一、http
1、含义:超文本传输协议
2、作用:定义了传输的格式
3、特点:
- 基于TCP/IP的高级协议
- 默认端口号:80
- 基于请求/响应模型的:一次请求对应一次响应
- 无状态的:每次请求之间相互独立,不能交互数据
4、历史:
- http1.0时代:每一次请求都要建立一次连接
- http1.1(2.0时代):基于tcp连接可以一次连接多次传输数据
二、http请求
请求过程:客户端发请求到服务器端
请求数据分为三部分:
1、请求行:请求数据的第一行 GET/HTTP/1.1
请求方式:GET/POST
特点:
GET:
- 请求参数在请求行中,在url后。(也就是地址栏)
- 请求的url长度有限制的
- 不太安全(在地址栏中会显示)
POST:
- 请求参数在请求体中
- 请求的url长度没有限制的
- 相对安全
2、请求头:客户端浏览器告诉服务器一些信息
常见的请求头:
User-Agent:浏览器告诉服务器,访问使用的浏览器版本信息可以在服务器端获取该头的信息,解决浏览器的兼容性问题
Referer:http://localhost/login.html告诉服务器,我(当前请求)从哪里来?
3、请求体:正文。
三、Request 继承体系
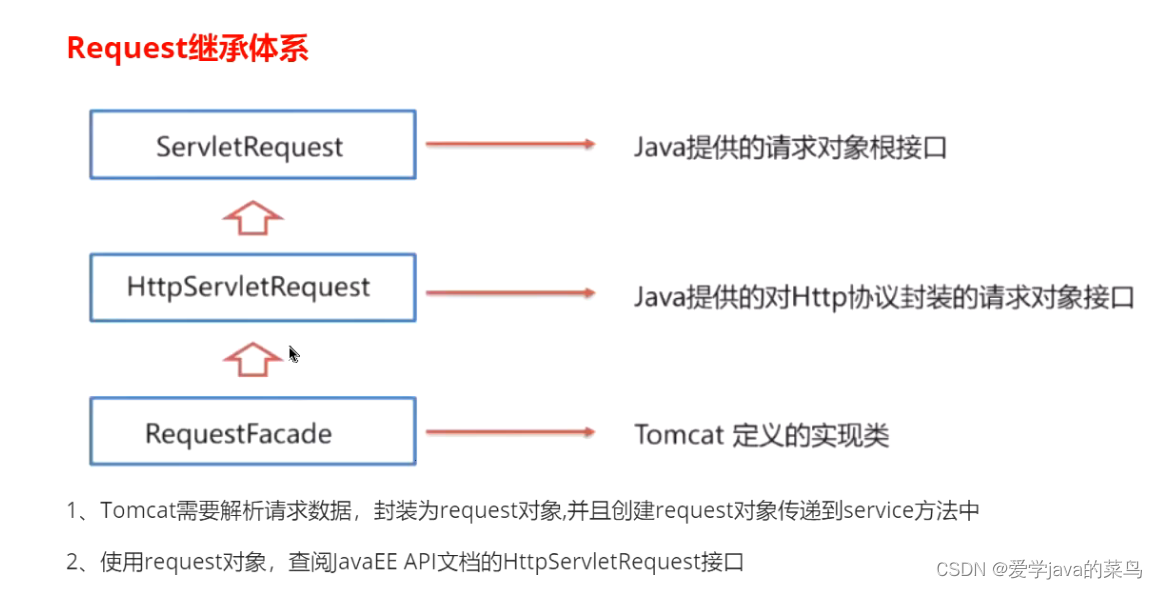
四、获取请求数据
1、获取请求行

URL:是Internet上资源的地址,可以定义为引用地址的字符串,用于指示资源的位置以及用于访问它的协议。
URI:标识逻辑或物理资源的字符序列,与URL类似,也是一串字符。通过使用位置,名称或两者来标识Internet上的资源;它允许统一识别资源。
2、获取请求头
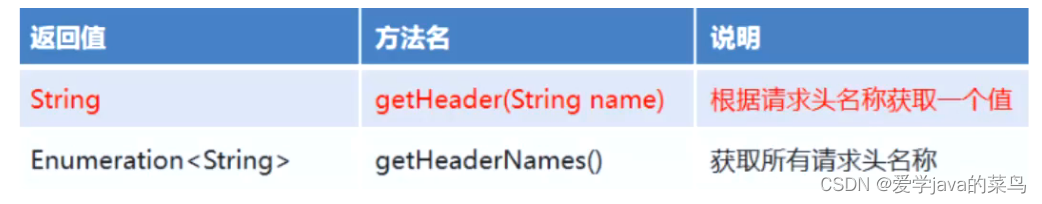
3、获取请求体

4、通用获取请求参数


五、快速入门
1、先创建好项目
2、在继承了HttpServlet的doPost方法中写如下内容(含义写在注释中)
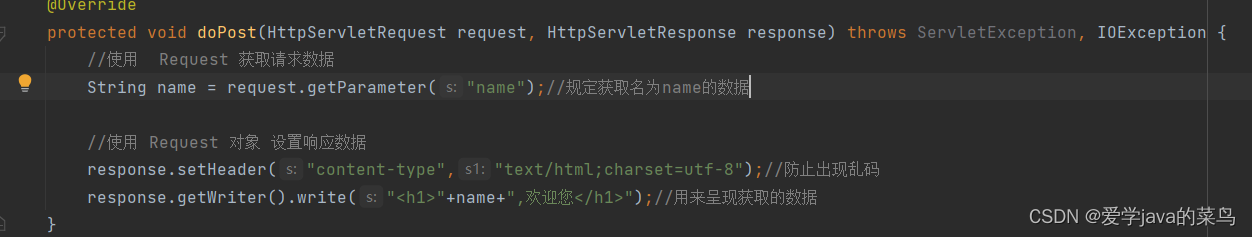
3、在jsp文件中写让用户填的数据

4、配置好项目后运行
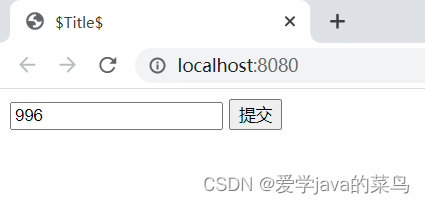
随便写个值,点击提交
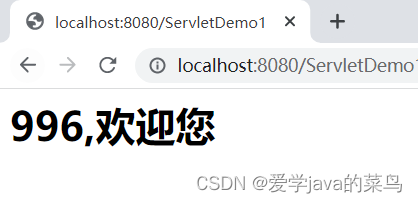
在doGet中运行doPost还可以换一中玩法
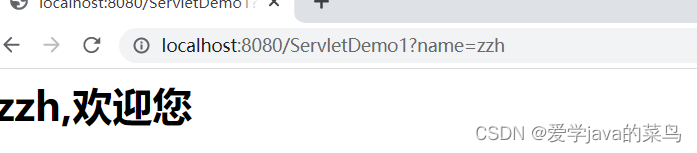
在后面加上?连接指定参数,由于我们让显示的数据是name,所以要给name一个值,如下
六、方法使用
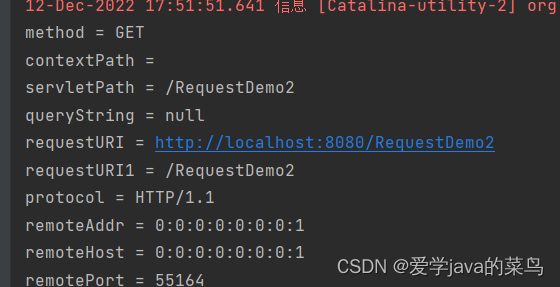
1、获取请求行
/获取请求方式 GET/POST
String method = request.getMethod();
System.out.println("method = " + method);
//获取虚拟路径
String contextPath = request.getContextPath();
System.out.println("contextPath = " + contextPath);
//获取servlet路径
String servletPath = request.getServletPath();
System.out.println("servletPath = " + servletPath);
//获取请求参数
String queryString = request.getQueryString();
System.out.println("queryString = " + queryString);
//获取请求资源定位符
StringBuffer requestURI = request.getRequestURL();
System.out.println("requestURI = " + requestURI);
//获取资源标识符
String requestURI1 = request.getRequestURI();
System.out.println("requestURI1 = " + requestURI1);
//获取版本协议
String protocol = request.getProtocol();
System.out.println("protocol = " + protocol);
//获取地址 主机号 端口号
String remoteAddr = request.getRemoteAddr();
System.out.println("remoteAddr = " + remoteAddr);
String remoteHost = request.getRemoteHost();
System.out.println("remoteHost = " + remoteHost);
int remotePort = request.getRemotePort();
System.out.println("remotePort = " + remotePort);访问地址
获取结果
2、获取请求头
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throw ServletException, IOException {
//获取请求头User-Agent:浏览器版本信息
String header = request.getHeader("User-Agent");
System.out.println("header = " + header);
//判断浏览器版本
if (header.contains("Chrome")){
System.out.println("这是谷歌");
请求访问
跳转查看控制台

3、获取请求体
编写HTML提交表单
<form action="/RequestDemo4" method="post">
<input type="text" name="usename" placeholder="用户名"><br>
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="密码"><br>
<input type="submit" value="注册">
</form>跳转
输入用户名密码提交并查看控制台

4、获取参数
前端页面
<form action="/RequestDemo6" method="post">
<input type="text" name="usename" placeholder="用户名"><br>
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="密码"><br>
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="1">游泳
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="2">爬山<br>
<input type="submit" value="注册">
</form>后端代码
//获取所有参数集合
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap();
//遍历集合
for (String key : parameterMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key+":");
String[] values = parameterMap.get(key);
for (String value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
//根据名称获取参数值
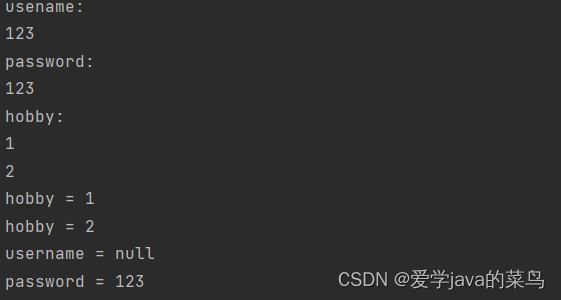
String[] hobbies = request.getParameterValues("hobby");
for (String hobby : hobbies) {
System.out.println("hobby = " + hobby);
}
//根据key 获取单个参数值
String username = request.getParameter("username");
System.out.println("username = " + username);
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("password = " + password);
结果
7、乱码问题
在调用get方法时,我们在表单中输入中文,获取到参数不会乱码,这是在tomcat8.5以上的版本已经修改了get方法编码为UTF-8.
在post方法中,输入中文仍然会乱码,这时候需要修改编码方式
在post方法的开头添加
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
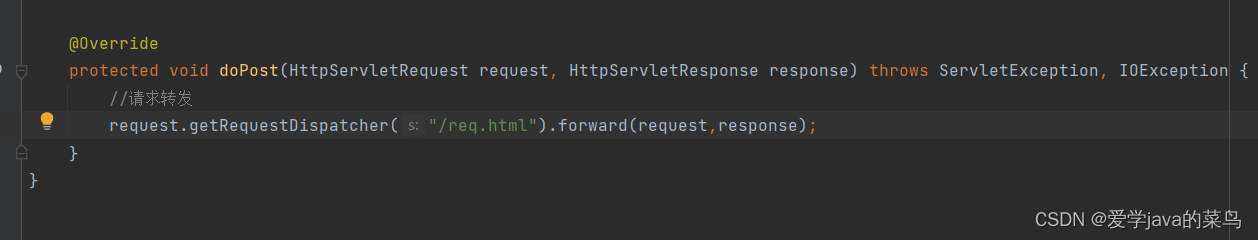
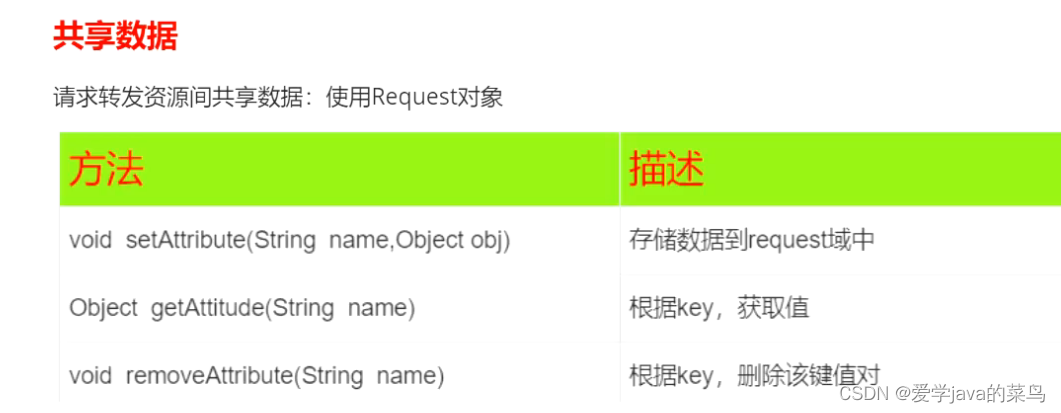
8、请求转发
在服务器内部进行资源跳转方式
request.getRequestDispatcher("路径").forward(request,response);
访问的时RequestDemo7的内容,跳转到了req.html上
最后
以上就是可爱黄蜂最近收集整理的关于javaWEB Request一、http二、http请求三、Request 继承体系 四、获取请求数据五、快速入门 六、方法使用 7、乱码问题8、请求转发的全部内容,更多相关javaWEB内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复