想了解更多数据结构以及算法题,可以关注微信公众号“数据结构和算法”,每天一题为你精彩解答。也可以扫描下面的二维码关注

java代码通过for循环删除list中的元素的时候,报下面这个错误ConcurrentModificationException,测试代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> mList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
mList.add("" + i);
}
for (String item : mList) {
System.out.println(mList.remove(item));
}
}
运行结果如下
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(ArrayList.java:909)
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(ArrayList.java:859)
我们来看下list的remove方法,其中有个值是modCount,list调用remove方法的时候modCount会执行加1

而foreach的背后实现原理其实就是Iterator,我们来看下他的代码,这里只截取其中的一部分
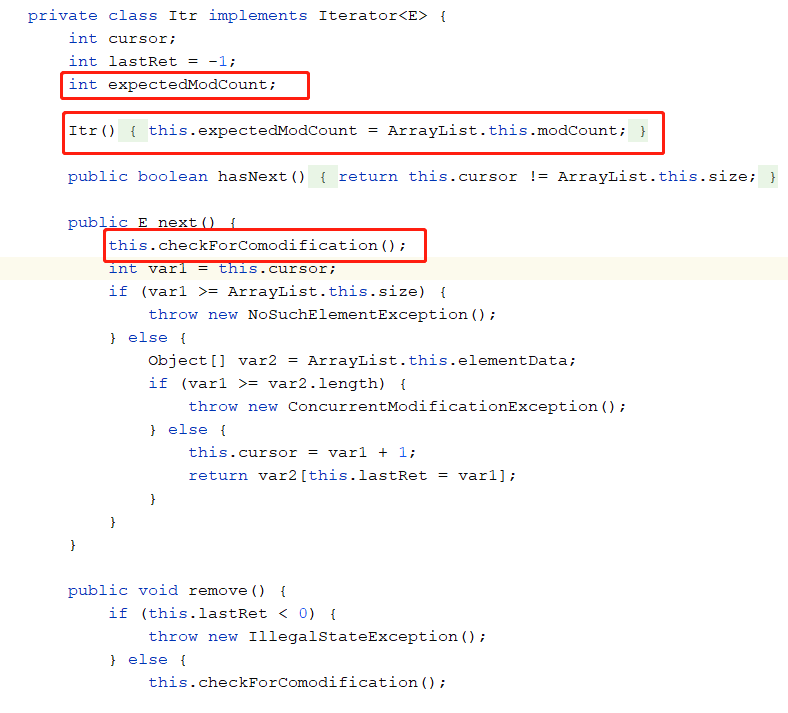
Iterator类中有一个expectedModCount变量,在Itr的构造函数中被初始化的,他其实就是ArrayList的modCount值,所以foreach一旦执行,expectedModCount就会被初始化,后面就不会在变了。正常情况下Iterator中的expectedModCount和ArrayList中modCount的值是一样的。但我们执行ArrayList的remove方法的时候,ArrayList中的modCount会加1,导致modCount和expectedModCount不再相等。而Iterator中的next方法中有这样一个函数
this.checkForComodification();
我们来看下他的实现
final void checkForComodification() {
if (ArrayList.this.modCount != this.expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
看到没,因为他俩不相等了,所以在这里就会抛异常。那么有没有解决方式呢,当然有的,我们来看下Iterator的remove方法
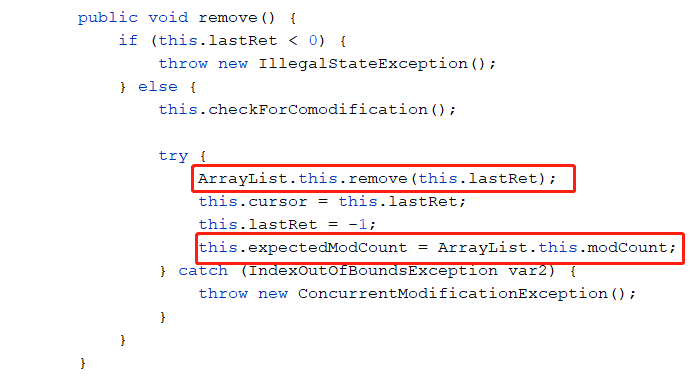
他在调用ArrayList的remove方法后,expectedModCount的值也会跟着变,所以这样就不会出现问题了,所以我们可以使用Iterator的remove方法来执行删除操作,代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> mList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
mList.add("" + i);
}
// for (String item : mList) {
// System.out.println(mList.remove(item));
// }
Iterator<String> iterator = mList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
}
}
这样删除就不会报错了

最后
以上就是如意老虎最近收集整理的关于java ConcurrentModificationException异常原理分析的全部内容,更多相关java内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复