写在前面
在这篇文章我们分析了springboot启动并且加载自动配置类的过程,其中加载自动配置类前,进行过滤(如果不提前过滤就需要将类加载到JVM中并解析类信息后才能过滤,因此这里提前过滤是一种性能优化的手段)的方法AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter,因为相对还比较复杂,因此放在这篇文章中来分析,作为补充。
先来看下调用filter方法时方法参数信息,方便调试,一共两个参数,一个是List<String> configurations,存储的是META-INF/spring.factories文件中key为EnableAutoConfiguration的自动配置类信息,另一个是AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata存储的是META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties文件中存储的自动配置类和条件注解信息的组合信息,分别如下:
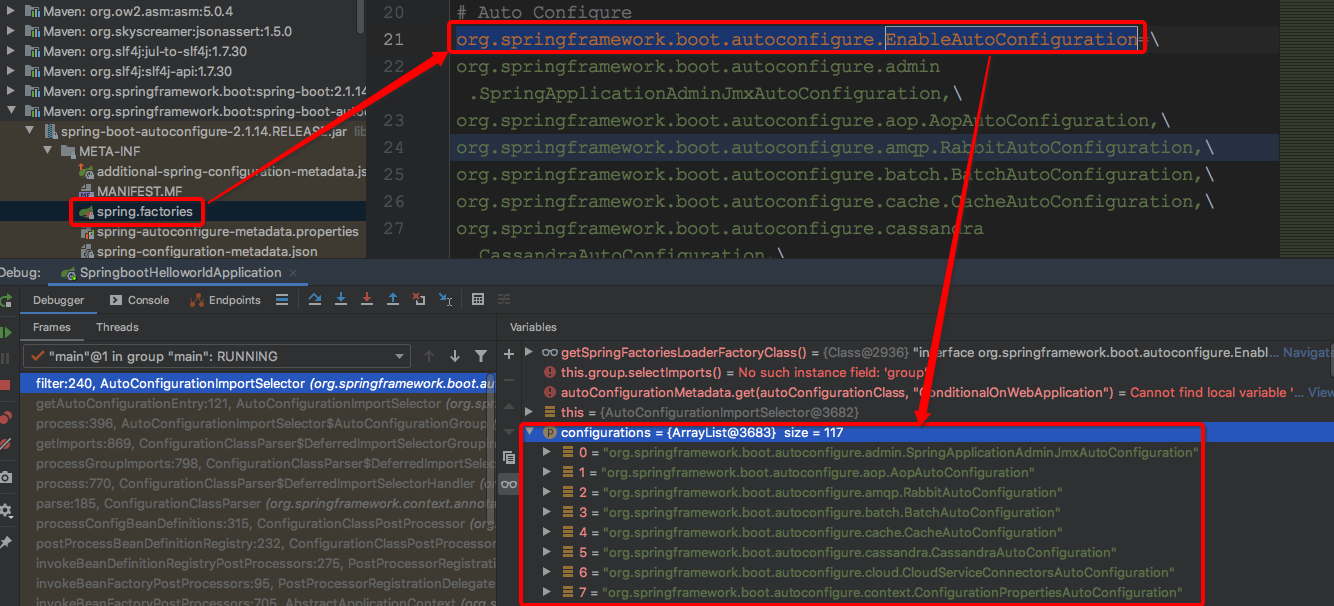
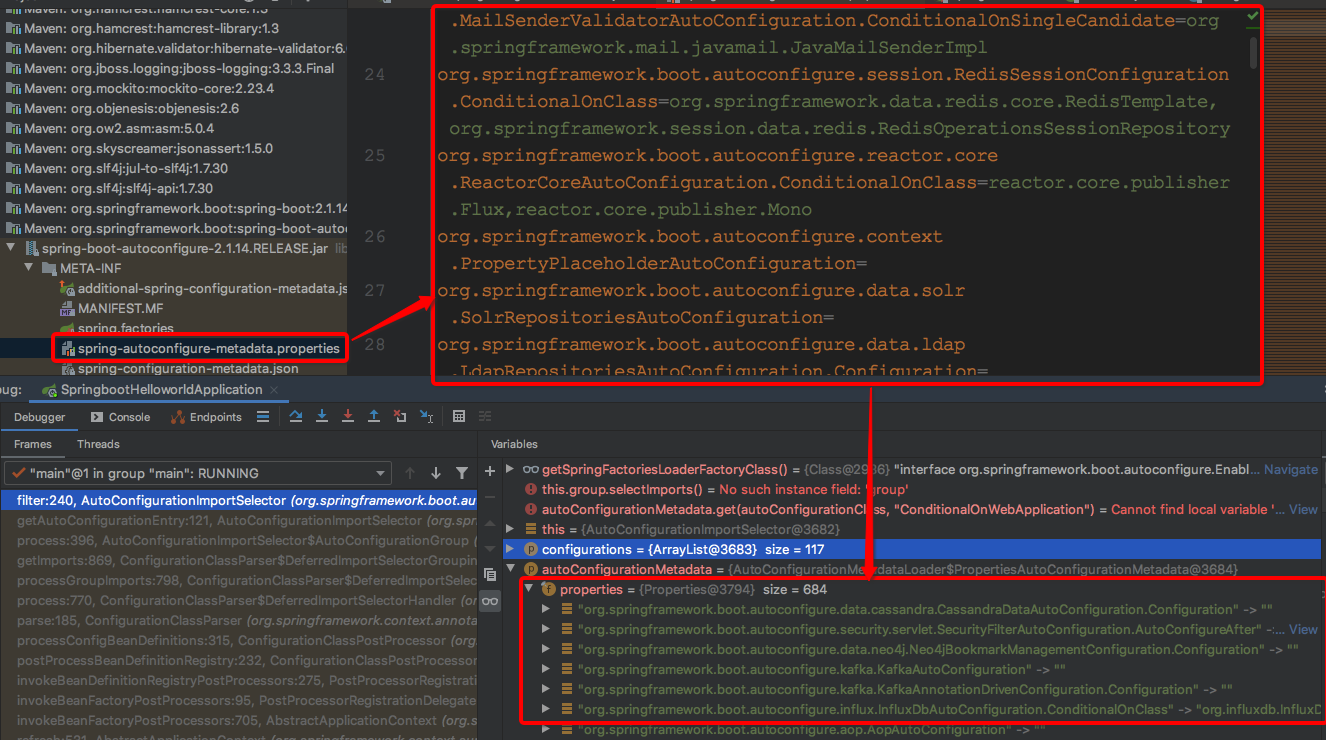
1:接口
执行这个自动配置类过滤过程的顶层接口是org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter,源码如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface AutoConfigurationImportFilter {
boolean[] match(String[] autoConfigurationClasses, AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata);
}
从注解@FunctionalInterface可以看出这是一个函数接口,按照函数接口的定义是只有一个抽象方法(注意不是一个方法,还可以有default方法)的接口,这里的方法是match(autoConfigurationClass, authConfigurationMetadata),第一个参数是需要判定的自动配置类的全限定名称的数组。第二个参数是待判断的自动配置类上的注解的元信息对象,主要是注解信息,用来判断配置类是否需要引入。先在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filterdebug看下:
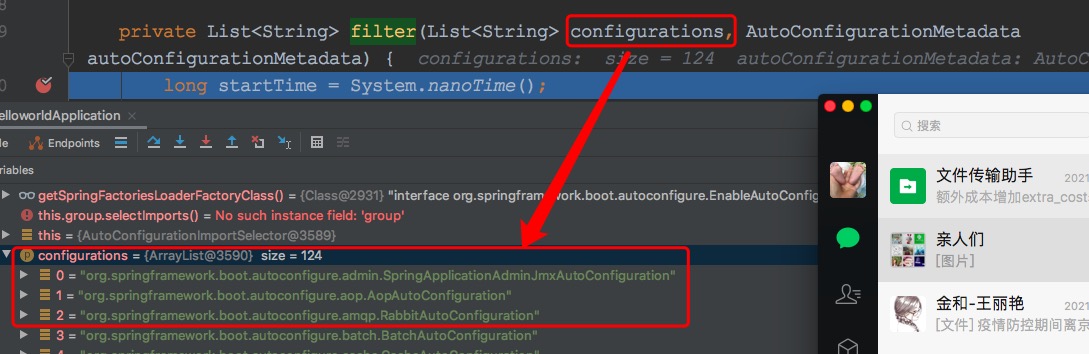
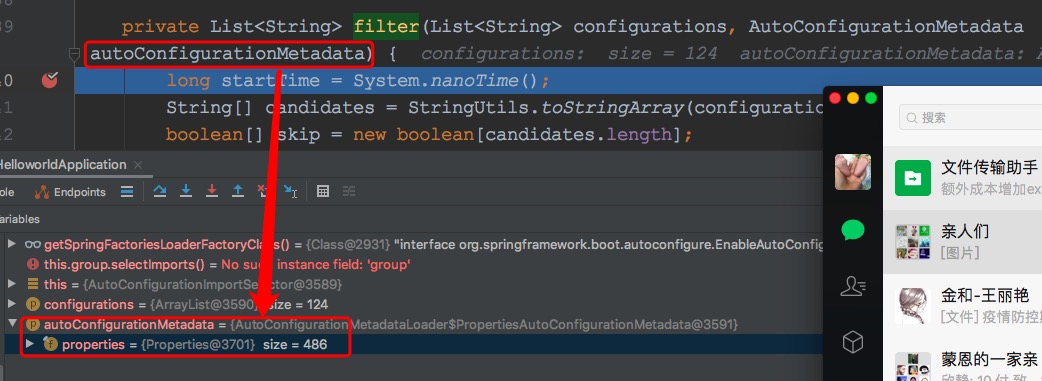
最后的返回值是一个布尔类型的数组,这里是和autoConfigurationClasses一一对应的,对应位置是true则代表对应的配置类需要加载,对应位置是false则代表对应的配置类不需要加载。接下来我们再看下AutoConfigurationImportFilter的类图:
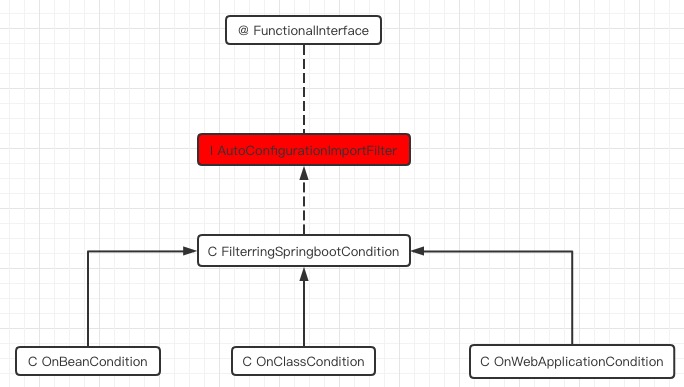
从类图中我们可以看到,AutoConfigurationImportFilter的直接子类是FilteringSpringbootCondition,通过这篇文章我们已经知道org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.FilteringSpringBootCondition同时也是SpringBootCondition的子类,而SpringBootCondition是对spring提供的Condition的扩展,因此FilteringSpringBootCondition就拥有了如下的两个能力:
1:spring原生的基于条件注解判断自动配置类是否需要加载,需要则加载,不需要则忽略
2:根据条件注解信息,同时判断一批自动配置类是否需要加载的能力(注意这里不会进行加载,加载过程要依赖于能力1)
可以看到一个是单个的判断,一个是批量的判断,可以认为只不过是多了一个for循环而已,因此spring设计放在一起,尽量复用可以复用的能力,减少代码量。
2:AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter
源码:
private List<String> filter(List<String> configurations, AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
// 转换自动配置类的List集合为String数组
String[] candidates = StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations);
// 存储最终的匹配结果,和candidates数组索引位置一一对应,true代表最终需要
// 自动引入,false代表不需要自动引入
boolean[] skip = new boolean[candidates.length];
boolean skipped = false;
// <AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter_1>见详细讲解
for (AutoConfigurationImportFilter filter : getAutoConfigurationImportFilters()) {
// <AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter_2>见详细讲解
invokeAwareMethods(filter);
// <AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter_3>见详细讲解
boolean[] match = filter.match(candidates, autoConfigurationMetadata);
// 循环当前的自动引入过滤器过滤结果,并记录过滤结果,用于后续逻辑过滤使用
for (int i = 0; i < match.length; i++) {
if (!match[i]) {
skip[i] = true;
candidates[i] = null;
skipped = true;
}
}
}
// 当没有需要过滤的自动配置类时,会进if直接返回,否则执行后续逻辑,通过布尔数组进行过滤
if (!skipped) {
return configurations;
}
// 存储过滤后需要自动配置的类
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(candidates.length);
for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
// 如果当前位置为fasle则说明不需要跳过,则添加到最终结果中
if (!skip[i]) {
result.add(candidates[i]);
}
}
// <AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter_4>见详细讲解
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
int numberFiltered = configurations.size() - result.size();
logger.trace("Filtered " + numberFiltered + " auto configuration class in "
+ TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startTime) + " ms");
}
// 返回结果,不知道为什么要再重新new一个
return new ArrayList<>(result);
}
<AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter_1>处的getAutoConfigurationImportFilters()是获取所有的自动配置导入过滤器,源码如下:
protected List<AutoConfigurationImportFilter> getAutoConfigurationImportFilters() {
// 从META-INF/spring.factories获取key为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter
// 的所有实现类,如下:
/*
# Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition
*/
// 可以看到配置的正是3个实现类
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AutoConfigurationImportFilter.class, this.beanClassLoader);
}
<AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter_2>处是回调AutoConfigurationImportFilter的相关Aware,源码不是很复杂,如下:
private void invokeAwareMethods(Object instance) {
if (instance instanceof Aware) {
if (instance instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) instance).setBeanClassLoader(this.beanClassLoader);
}
if (instance instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) instance).setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
}
if (instance instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) instance).setEnvironment(this.environment);
}
if (instance instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) instance).setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
}
}
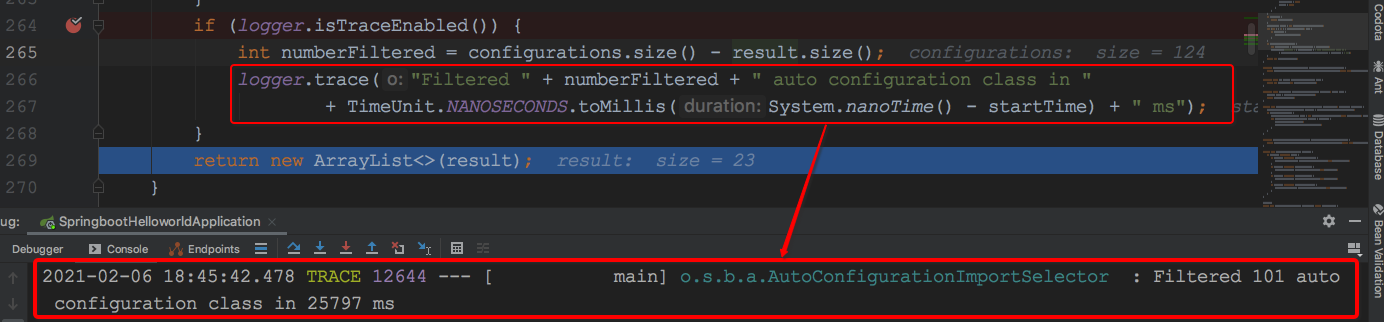
<AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter_3>处后续单起讲解。<AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter_4>处是打印自动配置导入过滤结果日志,修改application.properties文件增加logging.level.org.springframework=trace然后debug查看:
3:FilteringSpringBootCondition#match
在2:AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter部分的讲解中,过滤不需要加载的自动配置类的工作是通过OnClassCondition,OnWebApplicationCondition,OnBeanCondition三个条件类完成,调用的方法都是match,我们先来验证下。
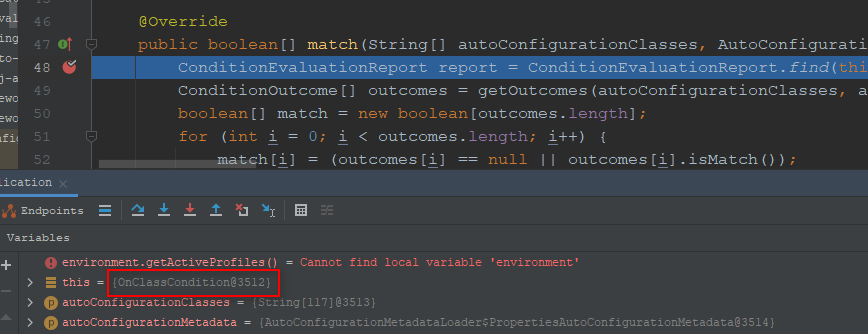
第1个条件类:
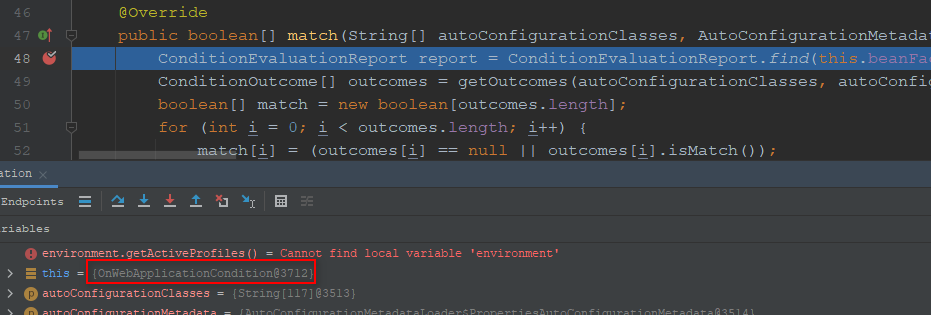
第2个条件类:
第3个条件类:
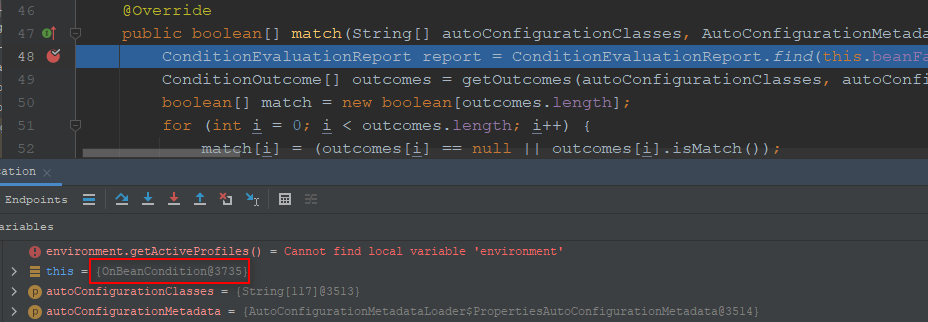
接着我们开始分析本部分的内容,即FilteringSpringbootCondition的骨架方法org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.FilteringSpringBootCondition#match,源码如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.FilteringSpringBootCondition#match
public boolean[] match(String[] autoConfigurationClasses, AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
// 创建负责记录某些信息的类,具体暂时不用深究,用到了再看
ConditionEvaluationReport report = ConditionEvaluationReport.find(this.beanFactory);
// <FilteringSpringBootCondition#match_1>
ConditionOutcome[] outcomes = getOutcomes(autoConfigurationClasses, autoConfigurationMetadata);
// 创建最终匹配结果集的数组
boolean[] match = new boolean[outcomes.length];
// 循环ConditionOutcome数组设置最终匹配的结果集
for (int i = 0; i < outcomes.length; i++) {
match[i] = (outcomes[i] == null || outcomes[i].isMatch());
// <FilteringSpringBootCondition#match_2>
// 如果是不匹配并且有ConditionOutCome信息则日志打印,
// 方便定位过滤了哪些自动配置类
if (!match[i] && outcomes[i] != null) {
logOutcome(autoConfigurationClasses[i], outcomes[i]);
if (report != null) {
report.recordConditionEvaluation(autoConfigurationClasses[i], this, outcomes[i]);
}
}
}
return match;
}
<FilteringSpringBootCondition#match_1>处与三个子类相关,因此需要在具体的子类中来分析该方法。<FilteringSpringBootCondition#match_2>,修改application.properties文件增加logging.level.org.springframework=trace然后debug查看:
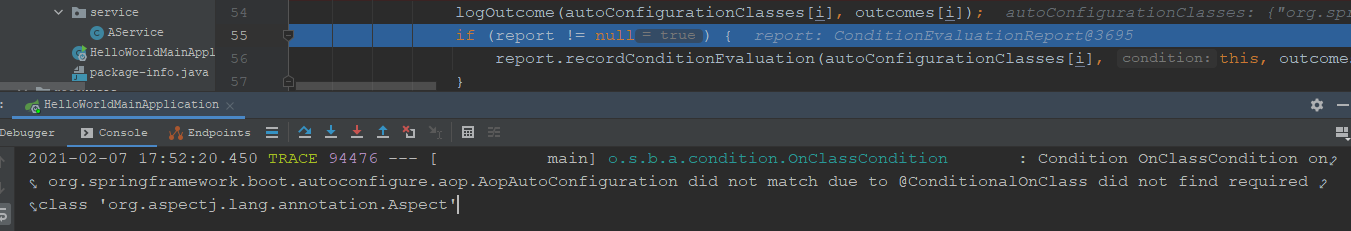
下面我们开始通过具体的子类OnClassCondition来开始吧!
4:OnClassCondition
为了方便我们调试,先增加如下的条件变量:
位置org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.FilteringSpringBootCondition#match
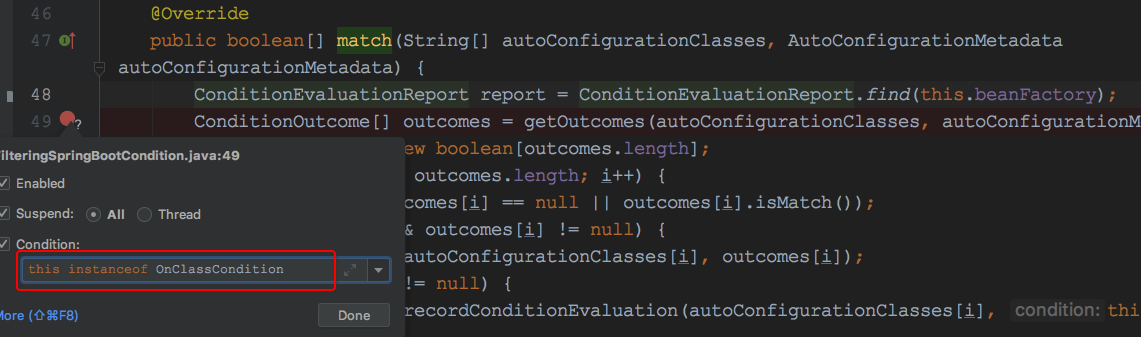
源码如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition#getOutcomes
protected final ConditionOutcome[] getOutcomes(String[] autoConfigurationClasses,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
// 用于将待过滤的自动配置类一分为二,具体是使用new Thread()创建
// 线程,另一半直接使用当前的主线程计算
// 这样做是为了提高自动配置类过滤的效率,因为自动配置类比较多
// 在2.1.14.RELEASE版本中有117个,在2.2.20版本中已经达到了124个
// 随着版本的不断的迭代会越来越多
int split = autoConfigurationClasses.length / 2;
// <OnClassCondition#getOutcomes_1>
// 创建线程执行过滤任务,后续详细分析,这行代码执行完创建的线程就开始执行过滤工作了
// 内部创建OutcomesResolver的子类ThreadedOutcomesResolver
OutcomesResolver firstHalfResolver = createOutcomesResolver(autoConfigurationClasses, 0, split,
autoConfigurationMetadata);
// 直接创建StandardOutcomesResolver对象用于执行过滤操作
OutcomesResolver secondHalfResolver = new StandardOutcomesResolver(autoConfigurationClasses, split,
autoConfigurationClasses.length, autoConfigurationMetadata, getBeanClassLoader());
// 解析输出结果数组,这里调用的是StandardOutcomesResolver的方法
ConditionOutcome[] secondHalf = secondHalfResolver.resolveOutcomes();
// <OnClassCondition#getOutcomes_2>
// 解析输出结果数组,这里调用的是ThreadedOutcomesResolver的方法
ConditionOutcome[] firstHalf = firstHalfResolver.resolveOutcomes();
// 创建结果数组,并使用System.arraycopy方法拷贝firstHalf和
// secondHalf到结果集中
ConditionOutcome[] outcomes = new ConditionOutcome[autoConfigurationClasses.length];
System.arraycopy(firstHalf, 0, outcomes, 0, firstHalf.length);
System.arraycopy(secondHalf, 0, outcomes, split, secondHalf.length);
// 返回结果集
return outcomes;
}
<OnClassCondition#getOutcomes_2>处源码如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition.ThreadedOutcomesResolver#resolveOutcomes
public ConditionOutcome[] resolveOutcomes() {
try {
// 这里强制让主线程即当前调用方法线程等待this.thread执行完毕,保证
// 创建的线程完成前一半自动配置类的工作,从而最终
// 设置this.outcomes
this.thread.join();
}
catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
// 返回最终的结果
return this.outcomes;
}
4.1:OutcomesResolver接口
该接口是一个内部接口,源码如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition.OutcomesResolver
private interface OutcomesResolver {
ConditionOutcome[] resolveOutcomes();
}
其有两个实现类,如下图:
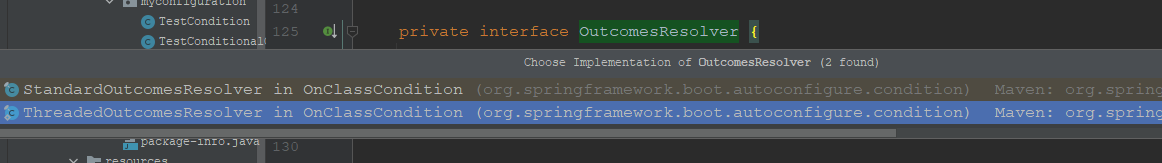
最终的过滤工作就是依赖于这两个类来完成的。
4.2:<OnClassCondition#getOutcomes_1>
回顾下代码位置:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition#getOutcomes
protected final ConditionOutcome[] getOutcomes(String[] autoConfigurationClasses,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
OutcomesResolver firstHalfResolver = createOutcomesResolver(autoConfigurationClasses, 0, split,
autoConfigurationMetadata);
}
createOutcomesResolver源码如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition#createOutcomesResolver
private OutcomesResolver createOutcomesResolver(String[] autoConfigurationClasses, int start, int end,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
// 创建StandardOutcomesResolver
OutcomesResolver outcomesResolver = new StandardOutcomesResolver(autoConfigurationClasses, start, end,
autoConfigurationMetadata, getBeanClassLoader());
try {
// <OnClassCondition#createOutcomesResolver_1>
// 创建ThreadedOutcomesResolver,并指定outcomesResolver参数
// 说明内部的自动配置类的过滤工作还是通过StandardOutcomesResolver
// 完成的
return new ThreadedOutcomesResolver(outcomesResolver);
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
return outcomesResolver;
}
}
<OnClassCondition#createOutcomesResolver_1>处源码如下:
private ThreadedOutcomesResolver(OutcomesResolver outcomesResolver) {
// 创建线程,并调用outcomesResolver(StandardOutcomesResolver)
// 的resolveOutcomes方法完成自动配置类的过滤
this.thread = new Thread(() -> this.outcomes = outcomesResolver.resolveOutcomes());
// 启动线程
this.thread.start();
}
从以上可以看到,最终自动配置类的过滤工作都是通过类org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition.StandardOutcomesResolver来完成的,那么我们接下来就重点分析这个类。
4.3:StandardOutcomesResolver
4.3.1:构造函数
源码:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition.StandardOutcomesResolver#StandardOutcomesResolver
private StandardOutcomesResolver(String[] autoConfigurationClasses, int start, int end,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata, ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
// 需要过滤的自动配置类class名称集合
this.autoConfigurationClasses = autoConfigurationClasses;
// 要过滤this.autoConfigurationClasses的开始位置
this.start = start;
// 要过滤this.autoConfigurationClasses的结束位置
this.end = end;
// <StandardOutcomesResolver#StandardOutcomesResolver_1>
// 自动配置类和条件注解组合的信息类,即每个配置类的每个
// 条件注解中设置的信息
this.autoConfigurationMetadata = autoConfigurationMetadata;
// 设置类加载器
this.beanClassLoader = beanClassLoader;
}
<StandardOutcomesResolver#StandardOutcomesResolver_1>处autoConfigurationMetadata存储的是每个自动配置类和条件注解组合对应的值信息,我们以WebMvcAutoConfiguration为例,先看下WebMvcAutoConfiguration源码:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {}
因为我们这里分析的是OnClassCondition的条件类,那么我们就以ConditionalOnClass条件注解类为例,来看下存储的信息,如下图:
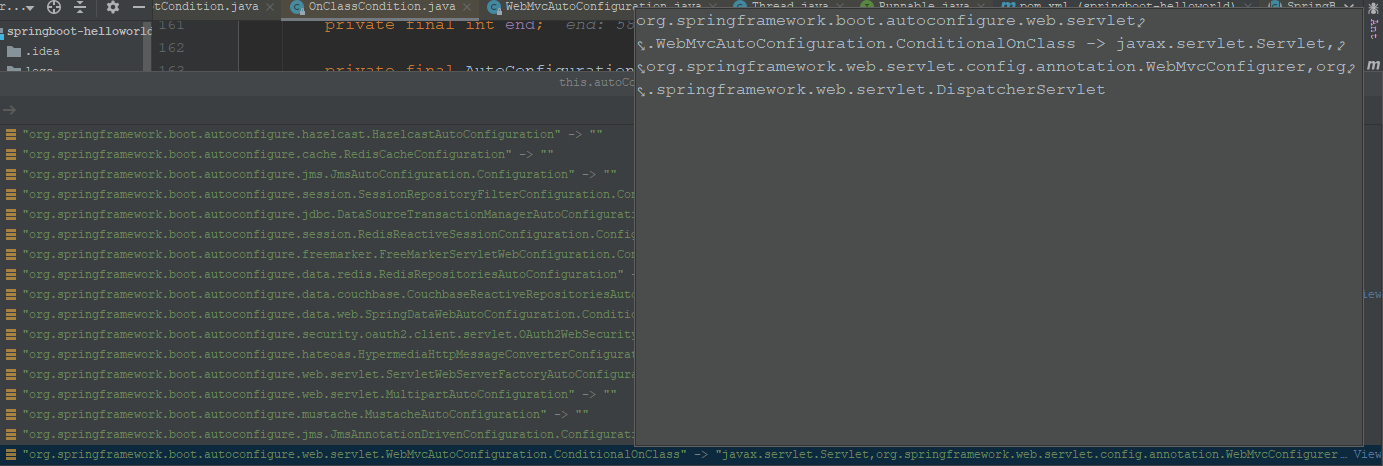
可以看到其格式是key:条件类全限定名+注解名,value:注解设置的值信息。
从前面的分析可以看到不管是使用ThreadedOutcomesResolver还是StandardOutcomesResolver都是使用的后者的resolveOutcomes方法来过滤自动配置类的,因此,我们只要分析清楚这个点流程基本上也就通了,下面开始分析。
4.3.2:StandardOutcomesResolver#resolveOutcomes
源码如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition.StandardOutcomesResolver#resolveOutcomes
public ConditionOutcome[] resolveOutcomes() {
return getOutcomes(this.autoConfigurationClasses, this.start, this.end, this.autoConfigurationMetadata);
}
继续:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition.StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcomes
private ConditionOutcome[] getOutcomes(String[] autoConfigurationClasses, int start, int end,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
// 根据end和start的差值大小创建ConditionOutcome结果数组
ConditionOutcome[] outcomes = new ConditionOutcome[end - start];
// 依次处理每个待过滤的自动配置类
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
// 获取当前自动配置类的全限定名,如
// org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration
String autoConfigurationClass = autoConfigurationClasses[i];
// 不为空则继续处理
if (autoConfigurationClass != null) {
// <StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcomes_1>
String candidates = autoConfigurationMetadata.get(autoConfigurationClass, "ConditionalOnClass");
if (candidates != null) {
// <StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcomes_2>
// 根据候选的待检测class类名称获取ConditionOutcome
// 并放到结果数组的对应位置
outcomes[i - start] = getOutcome(candidates);
}
}
}
// 返回ConditionOutcome结果数组
return outcomes;
}
<StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcomes_1>获取在ConditionalOnClass注解上配置的要求存在的类,如org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration配置如下(省略其它注解):
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {}
则结果就是Servlet.class,DispatcherServlet.class,WebMvcConfigurer.class这三个class对应的类的全限定名,下面开始看源码:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.PropertiesAutoConfigurationMetadata#get(java.lang.String, java.lang.String)
public String get(String className, String key) {
return get(className, key, null);
}
假定当前的className是org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,key值就是传入的ConditionalOnClass,debug如下:
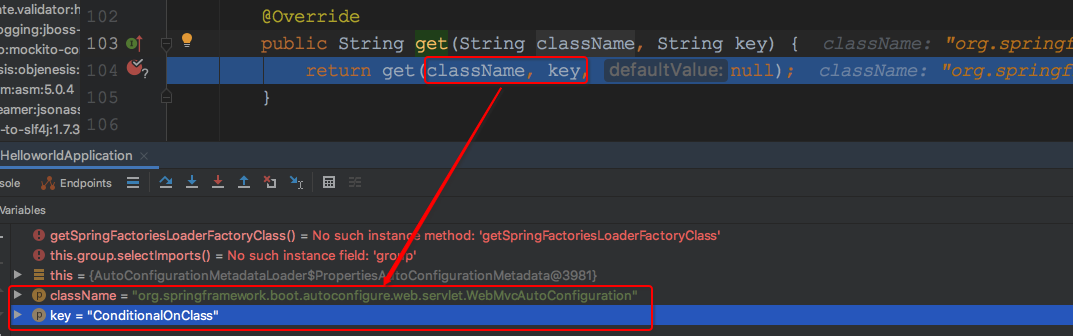
继续看get方法:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.PropertiesAutoConfigurationMetadata#get(java.lang.String, java.lang.String, java.lang.String)
public String get(String className, String key, String defaultValue) {
String value = this.properties.getProperty(className + "." + key);
return (value != null) ? value : defaultValue;
}
还是以WebMvcAutoConfiguration为例,如下:
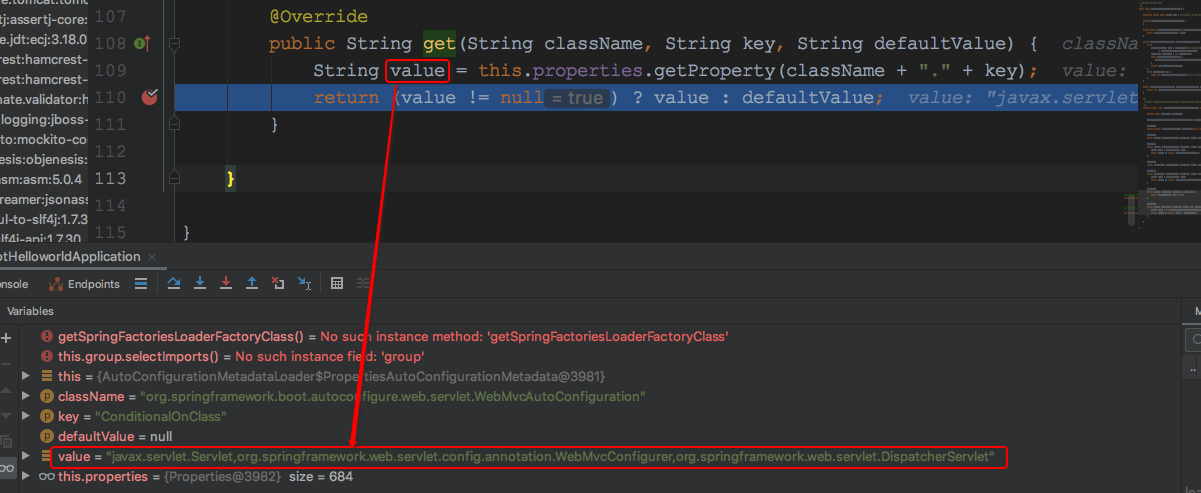
那么<StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcomes_1>处的结果就是javax.servlet.Servlet,org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer,org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet了,这个结果会被用作<StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcomes_2>的参数,源码如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition.StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcome(java.lang.String)
private ConditionOutcome getOutcome(String candidates) {
try {
// 待判断是否存在条件类只有一个情况
if (!candidates.contains(",")) {
return getOutcome(candidates, this.beanClassLoader);
}
// 包含逗号,说明待判断是否存在条件类有多个
for (String candidate : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(candidates)) {
// <StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcome_1>
// 获取过滤匹配结果
ConditionOutcome outcome = getOutcome(candidate, this.beanClassLoader);
// 这里一旦不为null则说明不匹配,就可以直接返回了
if (outcome != null) {
return outcome;
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// We'll get another chance later
}
return null;
}
<StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcome_1>处代码是执行最终的匹配工作,源码如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition.StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcome(className, classLoader)
private ConditionOutcome getOutcome(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) {
// <StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcome(className, classLoader)_1>
if (ClassNameFilter.MISSING.matches(className, classLoader)) {
// 如果是不匹配则直接携带有相关不匹配信息的ConditionOutcome对象
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnClass.class)
.didNotFind("required class").items(Style.QUOTE, className));
}
// 如果是到这里,则说明是匹配的,直接返回null
return null;
}
<StandardOutcomesResolver#getOutcome(className, classLoader)_1>处代码是使用ClassNameFilter.MISSING类的matches(className, classLoader)方法来判断指定的类是不是MISSING,如果是则返回true,否则返回false,源码如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.FilteringSpringBootCondition.ClassNameFilter
protected enum ClassNameFilter {
MISSING {
@Override
public boolean matches(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) {
return !isPresent(className, classLoader);
}
};
public abstract boolean matches(String className, ClassLoader classLoader);
}
可以看到其实是个枚举,个人觉得这样实现的代码还是挺优雅的,然后看下其中的isPresent(className, classLoader)方法,源码如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.FilteringSpringBootCondition.ClassNameFilter#isPresent
public static boolean isPresent(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 如果是传入的类加载器为null则获取默认的类加载器
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
try {
// <ClassNameFilter#isPresent_1>
forName(className, classLoader);
return true;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
return false;
}
}
<ClassNameFilter#isPresent_1>处源码:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.FilteringSpringBootCondition.ClassNameFilter#forName
private static Class<?> forName(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
if(classLoader != null) {
return classLoader.loadClass(className);
}
return Class.forName(className);
}
可以看到就是使用类加载器加载了,加载到则返回true,加载不到则返回false。
5:OnWebApplicationCondition
在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter设置如下条件变量,方便调试:
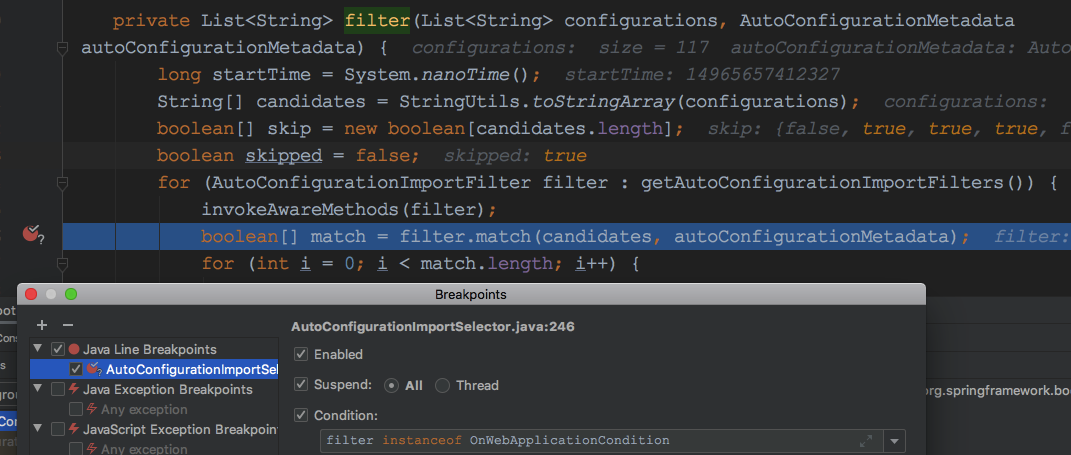
首先是执行FilterringSpringbootCondition的模板方法org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.FilteringSpringBootCondition#match如下:
public boolean[] match(String[] autoConfigurationClasses, AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
// 条件执行报告器
ConditionEvaluationReport report = ConditionEvaluationReport.find(this.beanFactory);
// <1>
// 调用具体类的方法实现,获取条件输出结果
// 这里调用的是OnWebApplicationCondition的实现类
ConditionOutcome[] outcomes = getOutcomes(autoConfigurationClasses, autoConfigurationMetadata);
// 定义自动配置类是否过滤的结果数组
boolean[] match = new boolean[outcomes.length];
// 循环条件输出结果,如果是条件输出为null或者是match属性为true则认为是匹配的
for (int i = 0; i < outcomes.length; i++) {
// 根据条件输出结果设置对应位置的匹配结果
match[i] = (outcomes[i] == null || outcomes[i].isMatch());
// 如果是是不匹配则日志记录匹配信息,以便知道哪些自动配置类被过滤了
if (!match[i] && outcomes[i] != null) {
// 日志记录
logOutcome(autoConfigurationClasses[i], outcomes[i]);
if (report != null) {
report.recordConditionEvaluation(autoConfigurationClasses[i], this, outcomes[i]);
}
}
}
// 返回匹配结果
return match;
}
其中<1>处代码是调用的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition#getOutcomes源码如下:
protected ConditionOutcome[] getOutcomes(String[] autoConfigurationClasses,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
// 创建条件输出的结果数组
ConditionOutcome[] outcomes = new ConditionOutcome[autoConfigurationClasses.length];
// 循环条件输出结果处理每个自动配置的过滤类
for (int i = 0; i < outcomes.length; i++) {
// 通过索引位置获取当前的自动配置了,并进行判断
String autoConfigurationClass = autoConfigurationClasses[i];
// 如果自动配置类不为null,则进行判断
if (autoConfigurationClass != null) {
// <OnWebApplicationCondition#getOutcomes_1>
// 调用getOutcome方法完成判断,并赋值到结果输出数组的
// 对应索引位置
outcomes[i] = getOutcome(
autoConfigurationMetadata.get(autoConfigurationClass, "ConditionalOnWebApplication"));
}
}
// 返回条件输出结果数组
return outcomes;
}
<OnWebApplicationCondition#getOutcomes_1>处代码我们还是以WebMvcAutoConfiguration为例,增加如下的条件变量:
方法autoConfigurationMetadata.get(autoConfigurationClass, "ConditionalOnWebApplication")结果如下图:
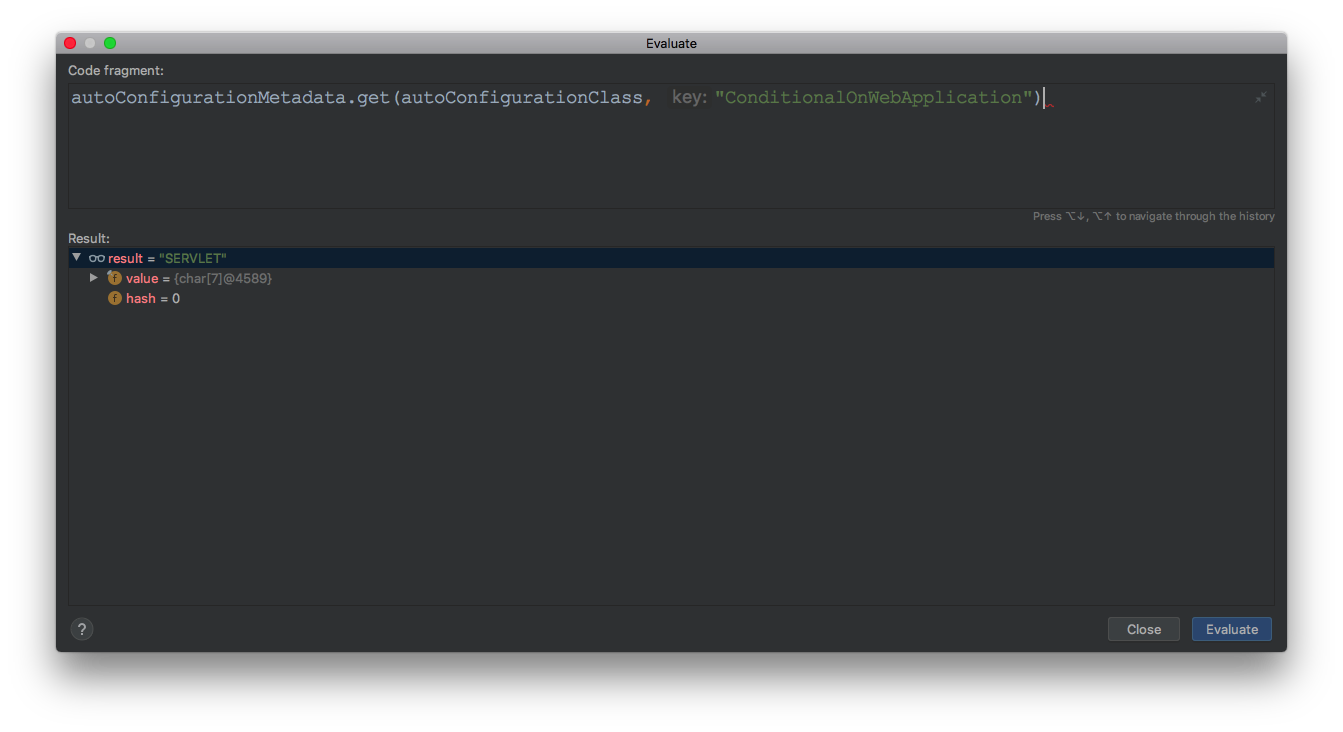
则方法getOutcome的参数就是SERVLET接着来看getOutcome方法:
private ConditionOutcome getOutcome(String type) {
// 如果是type为null,则直接返回null代表结果为匹配
if (type == null) {
return null;
}
// 使用构造器构造消息
ConditionMessage.Builder message = ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnWebApplication.class);
// 处理ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET类型的web应用程序,可以认为就是springmvc上下文环境
if (ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET.name().equals(type)) {
if (!ClassNameFilter.isPresent(SERVLET_WEB_APPLICATION_CLASS, getBeanClassLoader())) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.didNotFind("servlet web application classes").atAll());
}
}
// 处理ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.REACTIVE,暂时没用过
if (ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.REACTIVE.name().equals(type)) {
if (!ClassNameFilter.isPresent(REACTIVE_WEB_APPLICATION_CLASS, getBeanClassLoader())) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.didNotFind("reactive web application classes").atAll());
}
}
// 如果执行到这里则说明是任意的web类型org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type#ANY,其中
// 则判断servlet或者reactive二者存在其一即可SERVLET_WEB_APPLICATION_CLASS
// REACTIVE_WEB_APPLICATION_CLASS是二者用于判断的标记类
if (!ClassNameFilter.isPresent(SERVLET_WEB_APPLICATION_CLASS, getBeanClassLoader())
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(REACTIVE_WEB_APPLICATION_CLASS, getBeanClassLoader())) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.didNotFind("reactive or servlet web application classes").atAll());
}
// 返回null,认为匹配
return null;
}
注意到在上面的源码中都使用了org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.FilteringSpringBootCondition.ClassNameFilter#isPresent方法,该方法源码如下:
public static boolean isPresent(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
try {
forName(className, classLoader);
return true;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
return false;
}
}
看forName(className, classLoader);:
private static Class<?> forName(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
if (classLoader != null) {
return classLoader.loadClass(className);
}
return Class.forName(className);
}
其中的方法classLoader.loadClass(className);当加载的类在classpath下无法加载到时将会抛出java.lang.ClassNotFoundException该方法抛出该异常会被调用者通过catch (Throwable ex) {return false;}捕获,直接返回false,代表期望存在的类没有present,如下代码测试:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassLoader classLoader = Foo.class.getClassLoader();
String exitsClassFullName = "java.util.ArrayList";
String notExistClassFullName = "not.exits.class.name";
Class<?> exitsClass = classLoader.loadClass(exitsClassFullName);
System.out.println("exitsClass is: ");
System.out.println(exitsClass);
Class<?> notExistClass = classLoader.loadClass(notExistClassFullName);
System.out.println("notExistClass is: ");
System.out.println(notExistClass);
}
运行如下:
exitsClass is:
class java.util.ArrayList
notExistClass is:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: not.exits.class.name
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:381)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:424)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:349)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:357)
at Foo.main(Foo.java:14)
Process finished with exit code 1
6:OnBeanCondition
该条件类和ConditionalOnBean,ConditionalOnMIssingBean,ConditionalOnSingleCandidate等注解配合使用,我暂时还没有研究,等研究了再补充。
最后
以上就是执着海燕最近收集整理的关于springboot过滤不需要的自动配置类过程分析的全部内容,更多相关springboot过滤不需要内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复