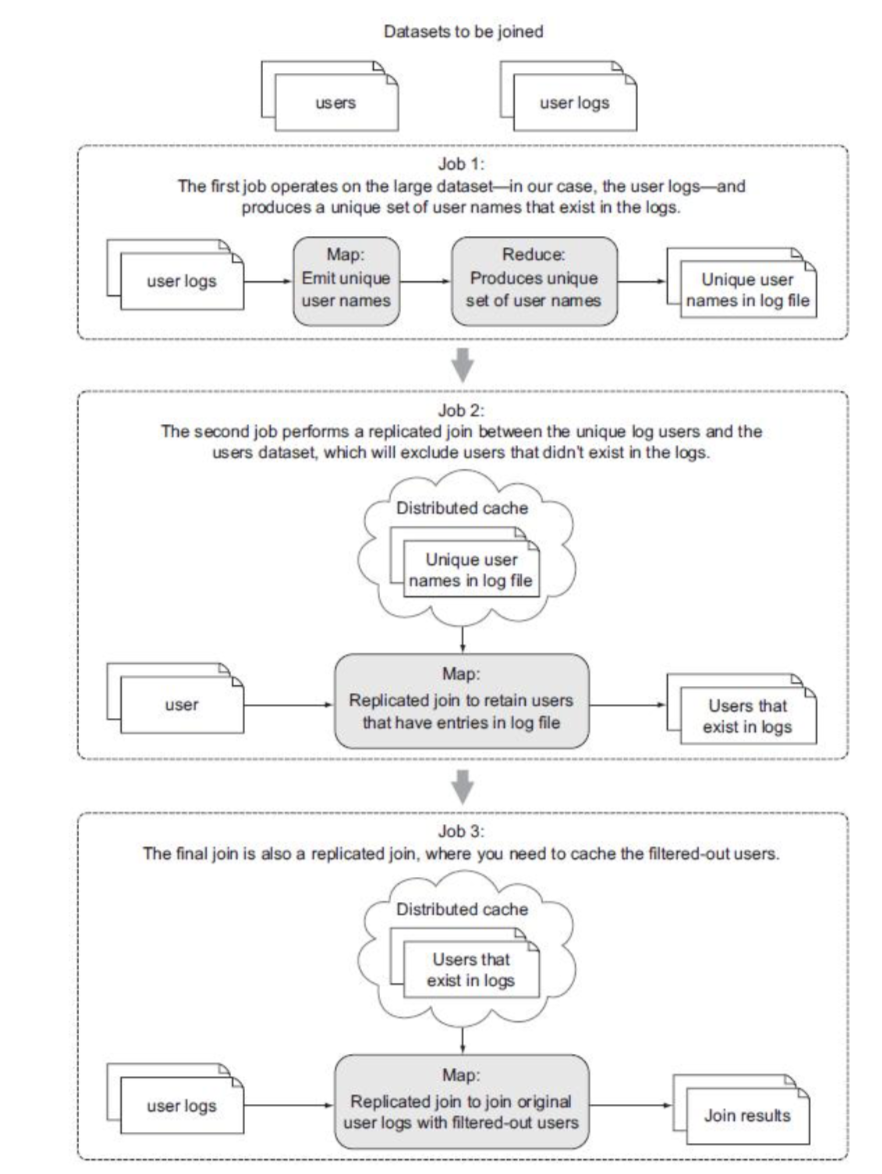
[例]使用半连接。
准备数据集:
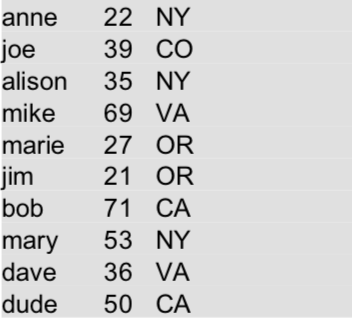
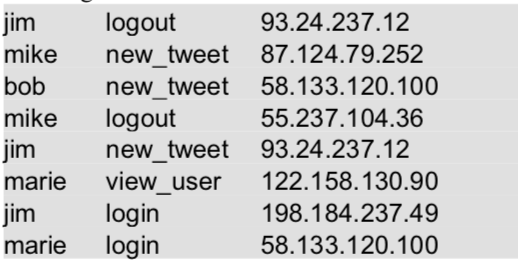
有两个数据集 logs.txt 和 users.txt。其中 users.txt 中为用户数据,包括用户名、年龄和所在地区;logs.txt为基于用户的一些活动(可从应用程序或 web 服务器日志中抽取出来),包括用户名、活动、源 IP 地址。
文件 users.txt:
文件 logs.txt:
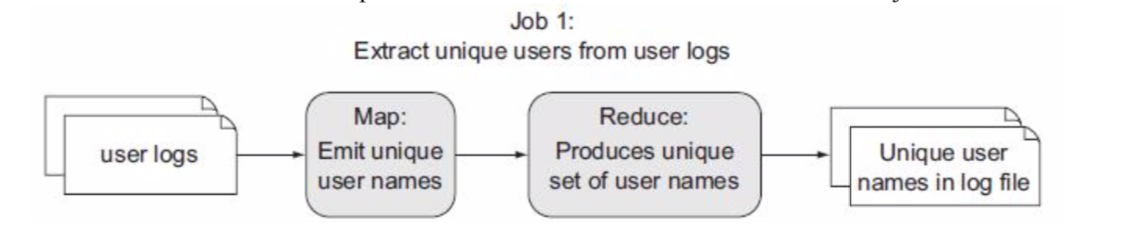
JOB 1:
第一个 MapReduce job 的功能是从日志文件中提取出用户名,用这些用户名生成一个用户名唯一的集合(Set)。这通过在 map 函数执行用户名的投影操作来实现,并反过来使用 reducer 来产生这些用户名。为了减少在 map 阶段和 reduce 阶段之间传输的数据量,采用如下方法:在 map 任务中采用哈希集 HashSet来缓存所有的用户名,并在 cleanup 方法中输出该 HashSet 的值。下图说明了这个 job 的流程:
作业1的代码:
package com.edu360.mapreduce;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.KeyValueTextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* java 一出 谁与争锋
* <p>
* .............................................
* 佛祖保佑
永无BUG
*
* @Auther: caozhan
* @Date: 2018/10/29 17:51
* @Description:
*/
//从logs.txt 表中抽取用户名(考虑外键引用关系,这里相当于先在从表中找出被引用的外键列唯一值)
public class SemiJoinJob1 extends Configured implements Tool {
//使用keyValueTextInputFormat 类,输入的是logs.txt 表中的每条记录
public static class Map extends Mapper<Text,Text, Text, NullWritable>{
//缓存用户名过滤后的小数据集
private Set<String> keys = new HashSet<>();
@Override
protected void map(Text key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//把用户名加入缓存,重复的用户名只会保留一个
keys.add(key.toString());
}
@Override
protected void cleanup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Text outputkey = new Text();
for(String key:keys){
outputkey.set(key);
//从mapper输出缓存的用户名
context.write(outputkey,NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<Text,NullWritable,Text,NullWritable>{
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//从reduce输出每个用户名一次
context.write(key,NullWritable.get());
}
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Path inputPath = new Path(args[0]);
Path outPath = new Path(args[1]);
Job job1= Job.getInstance(getConf(),"SemiJoinJob1");
job1.setJarByClass(getClass());
job1.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job1.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
job1.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job1.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job1.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job1.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job1.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class);
job1.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
//如果输出目录在 先删除
/*
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(outPath.toUri(),getConf());
if(fs.exists(outPath)){
fs.delete(outPath,true);
}
*/
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job1,inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job1,outPath);
if(job1.waitForCompletion(true)){
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
public static void main(String [] args)throws Exception{
int returnCode = ToolRunner.run(new SemiJoinJob1(),args);
System.exit(returnCode);
}
}
作业 1 的结果就是来自于日志文件中的所有用户的集合。集合中的用户名是唯一的。
Job2:
第二步是一个复杂的过滤 MapReduce job,目标是从全体用户的用户数据集中移除不存在于日志文件中的用户。这是一个 map-only job,它使用一个复制连接来缓存出现在日志文件中的用户名,并把他们和用户数据集进行连接。由于 job 1 输出的唯一用户的数据集实际上要远远小于整个用户数据集,所以很自然地就把来自 job 1 的唯一用户集放到缓存中了。下图说明了这个作业的流程:
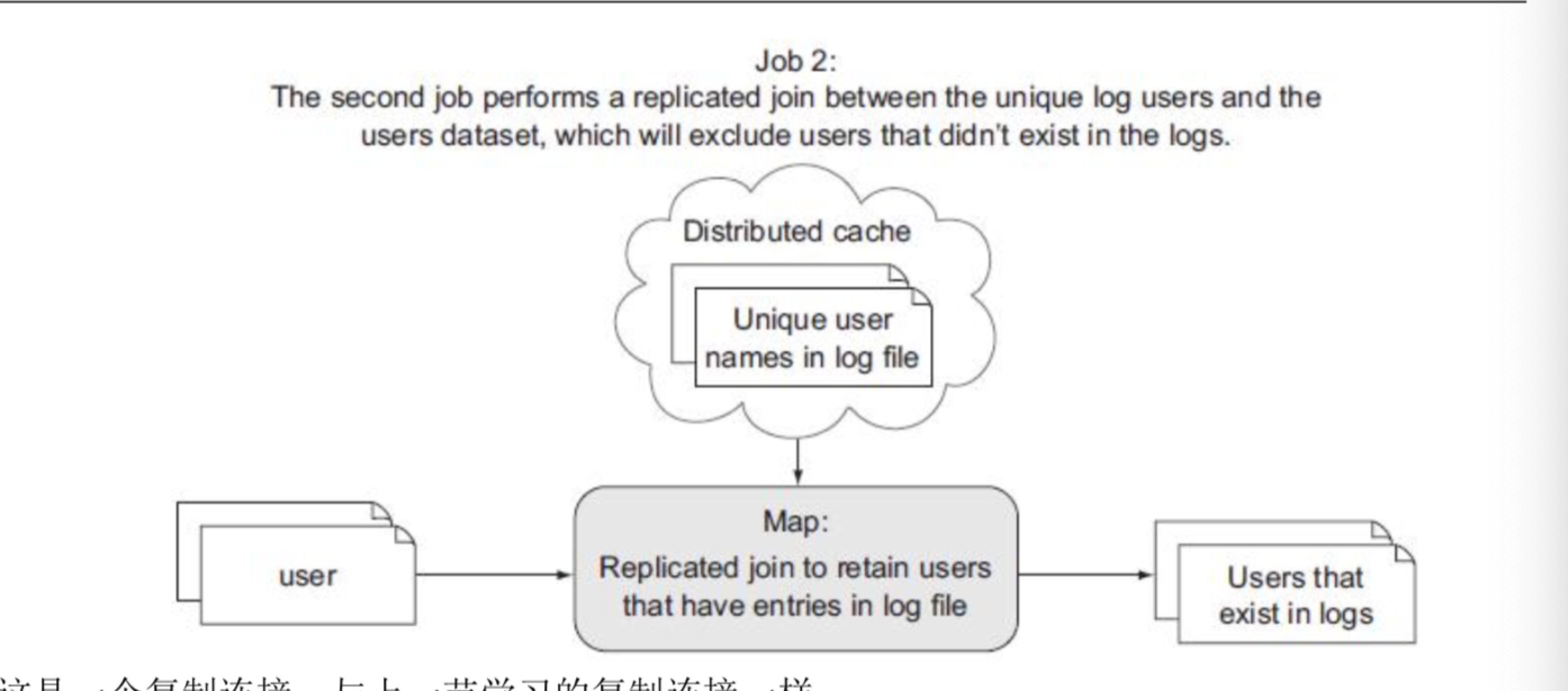
这是一个复制连接,与上一节学习的复制连接一样。
Job 2 的 mapper 代码如下:(注意,要先上传 job1 的输出文件 part-r-00000 到分布式缓存)
package com.edu360.mapreduce;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* java 一出 谁与争锋
* <p>
* .............................................
* 佛祖保佑
永无BUG
*
* @Auther: caozhan
* @Date: 2018/10/29 23:20
* @Description:
*/
public class SemiJoinJob2 extends Configured implements Tool {
public static class Map extends Mapper<Object, Text,Text, NullWritable>{
public static final String CATCH_USERNAME_FILENAME="part-000";
private Set<String> userSet=new HashSet<>();
private Text outputKey = new Text();
//在map()函数执行之前,从分布式缓存中读取被缓存到本地
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
URI[] patternsURIs = context.getCacheFiles(); // 获取缓存文件的 uri
Path patternsPath = new Path(patternsURIs[0].getPath()); // 这里我们只缓存了一个文件
String patternsFileName = patternsPath.getName(); // 获得缓存文件的文件名
System.out.println("patternsFileName: " + patternsFileName);
// 从分布式缓存中读取 job 1 的输出,并存入到 HashMap 中
if (CATCH_USERNAME_FILENAME.equals(patternsFileName)) {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("/hadoop/semijoin/output1/"));
String line = br.readLine();
while (line != null) {
String username = line; userSet.add(username); // 放入 HashSet 中 line = br.readLine();
}
br.close(); }
if (userSet.isEmpty()) {
throw new IOException("unable to load unique user table");
}
}
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String row = value.toString();
String[] tokens = row.split("t");
String username = tokens[0]; // 取每条用户记录中的用户名字段
if (userSet.contains(username)) { // 过滤
outputKey.set(row);
context.write(outputKey, NullWritable.get()); // 输出整行用户记录
}
}
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length < 3) {
System.err.println("用法: SemiJoinJob2 <userpath> <outpath> <catchpath>");
System.exit(-1);
}
Path inputPath = new Path(args[0]); // 应该为 job 1 的输出:part-r-00000
Path outputPath = new Path(args[1]);
Path cachePath = new Path(args[2]);
Job job2 = Job.getInstance(getConf(), "SemiJoinJob2");
// 将 part-r-00000 文件放入分布式缓存中 // "/hadoop/semijoin/output1/part-r-00000" job2.addCacheFile(cachePath.toUri());
job2.setJarByClass(getClass());
job2.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job2.setNumReduceTasks(0);
job2.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job2.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job2.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job2.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job2.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job2.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
// 如果输出目录存在,则先删除
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(outputPath.toUri(), getConf());
if (fs.exists(outputPath)) {
fs.delete(outputPath, true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job2, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job2, outputPath);
if (job2.waitForCompletion(true)) {
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int returnCode = ToolRunner.run(new SemiJoinJob2(), args);
System.exit(returnCode);
}
}
作业 2 的输出就是已被用户日志数据集的用户名过滤过的用户集了。
Job 3:
在这最后一步中,我们将合并从 job 2 输出的过滤后的用户和原始的用户日志。现在被过滤后的用户已经小到可以驻留在内存中了,这样就可以将它们放入分布式缓存中。下图演示了这个 job 的流程:
package com.edu360.mapreduce;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* java 一出 谁与争锋
* <p>
* .............................................
* 佛祖保佑
永无BUG
*
* @Auther: caozhan
* @Date: 2018/10/29 23:46
* @Description:
*/
public class SemiJoinJob3 extends Configured implements Tool {
public static class JoinMap extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> {
public static final String CATCH_USERS_FILENAME = "part-m-00000";
private Map<String, String> usersMap = new HashMap<>();
private Text outputKey = new Text();
private Text outputValue = new Text();
// 在 map()函数执行之前,从分布式缓存中读取被缓存到本地的文件
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
URI[] patternsURIs = context.getCacheFiles(); // 获取缓存文件的 uri
Path patternsPath = new Path(patternsURIs[0].getPath()); // 这里我们只缓存了一个文件
String patternsFileName = patternsPath.getName().toString(); // 获得缓存文件的文件名
// 从分布式缓存中读取 job 2 的输出,并存入到 HashMap 中
if (CATCH_USERS_FILENAME.equals(patternsFileName)) {
patternsFileName = "/hadoop/semijoin/output2/" + patternsFileName;
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(patternsFileName));
String line = br.readLine();
while (line != null) {
String[] tokens = line.split("t");
String username = tokens[0];
String content = line;
usersMap.put(username, content); // 放入 HashMap 中
line = br.readLine();
}
br.close();
}
if (usersMap.isEmpty()) {
throw new IOException("unable to load users catch table");
}
}
// 输入的是 logs.txt 中的日志信息,需要和缓存中的用户信息连接 @Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Mapper.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String row = value.toString();
String[] tokens = row.split("t");
String username = tokens[0]; // 取每条日志记录的用户名字段
String user = usersMap.get(username); // 根据 username,找到对应的(缓存的)用户记录
outputKey.set(row);
outputValue.set(user);
context.write(outputKey, outputValue);
}
}
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception { if (args.length < 3) {
System.err.println("用法: SemiJoinJob3 <logspath> <outpath> <catchpath>");
System.exit(-1); }
Path inputPath = new Path(args[0]); // 应该为 job 2 的输出:part-r-00000
Path outputPath = new Path(args[1]);
Path cachePath = new Path(args[2]);
Job job3 = Job.getInstance(getConf(), "SemiJoinJob3");
// 将 part-r-00000 文件放入分布式缓存中
// "/hadoop/semijoin/output2/part-m-00000" job3.addCacheFile(cachePath.toUri());
job3.setJarByClass(getClass());
job3.setMapperClass(JoinMap.class);
job3.setNumReduceTasks(0);
job3.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job3.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job3.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job3.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job3.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job3.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
// 如果输出目录存在,则先删除
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(outputPath.toUri(), getConf());
if (fs.exists(outputPath)) {
fs.delete(outputPath, true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job3, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job3, outputPath);
if (job3.waitForCompletion(true)) {
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int returnCode = ToolRunner.run(new SemiJoinJob3(), args);
System.exit(returnCode);
}
}
小结:
这一节学习了怎样使用一个半连接(semi-join)来合并两个数据集。半连接结构包含比其他连接更多的步骤,但是当处理大数据集时(其中有一个数据集必须可被消减到适合放入内存的大小),使用半连接是很给力的方式。
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/u/4009325/blog/2396202
最后
以上就是受伤手套最近收集整理的关于半连接(Semi-join)的全部内容,更多相关半连接(Semi-join)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复