Sentinel注解支持详述
☞ 博客导航,带你有序的阅读和学习!
官方文档:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E6%B3%A8%E8%A7%A3%E6%94%AF%E6%8C%81
这一节,我们首先做一个小的案例,然后把官方文档中的介绍过一遍,再把文档所述的特性在代码中找到。
案例
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
属性文件
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: 127.0.0.1:8080
port: 8719
application:
name: sentinel-annotaion
server:
port: 9999
说明:
spring.application.name定义应用名,如图所示的名称
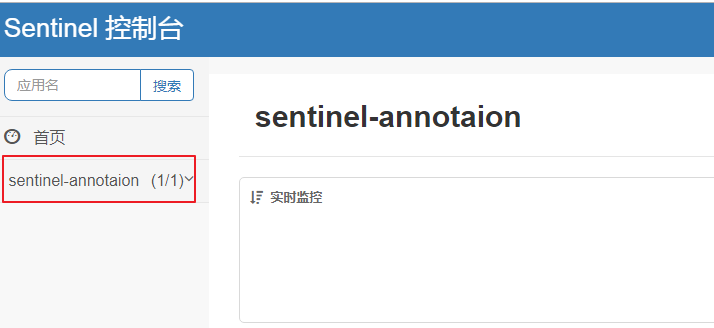
server.port:应用端口spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.dashboard:sentinel的IP:端口spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.port:sentinel 与服务的通讯端口
切面
如果使用的是Spring Boot/Cloud ,即没有导入前面的依赖,需要自己将切面纳入到Spring容器中去:
@Bean
public SentinelResourceAspect sentinelResourceAspect() {
return new SentinelResourceAspect();
}
由于我们导入了springcloud的依赖,所以会自动配置好这个切面,源码如下:
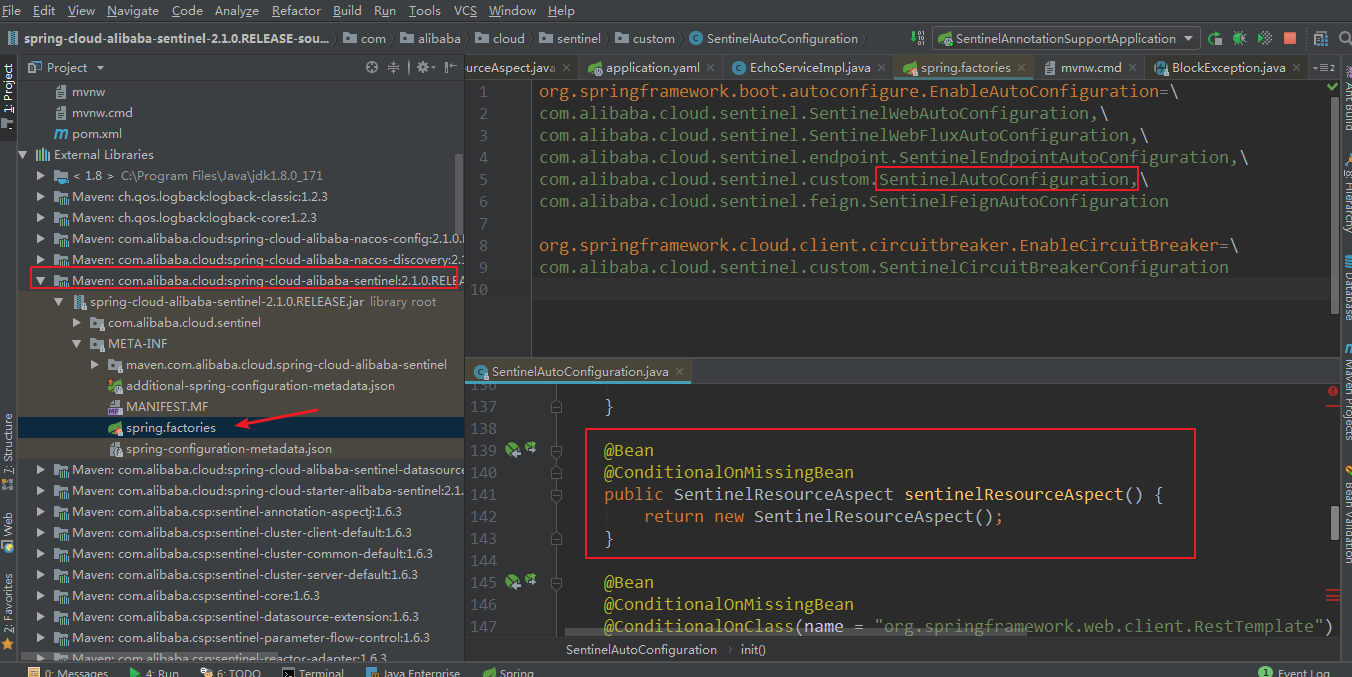
EchoService
public interface EchoService {
String echoMessage(String message);
String hello();
}
EchoServiceImpl
@Service
public class EchoServiceImpl implements EchoService {
@Override
@SentinelResource(value = "echo.message",blockHandler = "handleException",
blockHandlerClass = ExceptionUtil.class)
public String echoMessage(String message) {
return "echo message:"+message;
}
@Override
@SentinelResource(value = "hello",blockHandler = "handleHello")
public String hello() {
return "echo hello";
}
public String handleHello(BlockException ex){
return "handle hello ; exception:"+ex;
}
}
ExceptionUtil
public class ExceptionUtil {
public static String handleException(String message, BlockException ex){
return "exception handle "+message + " exception:"+ex;
}
}
EchoController
@RestController
public class EchoController {
@Autowired
private EchoService echoService;
@GetMapping("/echo/message/{message}")
public String echoMessage(@PathVariable String message){
return echoService.echoMessage(message);
}
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return echoService.hello();
}
}
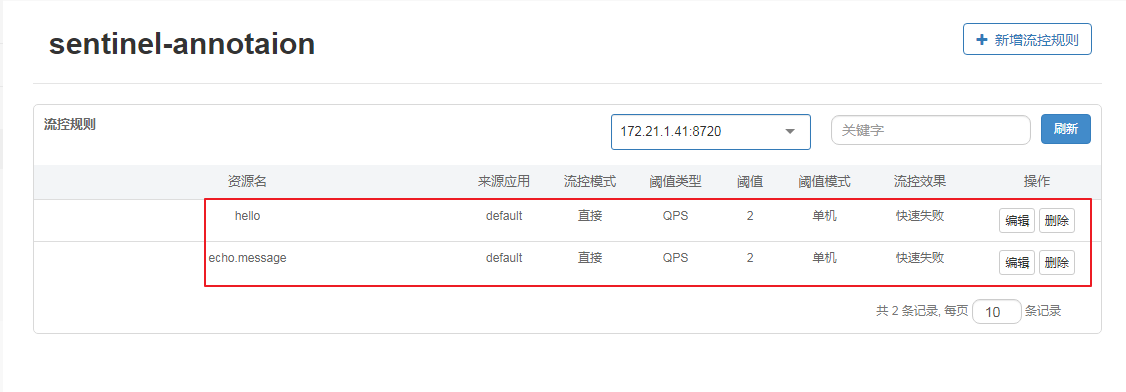
页面控制流控
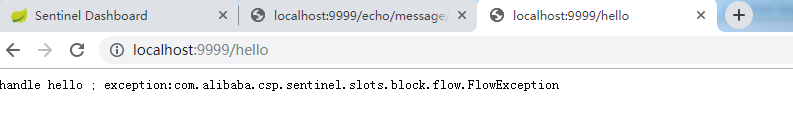
流控限制如下,简单使用基于QPS的流控规则(规则后续会详细说到),阈值为2,流控效果选的是快速失败。
通过测试,当我们在页面快速刷新(达到一秒访问3次或3次以上)可以看到下面的效果。
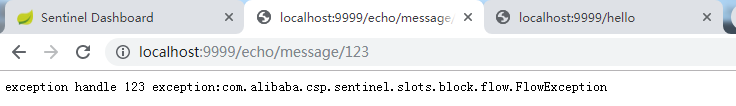
@SentinelResource 注解
@sentinelResource 注解用于定义资源,并提供可选的异常处理和fallback配置项,@sentinelResource 注解包含以下属性:
注解源码
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
public @interface SentinelResource {
//资源名
String value() default "";
//entry 类型
EntryType entryType() default EntryType.OUT;
//指定异常处理函数名
String blockHandler() default "";
//如果异常处理函数不与目标方法在同一个类,则需要指定类,并且异常处理函数需要声明为static
Class<?>[] blockHandlerClass() default {};
//fallback函数名,默认为空
String fallback() default "";
//指定默认fallback函数
String defaultFallback() default "";
//同样,fallback函数需要和目标方法在同一个类,如果不再,则需要指定,并且对应的函数需要声明为static
Class<?>[] fallbackClass() default {};
//
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToTrace() default {Throwable.class};
//指定排除的异常类型,不进入异常统计,也不会进入fallback函数处理,而是原样抛出。
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore() default {};
}
文档原文
@SentinelResource 用于定义资源,并提供可选的异常处理和 fallback 配置项。 @SentinelResource 注解包含以下属性:
value:资源名称,必需项(不能为空)entryType:entry 类型,可选项(默认为EntryType.OUT)blockHandler/blockHandlerClass:blockHandler对应处理BlockException的函数名称,可选项。blockHandler 函数访问范围需要是public,返回类型需要与原方法相匹配,参数类型需要和原方法相匹配并且最后加一个额外的参数,类型为BlockException。blockHandler 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定blockHandlerClass为对应的类的Class对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。fallback:fallback 函数名称,可选项,用于在抛出异常的时候提供 fallback 处理逻辑。fallback 函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了exceptionsToIgnore里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。fallback 函数签名和位置要求:返回值类型必须与原函数返回值类型一致;方法参数列表需要和原函数一致,或者可以额外多一个Throwable类型的参数用于接收对应的异常。fallback 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定fallbackClass为对应的类的Class对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。defaultFallback(since 1.6.0):默认的 fallback 函数名称,可选项,通常用于通用的 fallback 逻辑(即可以用于很多服务或方法)。默认 fallback 函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了exceptionsToIgnore里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。若同时配置了 fallback 和 defaultFallback,则只有 fallback 会生效。defaultFallback 函数签名要求:返回值类型必须与原函数返回值类型一致;方法参数列表需要为空,或者可以额外多一个Throwable类型的参数用于接收对应的异常。defaultFallback 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定fallbackClass为对应的类的Class对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。exceptionsToIgnore(since 1.6.0):用于指定哪些异常被排除掉,不会计入异常统计中,也不会进入 fallback 逻辑中,而是会原样抛出。
注:1.6.0 之前的版本 fallback 函数只针对降级异常(
DegradeException)进行处理,不能针对业务异常进行处理。
特别地,若 blockHandler 和 fallback 都进行了配置,则被限流降级而抛出 BlockException 时只会进入 blockHandler 处理逻辑。若未配置 blockHandler、fallback 和 defaultFallback,则被限流降级时会将 BlockException 直接抛出
@SentinelResource逻辑分析
源码分析
@Around("sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut()")
public Object invokeResourceWithSentinel(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//标有注解(@SentinelResource)的目标原始方法
Method originMethod = resolveMethod(pjp);
//获取注解对象(@SentinelResource)
SentinelResource annotation = originMethod.getAnnotation(SentinelResource.class);
if (annotation == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong state for SentinelResource annotation");
}
//资源名称
String resourceName = getResourceName(annotation.value(), originMethod);
EntryType entryType = annotation.entryType();
Entry entry = null;
try {
//sentinel 逻辑代码
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, entryType, 1, pjp.getArgs());
//执行目标方法
Object result = pjp.proceed();
return result;
} catch (BlockException ex) {
// 处理BlockException
return handleBlockException(pjp, annotation, ex);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 处理非BlockException
// 获取忽略处理的异常
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore = annotation.exceptionsToIgnore();
//判断当前异常是否在 忽略异常列表中,如果存在,则直接抛出
if (exceptionsToIgnore.length > 0 && exceptionBelongsTo(ex, exceptionsToIgnore)) {
throw ex;
}
//如果当前异常在exceptionsToTrace属性中定义了,就进行处理
if (exceptionBelongsTo(ex, annotation.exceptionsToTrace())) {
traceException(ex);
return handleFallback(pjp, annotation, ex);
}
//前面的条件都不符合,则直接抛出异常
throw ex;
} finally {
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit(1, pjp.getArgs());
}
}
}
我们主要看 catch 中的handleBlockException() 方法。
第一步:执行 blockHandler所配置的方法
protected Object handleBlockException(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, SentinelResource annotation, BlockException ex)
throws Throwable {
//第一步:处理blockHandler方法。
// 如果配置了blockHandler 处理函数,则进行执行处理,获取blockHandler处理方法
Method blockHandlerMethod = extractBlockHandlerMethod(pjp, annotation.blockHandler(),
annotation.blockHandlerClass());
//存在blockHandlerMethod的方法
if (blockHandlerMethod != null) {
//获取目标方法的参数
Object[] originArgs = pjp.getArgs();
// 构建参数
Object[] args = Arrays.copyOf(originArgs, originArgs.length + 1);
args[args.length - 1] = ex;
try {
//静态方法
if (isStatic(blockHandlerMethod)) {
//反射调用方法,静态方法不需要传入obj
return blockHandlerMethod.invoke(null, args);
}
//非静态方法。
return blockHandlerMethod.invoke(pjp.getTarget(), args);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// throw the actual exception
throw e.getTargetException();
}
}
//如果没有配置blockHandler 异常处理函数。则执行fallback
//第二步执行fallback 处理函数
return handleFallback(pjp, annotation, ex);
}
//========================进入extractBlockHandlerMethod方法========================
/**
* name:异常处理函数名,locationClass:异常处理函数所在类,如果没有配置,则说明不是静态方法
*/
//注意:这里可以看到,如果使用blockHandler函数,则先处理普通的,其次在去处理静态的。
private Method extractBlockHandlerMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, String name,
Class<?>[] locationClass) {
if (StringUtil.isBlank(name)) {
return null;
}
// locationClass 如果配置了类,说明异常处理方法是静态方法。
boolean mustStatic = locationClass != null && locationClass.length >= 1;
Class<?> clazz;
//是不是配置了方法所在的类
if (mustStatic) {
//如果传入了blockHandlerClass,则取第一个class
clazz = locationClass[0];
} else {
// 如果为空,就取当前类
clazz = pjp.getTarget().getClass();
}
//从缓存中取MethodWrapper
MethodWrapper m = ResourceMetadataRegistry.lookupBlockHandler(clazz, name);
//缓存中没有
if (m == null) {
// name是异常处理方法的名称,clazz是方法所在的类,mustStatic 是 是否为静态方法
// 获取 异常处理方法在当前类(及所有父类)的异常处理方法
Method method = resolveBlockHandlerInternal(pjp, name, clazz, mustStatic);
//缓存当前方法的MethodWrapper实例
ResourceMetadataRegistry.updateBlockHandlerFor(clazz, name, method);
return method;
}
if (!m.isPresent()) {
return null;
}
//从缓存中取
return m.getMethod();
}
//===============进入resolveBlockHandlerInternal()方法================================
//name: 异常处理方法;class:异常处理方法所在的类,mustStatic是否为静态方法
//注意:通过这个方法可以看到:blockHandler异常处理函数的参数列表是在原方法的基础上,在末尾添加一个
// BlockException类型的形参
private Method resolveBlockHandlerInternal(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, /*@NonNull*/ String name,
Class<?> clazz,boolean mustStatic) {
//获取目标方法的Method对象
Method originMethod = resolveMethod(pjp);
//获取方法参数数组
Class<?>[] originList = originMethod.getParameterTypes();
//获取异常处理方法的参数列表
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = Arrays.copyOf(originList, originList.length + 1);
//添加了一个新的参数,所以,我们定义降级的方法时,在末尾需要添加一个BlockException。
parameterTypes[parameterTypes.length - 1] = BlockException.class;
//查找处理异常方法的Method对象(handleException)
return findMethod(mustStatic, clazz, name, originMethod.getReturnType(), parameterTypes);
}
//=================进入findMethod()方法==========================
//注意:这里可以发现,如果使用的是非静态的方法的处理方式,如果本类没有对应的异常处理函数,会递归追溯到父类,
// 父类的父类......
/*递归查询方法对象*/
private Method findMethod(boolean mustStatic, Class<?> clazz, String name, Class<?> returnType,
Class<?>... parameterTypes) {
//获取当前类对象的所有方法对象
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (name.equals(method.getName()) && checkStatic(mustStatic, method)
&& returnType.isAssignableFrom(method.getReturnType())
&& Arrays.equals(parameterTypes, method.getParameterTypes())) {
RecordLog.info("Resolved method [{0}] in class [{1}]", name, clazz.getCanonicalName());
return method;
}
}
// 本类没有,则向它的父类查找
Class<?> superClass = clazz.getSuperclass();
if (superClass != null && !Object.class.equals(superClass)) {
return findMethod(mustStatic, superClass, name, returnType, parameterTypes);
} else {
String methodType = mustStatic ? " static" : "";
RecordLog.warn("Cannot find{0} method [{1}] in class [{2}] with parameters {3}",
methodType, name, clazz.getCanonicalName(), Arrays.toString(parameterTypes));
return null;
}
}
第二步:执行fallback所配置的方法,进入handleFallback()方法
protected Object handleFallback(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, SentinelResource annotation, Throwable ex)
throws Throwable {
return handleFallback(pjp, annotation.fallback(), annotation.defaultFallback(),
annotation.fallbackClass(), ex);
}
protected Object handleFallback(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, String fallback, String defaultFallback,
Class<?>[] fallbackClass, Throwable ex) throws Throwable {
//目标方法的参数数组
Object[] originArgs = pjp.getArgs();
// 如果配置了fallback处理函数,则执行
Method fallbackMethod = extractFallbackMethod(pjp, fallback, fallbackClass);
if (fallbackMethod != null) {
// 构造参数列表
int paramCount = fallbackMethod.getParameterTypes().length;
Object[] args;
if (paramCount == originArgs.length) {
args = originArgs;
} else {
args = Arrays.copyOf(originArgs, originArgs.length + 1);
args[args.length - 1] = ex;
}
try {
if (isStatic(fallbackMethod)) {
//静态方法调用
return fallbackMethod.invoke(null, args);
}
//普通方法调用
return fallbackMethod.invoke(pjp.getTarget(), args);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// throw the actual exception
throw e.getTargetException();
}
}
// If fallback is absent, we'll try the defaultFallback if provided.
// 如果fallback 方法没有,则执行默认的fallback方法
//第三步处理默认的fallback配置的函数
return handleDefaultFallback(pjp, defaultFallback, fallbackClass, ex);
}
//==================进入extractFallbackMethod()方法==================
private Method extractFallbackMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, String fallbackName,
Class<?>[] locationClass) {
if (StringUtil.isBlank(fallbackName)) {
return null;
}
//判断配置为静态方法
boolean mustStatic = locationClass != null && locationClass.length >= 1;
//同样,如果是配置为静态的,直接取,如果不是,则使用目标方法所在类
Class<?> clazz = mustStatic ? locationClass[0] : pjp.getTarget().getClass();
//从缓存中取
MethodWrapper m = ResourceMetadataRegistry.lookupFallback(clazz, fallbackName);
if (m == null) {
// 获取fallback方法的Method对象
Method method = resolveFallbackInternal(pjp, fallbackName, clazz, mustStatic);
// 加入到缓存中
ResourceMetadataRegistry.updateFallbackFor(clazz, fallbackName, method);
return method;
}
if (!m.isPresent()) {
return null;
}
return m.getMethod();
}
//===========进入resolveFallbackInternal()方法中=================
private Method resolveFallbackInternal(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, /*@NonNull*/ String name,
Class<?> clazz,boolean mustStatic) {
//获取原方法(目标增强方法)
Method originMethod = resolveMethod(pjp);
// Fallback function allows two kinds of parameter list.
// Fallback函数是支持两种类型的参数列表的,这里不像BlockHandler函数
// 第一种:与原参数列表一直;第二种:在原参数列表的最后添加一个Throwable类型
Class<?>[] defaultParamTypes = originMethod.getParameterTypes();
Class<?>[] paramTypesWithException = Arrays.copyOf(defaultParamTypes, defaultParamTypes.length + 1);
paramTypesWithException[paramTypesWithException.length - 1] = Throwable.class;
// We first find the fallback matching the signature of origin method.
// 先查找第一个参数列表的方法
Method method = findMethod(mustStatic, clazz, name, originMethod.getReturnType(),
defaultParamTypes);
// If fallback matching the origin method is absent, we then try to find the other one.
if (method == null) {
// 如果第一种没有找到,则查询第二个加了异常类型的方法列表的方法
method = findMethod(mustStatic, clazz, name, originMethod.getReturnType(),
paramTypesWithException);
}
return method;
}
第三步:执行defaultFallback属性配置的函数,进入handleDefaultFallback()方法
protected Object handleDefaultFallback(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, String defaultFallback,
Class<?>[] fallbackClass, Throwable ex) throws Throwable {
// 如果配置了默认的fallback方法,如果配置了的话
Method fallbackMethod = extractDefaultFallbackMethod(pjp, defaultFallback, fallbackClass);
if (fallbackMethod != null) {
// 构造参数
Object[] args = fallbackMethod.getParameterTypes().length == 0 ? new Object[0] :
new Object[] {ex};
try {
if (isStatic(fallbackMethod)) {
//静态方法调用
return fallbackMethod.invoke(null, args);
}
//普通方法调用
return fallbackMethod.invoke(pjp.getTarget(), args);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// 抛出实际异常
throw e.getTargetException();
}
}
// 如果没有配置任何的fallback函数(fallback函数和默认的fallback函数,则直接抛出异常 BlockException)
throw ex;
}
//====================进入extractDefaultFallbackMethod()方法====================
private Method extractDefaultFallbackMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, String defaultFallback,
Class<?>[] locationClass) {
if (StringUtil.isBlank(defaultFallback)) {
return null;
}
//判断配置的是否是其他类的静态方法
boolean mustStatic = locationClass != null && locationClass.length >= 1;
//获取方法所在的类名
Class<?> clazz = mustStatic ? locationClass[0] : pjp.getTarget().getClass();
//查询缓存
MethodWrapper m = ResourceMetadataRegistry.lookupDefaultFallback(clazz, defaultFallback);
if (m == null) {
Class<?> originReturnType = resolveMethod(pjp).getReturnType();
// Default fallback allows two kinds of parameter list.
// 默认的fallback方法支持两种参数列表
// One is empty parameter list.
// 第一种是空参数
Class<?>[] defaultParamTypes = new Class<?>[0];
// The other is a single parameter {@link Throwable} to get relevant exception info.
// 第二种是只有一个Throwable类型的参数
Class<?>[] paramTypeWithException = new Class<?>[] {Throwable.class};
// We first find the default fallback with empty parameter list.
// 先查找空参数
Method method = findMethod(mustStatic, clazz, defaultFallback, originReturnType, defaultParamTypes);
// If default fallback with empty params is absent, we then try to find the other one.
if (method == null) {
// 再查询有参数的方法
method = findMethod(mustStatic, clazz, defaultFallback, originReturnType,
paramTypeWithException);
}
// 缓存方法
ResourceMetadataRegistry.updateDefaultFallbackFor(clazz, defaultFallback, method);
return method;
}
if (!m.isPresent()) {
return null;
}
return m.getMethod();
}
如果把上面的代码过一遍的话,前面文档中总结的要点基本都理解了。
执行方法顺序: blockHandler --> fallback --> defaultFallback
处理BlockException
属性方法形参:
-
blockHandler:在原方法的形参列表基础上,需要在最后添加一个
BlockException类型的参数。//获取方法参数数组 Class<?>[] originList = originMethod.getParameterTypes(); //获取异常处理方法的参数列表 Class<?>[] parameterTypes = Arrays.copyOf(originList, originList.length + 1); //添加了一个新的参数,所以,我们定义降级的方法时,在末尾需要添加一个BlockException。 parameterTypes[parameterTypes.length - 1] = BlockException.class; -
fallback:有两种:1:方法参数列表与原方法参数列表一致,2:在原方法列表后添加一个
Throwable类型的参数// Fallback函数是支持两种类型的参数列表的,这里不像BlockHandler函数 // 第一种:与原参数列表一致;第二种:在原参数列表的最后添加一个Throwable类型 Class<?>[] defaultParamTypes = originMethod.getParameterTypes(); Class<?>[] paramTypesWithException = Arrays.copyOf(defaultParamTypes, defaultParamTypes.length + 1); paramTypesWithException[paramTypesWithException.length - 1] = Throwable.class; -
defaultFallback:有两种,1:方法参数列表为空,2:仅有一个
Thowable的参数列表// Default fallback allows two kinds of parameter list. // 默认的fallback方法支持两种参数列表 // One is empty parameter list. // 第一种是空参数 Class<?>[] defaultParamTypes = new Class<?>[0]; // The other is a single parameter {@link Throwable} to get relevant exception info. // 第二种是只有一个Throwable类型的参数 Class<?>[] paramTypeWithException = new Class<?>[] {Throwable.class};
处理非BlockException
如果配置了在忽略异常列表中,则直接抛出原始异常,否则使用exceptionToTrace 配置进行处理,如果没有配置,则直接抛出原始异常。
// 处理非BlockException
// 获取忽略处理的异常
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore = annotation.exceptionsToIgnore();
//判断当前异常是否在 忽略异常列表中,如果存在,则直接抛出
if (exceptionsToIgnore.length > 0 && exceptionBelongsTo(ex, exceptionsToIgnore)) {
throw ex;
}
//如果当前异常在exceptionsToTrace属性中定义了,就进行fallback和defaultFallback处理
if (exceptionBelongsTo(ex, annotation.exceptionsToTrace())) {
traceException(ex);
return handleFallback(pjp, annotation, ex);
}
//前面的条件都不符合,则直接抛出异常
throw ex;
annotation.exceptionsToTrace() 默认是Throwable.class类型的,所以,理论上fallback是可以处理任何异常,排序在忽略异常列表中的异常。
这一节通过阅读源码的方式来学习sentinel的注解支持,后面我们看一下sentinel的几种控制规则。
最后
以上就是凶狠大地最近收集整理的关于Sentinel注解支持详述Sentinel注解支持详述的全部内容,更多相关Sentinel注解支持详述Sentinel注解支持详述内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复