使用 java.nio.ByteBuffer 转换
private static byte[] intToByte(int intValue) {
ByteBuffer byteBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
byteBuf.putInt(intValue);
return byteBuf.array();
}
private static int byteToInt(byte[] bytes) {
ByteBuffer byteBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
byteBuf.put(bytes);
return byteBuf.getInt(0);
}
使用位运算转换
private static byte[] intToByte2(int intValue) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
bytes[0] = (byte) (intValue >> 24);
bytes[1] = (byte) (intValue >> 16);
bytes[2] = (byte) (intValue >> 8);
bytes[3] = (byte) (intValue);
return bytes;
}
private static int byteToInt2(byte[] bytes) {
return bytes[0] << 24 & 0xFF000000 |
bytes[1] << 16 & 0x00FF0000 |
bytes[2] << 8 & 0x0000FF00 |
bytes[3] & 0x000000FF;
}
验证
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("验证结果: " + verify());
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("运行耗时: " + (end-start) + "ms");
}
private static boolean verify(){
for (int i=Integer.MIN_VALUE; i<Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++){
int b = byteToInt(intToByte(i));
if(b != i){
System.out.println("验证不通过的值为: " + i);
return false;
}
}
// 验证最大值
int c = byteToInt(intToByte(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
return c == Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
第一种方式验证结果:
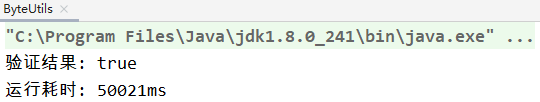
第二种方式验证结果:
int b = byteToInt2(intToByte2(i));
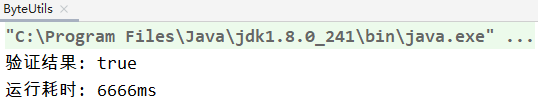
交叉验证结果:
int b = byteToInt2(intToByte(i));
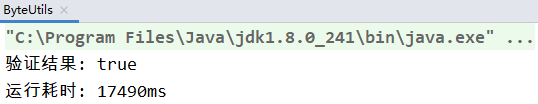
int b = byteToInt(intToByte2(i));
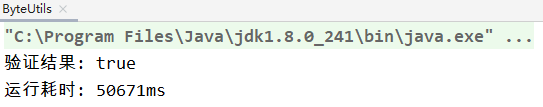
应用场景
当网络传输的数据格式是字节流 且 字节流包含了多部分数据时,可以将各部分数据的长度作为前置内容。前置内容编码时需要 int 转 bytes;解码时需要 bytes 转 int。
总结
第一种实现方式算是常规的方式,没有什么变化性。第二种实现方式样式比较多。
本篇以记录为主,原理性的知识可阅读参考文章。
位运算的思路是:int 转 bytes 拆分字节;bytes 转 int 组合字节。
基本知识点:字节数组低位在前;int 转 byte 截取低八位;0xFF 用来清零。
参考资料:
ByteBuffer原理:https://blog.csdn.net/mrliuzhao/article/details/89453082
位运算原理:http://blog.csdn.net/tang9140/article/details/43404385
最后
以上就是娇气小刺猬最近收集整理的关于【Java】int 与 bytes 相关转换的两种方式的全部内容,更多相关【Java】int内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。


![maya中出现错误Cannot cast data of type string_to_string[]的解决方法](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg1.png)
![byte[]数组和int之间的转换](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg2.png)




发表评论 取消回复