(⊙o⊙)…,一部分注释的代码直接被吞了~汗~坑~有空再折腾
仅是学习算法时使用一下~(个人感觉不是个多好用的算法,毕竟写起来就很麻烦)
题目:
设某一机器由n个部件组成,每一种部件都可以从m个不同的供应商处购得。设w[i][j]是从供应商j处购得的部件i的重量,c[i][j]是相应的价格,给出总价格不超过d的最小重量机器设计。
算法设计:
对于给定的机器部件重量和机器部件价格,计算总价格不超过d的最小重量机器设计、
数据输入:
第一行有3个整数,n,m,d。接下来2n行,每行n个数,前n行是c,后n行是w
数据输出:
将计算出的最小重量,以及每个部件的供应商输出
其实自己的优先队列priority_queue的优先级设定是有个改进的空间的。
- 优先级的设定,当队列中有两个结点的重量是相同的时候,那么设定为,level大的优先级就更高一点,也就是说,更接近于叶子结点的那个结点更优先。目的就是为了更快的刷新出最小的重量,方便后面的剪枝。如果说没有两个结点重量相同,那就重量更小的优先。
就是:
物品1
物品2
物品3
假如,物品1已经入队了,且当前重量为3,剩余的最小重量之和为2+1 = 3(物品2和物品3中)总和为5
然后,假如物品2,已经入队了,且当前重量为1+3 =4(第一个物品选择的是1,第二个物品选择的是2),剩余最小重量和为1,总和为5。
也就是说,先执行的其实就是第二个方案。
这种优先级的设定,对于处于不同level的结点,还是有一定的优化作用,毕竟目的就是为了,最快,最先找到一个最小重量,便于后面的剪枝操作。
C++语言
 0
0

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n , m , d;
int MinWeight;
int MinValue;
int ** c
int ** w = NULL;
struct Node
{
};
//原始的优先级设定
//优化的优先级设定
bool operator <(Nodea,Node b)
{
}
Node *MinLeaf;
void MinWeightMachine()
{
}
int main()
{
}
using namespace std;
int n , m , d;
int MinWeight;
int MinValue;
int ** c
int ** w = NULL;
struct Node
{
};
//原始的优先级设定
//优化的优先级设定
bool operator <(Nodea,Node b)
{
}
Node *MinLeaf;
void MinWeightMachine()
{
}
int main()
{
}
测试案例:
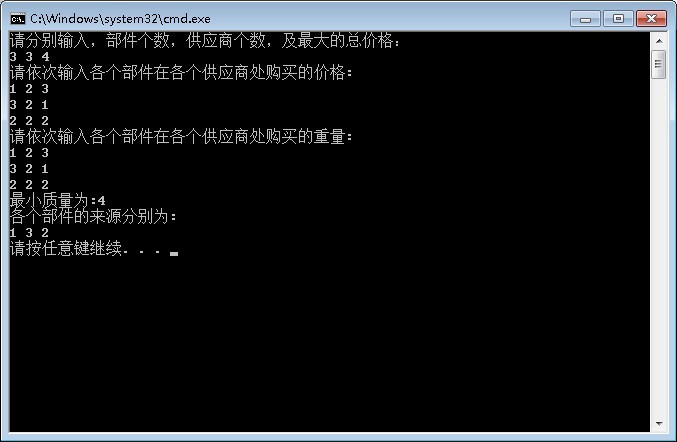
3 3 4
1 2 3
3 2 1
2 2 2
1 2 3
3 2 1
2 2 2
结果:1 3 2
3 3 4
1 2 3
3 2 1
2 2 2
1 2 3
3 2 1
2 2 2
结果:1 3 2
3 3 7
1 4 5
6 2 1
4 5 1
3 3 3
1 3 4
4 3 2
结果:
8
1 2 3
1 4 5
6 2 1
4 5 1
3 3 3
1 3 4
4 3 2
结果:
8
1 2 3
 0
0
关于STL中优先队列的使用问题,请看上一篇转载的博文
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_8a24b3a301019q23.html
最后
以上就是失眠魔镜最近收集整理的关于#分支限界法#最小机器重量设计问题(优先队列)的全部内容,更多相关#分支限界法#最小机器重量设计问题(优先队列)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复