Android Accessibility是为了帮助残障人士更好使用手机开发出来一个模块,比如屏幕阅读器,手势等等,当然现在已经被玩坏了,各种外挂,比如微信抢红包的外挂,也是基于Accessibility写出来的。
Android developer有关于Accessibility的介绍(需要科学上网),我自己也基于这个有一篇笔记Android-Accessibility(Android 8.0以上)。
Accessibility Architecture
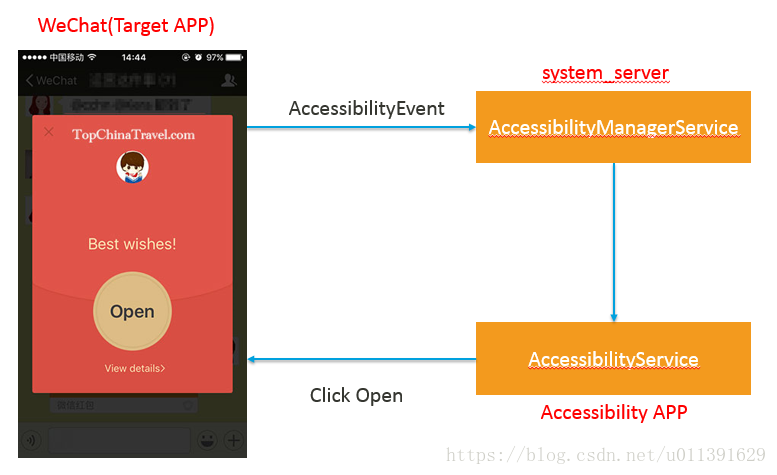
先拿一个具体的例子来看,这是一个抢红包的外挂,把WeChat称作Target APP,就是被监控的APP,当跳出来一个红包,触发了一个AccessibilityEvent,system_server中的AccessibilityManagerService将AccessibilityEvent分发给有AccessibilityService的APP,称为Accessibility APP,这个AccessibilityService受到这个AccessibilityEvent后,会找到这个页面的Open Button,模拟点击。(Target APP和Accessibility APP是我看别的博客这么取的)
Core Class
刚才举得例子是表象,那么程序内部,这个过程其实就是三个类之间的交互,当然实际不止这么简单啦,这个后面再讲,现在只要记住这三个是核心的类就好了。(以下都会用缩写代替)
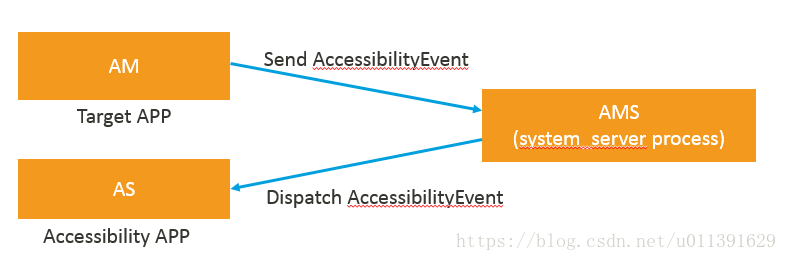
- AccessibilityManager(AM):Send AccessibilityEvent
- AccessibilityServiceManager(AMS):Dispatch
- AccessibilityService(AS):Response
File List
| File Name | File Path |
|---|---|
| View.java | /frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java |
| ViewRootImpl.java | /frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java |
| AccessibilityManager.java | /frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/accessibility/AccessibilityManager.java |
| AccessibilityManagerService.java | /frameworks/base/services/accessibility/java/com/android/server/accessibility/AccessibilityManagerService.java |
| AbstractAccessibilityServiceConnection.java | /frameworks/base/services/accessibility/java/com/android/server/accessibility/AbstractAccessibilityServiceConnection.java |
| AccessibilityServiceConnection.java | /frameworks/base/services/accessibility/java/com/android/server/accessibility/AccessibilityServiceConnection.java |
| AccessibilityManagerService.java | /frameworks/base/services/accessibility/java/com/android/server/accessibility/AccessibilityManagerService.java |
| AccessibilityService.java | /frameworks/base/core/java/android/accessibilityservice/AccessibilityService.java |
Accessibility Flow
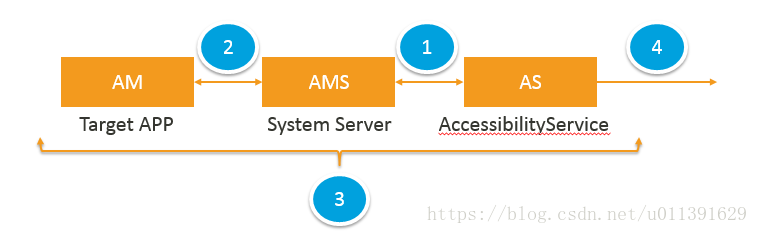
Accessibility Flow主要有下面几个Flow了:
- AMS绑定AS
- AM与AMS联系
- AccessibilityEvent Dispatch
- Response to AccessibilityEvent
AMS绑定AS
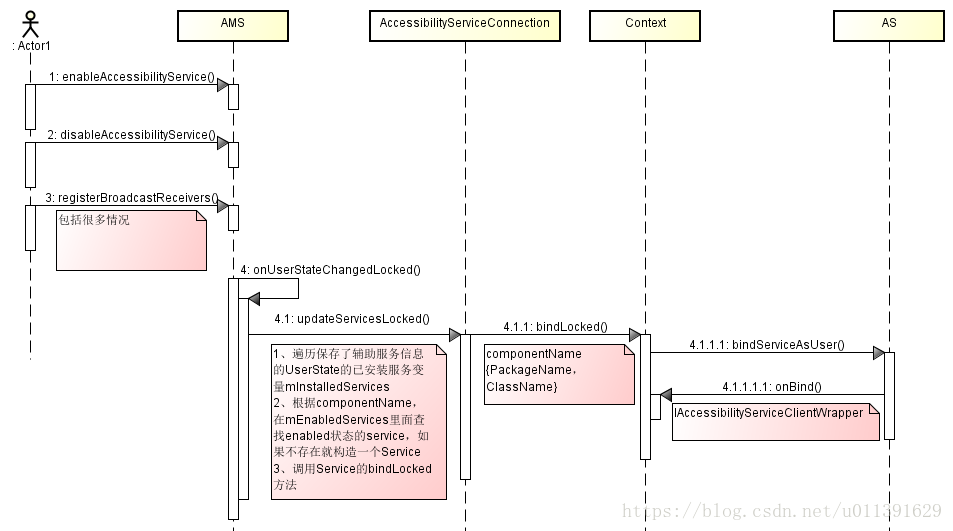
上图是AMS与AS联系的flow,下面一步一步的来说。
Step1:什么时候AMS会绑定AS?
- Settings->Accessibility->enable(
enableAccessibilityServiceLocked()) - Settings->Accessibility->disable(
disableAccessibilityServiceLocked()) - Some RegisterBroadcastReceivers (
registerBroadcastReceivers())onSomePackagesChanged()onPackageUpdateFinished()onHandleForceStop()onPackageRemoved()
- Others State Change
当用户在设置->无障碍里面选择了开启或关闭一个辅助功能,会导致一些系统状态会变化;Accessibility APP的安装状态会以BroadcastReceivers的方式会通知状态改变;还有其他的一些状态改变。这些变化最终会调用到AMS的onUserStateChangedLocked()方法。
AccessibilityManagerService.java – enableAccessibilityServiceLocked()
/**
2333 * Enables accessibility service specified by {@param componentName} for the {@param userId}.
2334 */
2335 private void enableAccessibilityServiceLocked(ComponentName componentName, int userId) {
2336 final SettingStringHelper setting =
2337 new SettingStringHelper(
2338 mContext.getContentResolver(),
2339 Settings.Secure.ENABLED_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICES,
2340 userId);
2341 setting.write(ComponentNameSet.add(setting.read(), componentName));
2342
2343 UserState userState = getUserStateLocked(userId);
2344 if (userState.mEnabledServices.add(componentName)) {
2345 onUserStateChangedLocked(userState);
2346 }
2347 }
AccessibilityManagerService.java – disableAccessibilityServiceLocked()
/**
2350 * Disables accessibility service specified by {@param componentName} for the {@param userId}.
2351 */
2352 private void disableAccessibilityServiceLocked(ComponentName componentName, int userId) {
2353 final SettingsStringUtil.SettingStringHelper setting =
2354 new SettingStringHelper(
2355 mContext.getContentResolver(),
2356 Settings.Secure.ENABLED_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICES,
2357 userId);
2358 setting.write(ComponentNameSet.remove(setting.read(), componentName));
2359
2360 UserState userState = getUserStateLocked(userId);
2361 if (userState.mEnabledServices.remove(componentName)) {
2362 onUserStateChangedLocked(userState);
2363 }
2364 }
AccessibilityManagerService.java – registerBroadcastReceivers()
private void registerBroadcastReceivers() {
324 PackageMonitor monitor = new PackageMonitor() {
325 @Override
326 public void onSomePackagesChanged() {
327 synchronized (mLock) {
328 // Only the profile parent can install accessibility services.
329 // Therefore we ignore packages from linked profiles.
330 if (getChangingUserId() != mCurrentUserId) {
331 return;
332 }
333 // We will update when the automation service dies.
334 UserState userState = getCurrentUserStateLocked();
335 // We have to reload the installed services since some services may
336 // have different attributes, resolve info (does not support equals),
337 // etc. Remove them then to force reload.
338 userState.mInstalledServices.clear();
339 if (readConfigurationForUserStateLocked(userState)) {
340 onUserStateChangedLocked(userState);
341 }
342 }
343 }
344
345 @Override
346 public void onPackageUpdateFinished(String packageName, int uid) {
347 // Unbind all services from this package, and then update the user state to
348 // re-bind new versions of them.
349 synchronized (mLock) {
350 final int userId = getChangingUserId();
351 if (userId != mCurrentUserId) {
352 return;
353 }
354 UserState userState = getUserStateLocked(userId);
355 boolean unboundAService = false;
356 for (int i = userState.mBoundServices.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
357 AccessibilityServiceConnection boundService =
358 userState.mBoundServices.get(i);
359 String servicePkg = boundService.mComponentName.getPackageName();
360 if (servicePkg.equals(packageName)) {
361 boundService.unbindLocked();
362 unboundAService = true;
363 }
364 }
365 if (unboundAService) {
366 onUserStateChangedLocked(userState);
367 }
368 }
369 }
370
371 @Override
372 public void onPackageRemoved(String packageName, int uid) {
373 synchronized (mLock) {
374 final int userId = getChangingUserId();
375 // Only the profile parent can install accessibility services.
376 // Therefore we ignore packages from linked profiles.
377 if (userId != mCurrentUserId) {
378 return;
379 }
380 UserState userState = getUserStateLocked(userId);
381 Iterator<ComponentName> it = userState.mEnabledServices.iterator();
382 while (it.hasNext()) {
383 ComponentName comp = it.next();
384 String compPkg = comp.getPackageName();
385 if (compPkg.equals(packageName)) {
386 it.remove();
387 // Update the enabled services setting.
388 persistComponentNamesToSettingLocked(
389 Settings.Secure.ENABLED_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICES,
390 userState.mEnabledServices, userId);
391 // Update the touch exploration granted services setting.
392 userState.mTouchExplorationGrantedServices.remove(comp);
393 persistComponentNamesToSettingLocked(
394 Settings.Secure.
395 TOUCH_EXPLORATION_GRANTED_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICES,
396 userState.mTouchExplorationGrantedServices, userId);
397 onUserStateChangedLocked(userState);
398 return;
399 }
400 }
401 }
402 }
403
404 @Override
405 public boolean onHandleForceStop(Intent intent, String[] packages,
406 int uid, boolean doit) {
407 synchronized (mLock) {
408 final int userId = getChangingUserId();
409 // Only the profile parent can install accessibility services.
410 // Therefore we ignore packages from linked profiles.
411 if (userId != mCurrentUserId) {
412 return false;
413 }
414 UserState userState = getUserStateLocked(userId);
415 Iterator<ComponentName> it = userState.mEnabledServices.iterator();
416 while (it.hasNext()) {
417 ComponentName comp = it.next();
418 String compPkg = comp.getPackageName();
419 for (String pkg : packages) {
420 if (compPkg.equals(pkg)) {
421 if (!doit) {
422 return true;
423 }
424 it.remove();
425 persistComponentNamesToSettingLocked(
426 Settings.Secure.ENABLED_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICES,
427 userState.mEnabledServices, userId);
428 onUserStateChangedLocked(userState);
429 }
430 }
431 }
432 return false;
433 }
434 }
435 };
436
437 // package changes
438 monitor.register(mContext, null, UserHandle.ALL, true);
439
440 // user change and unlock
441 IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
442 intentFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_SWITCHED);
443 intentFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED);
444 intentFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_REMOVED);
445 intentFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_PRESENT);
446 intentFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_SETTING_RESTORED);
447
448 mContext.registerReceiverAsUser(new BroadcastReceiver() {
449 @Override
450 public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
451 String action = intent.getAction();
452 if (Intent.ACTION_USER_SWITCHED.equals(action)) {
453 switchUser(intent.getIntExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER_HANDLE, 0));
454 } else if (Intent.ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED.equals(action)) {
455 unlockUser(intent.getIntExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER_HANDLE, 0));
456 } else if (Intent.ACTION_USER_REMOVED.equals(action)) {
457 removeUser(intent.getIntExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER_HANDLE, 0));
458 } else if (Intent.ACTION_USER_PRESENT.equals(action)) {
459 // We will update when the automation service dies.
460 synchronized (mLock) {
461 UserState userState = getCurrentUserStateLocked();
462 if (readConfigurationForUserStateLocked(userState)) {
463 onUserStateChangedLocked(userState);
464 }
465 }
466 } else if (Intent.ACTION_SETTING_RESTORED.equals(action)) {
467 final String which = intent.getStringExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SETTING_NAME);
468 if (Settings.Secure.ENABLED_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICES.equals(which)) {
469 synchronized (mLock) {
470 restoreEnabledAccessibilityServicesLocked(
471 intent.getStringExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SETTING_PREVIOUS_VALUE),
472 intent.getStringExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SETTING_NEW_VALUE));
473 }
474 }
475 }
476 }
477 }, UserHandle.ALL, intentFilter, null, null);
478 }
这些状态的变化都会调用到AMS的onUserStateChangedLocked()。
在onUserStateChangedLocked()中,我们关注updateServicesLocked(userState)这个函数,其他的函数是一些特定状态的更新。
AccessibilityManagerService.java – onUserStateChangedLocked()
/**
1765 * Called when any property of the user state has changed.
1766 *
1767 * @param userState the new user state
1768 */
1769 private void onUserStateChangedLocked(UserState userState) {
1770 // TODO: Remove this hack
1771 mInitialized = true;
1772 updateLegacyCapabilitiesLocked(userState);
1773 updateServicesLocked(userState);
1774 updateAccessibilityShortcutLocked(userState);
1775 updateWindowsForAccessibilityCallbackLocked(userState);
1776 updateAccessibilityFocusBehaviorLocked(userState);
1777 updateFilterKeyEventsLocked(userState);
1778 updateTouchExplorationLocked(userState);
1779 updatePerformGesturesLocked(userState);
1780 updateDisplayDaltonizerLocked(userState);
1781 updateDisplayInversionLocked(userState);
1782 updateMagnificationLocked(userState);
1783 updateSoftKeyboardShowModeLocked(userState);
1784 scheduleUpdateFingerprintGestureHandling(userState);
1785 scheduleUpdateInputFilter(userState);
1786 scheduleUpdateClientsIfNeededLocked(userState);
1787 updateRelevantEventsLocked(userState);
1788 updateAccessibilityButtonTargetsLocked(userState);
1789 }
AccessibilityManagerService.java – updateServicesLocked(userState)
1541 private void updateServicesLocked(UserState userState) {
1542 Map<ComponentName, AccessibilityServiceConnection> componentNameToServiceMap =
1543 userState.mComponentNameToServiceMap;
1544 boolean isUnlockingOrUnlocked = LocalServices.getService(UserManagerInternal.class)
1545 .isUserUnlockingOrUnlocked(userState.mUserId);
1546
1547 for (int i = 0, count = userState.mInstalledServices.size(); i < count; i++) {
1548 AccessibilityServiceInfo installedService = userState.mInstalledServices.get(i);
1549 ComponentName componentName = ComponentName.unflattenFromString(
1550 installedService.getId());
1551
1552 AccessibilityServiceConnection service = componentNameToServiceMap.get(componentName);
1553
1554 // Ignore non-encryption-aware services until user is unlocked
1555 if (!isUnlockingOrUnlocked && !installedService.isDirectBootAware()) {
1556 Slog.d(LOG_TAG, "Ignoring non-encryption-aware service " + componentName);
1557 continue;
1558 }
1559
1560 // Wait for the binding if it is in process.
1561 if (userState.mBindingServices.contains(componentName)) {
1562 continue;
1563 }
1564 if (userState.mEnabledServices.contains(componentName)
1565 && !mUiAutomationManager.suppressingAccessibilityServicesLocked()) {
1566 if (service == null) {
1567 service = new AccessibilityServiceConnection(userState, mContext, componentName,
1568 installedService, sIdCounter++, mMainHandler, mLock, mSecurityPolicy,
1569 this, mWindowManagerService, mGlobalActionPerformer);
1570 } else if (userState.mBoundServices.contains(service)) {
1571 continue;
1572 }
1573 service.bindLocked();
1574 } else {
1575 if (service != null) {
1576 service.unbindLocked();
1577 }
1578 }
1579 }
1580
1581 final int count = userState.mBoundServices.size();
1582 mTempIntArray.clear();
1583 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
1584 final ResolveInfo resolveInfo =
1585 userState.mBoundServices.get(i).mAccessibilityServiceInfo.getResolveInfo();
1586 if (resolveInfo != null) {
1587 mTempIntArray.add(resolveInfo.serviceInfo.applicationInfo.uid);
1588 }
1589 }
1590 // Calling out with lock held, but to a lower-level service
1591 final AudioManagerInternal audioManager =
1592 LocalServices.getService(AudioManagerInternal.class);
1593 if (audioManager != null) {
1594 audioManager.setAccessibilityServiceUids(mTempIntArray);
1595 }
1596 updateAccessibilityEnabledSetting(userState);
1597 }
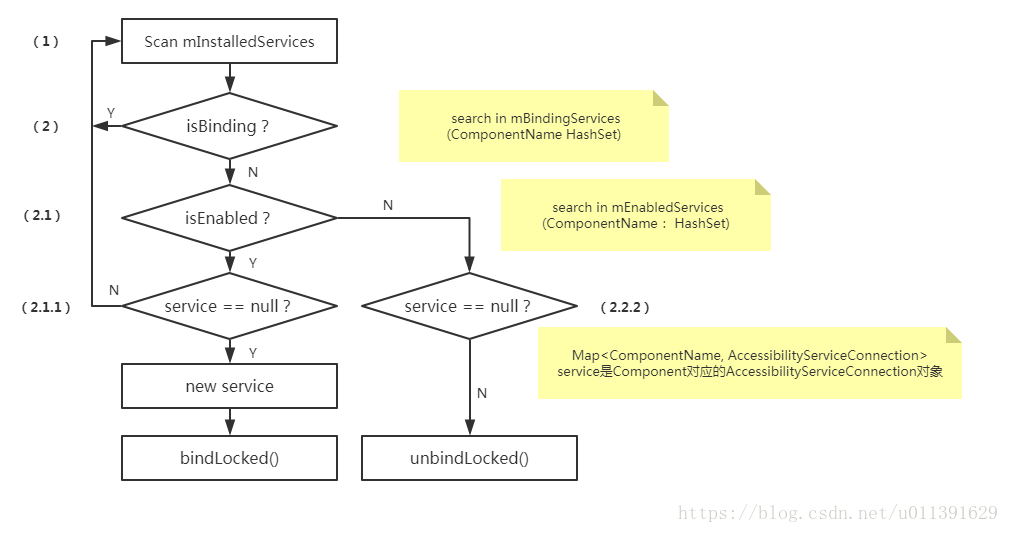
这个函数做了很多判断,我画了一个流程图,首先要知道在AMS中,有这么几个List,看名字就知道每个List是什么意思了。
mInstalledServices中,AccessibilityServiceInfo代表一个AccessibilityService的一些信息。
mEnabledServices中,ComponentName包含了className和packageName,ComponentName信息可以通过AccessibilityServiceInfo得到。
mComponentNameToServiceMap中,保存了ComponentName与AccessibilityServiceConnection的对应关系,每一个AccessibilityServiceConnection对应一个连接的AccessibilityService。
3650 public final ArrayList<AccessibilityServiceConnection> mBoundServices = new ArrayList<>();
3651
3652 public final Map<ComponentName, AccessibilityServiceConnection> mComponentNameToServiceMap =
3653 new HashMap<>();
3654
3655 public final List<AccessibilityServiceInfo> mInstalledServices =
3656 new ArrayList<>();
3657
3658 private final Set<ComponentName> mBindingServices = new HashSet<>();
3659
3660 public final Set<ComponentName> mEnabledServices = new HashSet<>();
(1)先遍历mInstalledServices这个List,它会先判断,这个AccessibilityService是否绑定了,如果绑定了,处理下一个;
(2)如果没有绑定了,会判断这个AccessibilityService是否处于enable状态,怎么判断是否处于enable状态呢?可以在mEnabledServices这个HashSet中查找。
(2.1)如果是处于enable状态,会在mComponentNameToServiceMap中通过ComponentName查找对应的AccessibilityServiceConnection是否为空(也就是流程图中的service)
(2.1.1)如果为空,会根据ComponentName,还有其他的一些信息new一个AccessibilityServiceConnection对象,然后调用里面的bindLocked()去绑定AccessibilityService。
(2.1.2)如果不为空,则处理下一个
(2.2)如果处于disable状态,会在mComponentNameToServiceMap中通过ComponentName查找对应的AccessibilityServiceConnection是否不为空(也就是流程图中的service)
(2.2.1)如果为空,则处理下一个
(2.2.2)如果不为空,会调用AccessibilityServiceConnection的unbindLocked()
Step2:绑定过程
AccessibilityServiceConnection.java – bindLocked()
91 public void bindLocked() {
92 UserState userState = mUserStateWeakReference.get();
93 if (userState == null) return;
94 final long identity = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
95 try {
96 int flags = Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE | Context.BIND_FOREGROUND_SERVICE_WHILE_AWAKE;
97 if (userState.mBindInstantServiceAllowed) {
98 flags |= Context.BIND_ALLOW_INSTANT;
99 }
100 if (mService == null && mContext.bindServiceAsUser(
101 mIntent, this, flags, new UserHandle(userState.mUserId))) {
102 userState.getBindingServicesLocked().add(mComponentName);
103 }
104 } finally {
105 Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(identity);
106 }
107 }
进而调用到Context中的bindServiceAsUser(),它传入了Intent信息,这个Intent包含了ComponentName等信息,进而绑定了AS。接下来的过程其实就相当于是跨进程的IPC(也就是Binder了)。AS会通过onBind(Intent intent)这个函数返回一个IAccessibilityServiceClientWrapper对象给AccessibilityServiceConnection,这个对象就是AS的本地Binder,AccessibilityServiceConnection通过这个本地Binder去和AS通信。
return new IAccessibilityServiceClientWrapper(this, getMainLooper(), new Callbacks();
AccessibilityServiceConnection会在onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder service)的IBinder参数中传入IAccessibilityServiceClientWrapper,然后通过IAccessibilityServiceClient.Stub.asInterface(service)生成IAccessibilityServiceClient类型代理对象mServiceInterface,这个代理对象包含了AS的Callbacks函数,AMS通过这个代理对象去调用AS中的方法。
141 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder service) {
142 synchronized (mLock) {
143 if (mService != service) {
144 if (mService != null) {
145 mService.unlinkToDeath(this, 0);
146 }
147 mService = service;
148 try {
149 mService.linkToDeath(this, 0);
150 } catch (RemoteException re) {
151 Slog.e(LOG_TAG, "Failed registering death link");
152 binderDied();
153 return;
154 }
155 }
156 mServiceInterface = IAccessibilityServiceClient.Stub.asInterface(service);
157 UserState userState = mUserStateWeakReference.get();
158 if (userState == null) return;
159 userState.addServiceLocked(this);
160 mSystemSupport.onClientChange(false);
161 // Initialize the service on the main handler after we're done setting up for
162 // the new configuration (for example, initializing the input filter).
163 mMainHandler.sendMessage(obtainMessage(
164 AccessibilityServiceConnection::initializeService, this));
165 }
166 }
AccessibilityService.java – Callbacks{}
AS中的Callbacks函数接口
373 /**
374 * Interface used by IAccessibilityServiceWrapper to call the service from its main thread.
375 * @hide
376 */
377 public interface Callbacks {
378 void onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event);
379 void onInterrupt();
380 void onServiceConnected();
381 void init(int connectionId, IBinder windowToken);
382 boolean onGesture(int gestureId);
383 boolean onKeyEvent(KeyEvent event);
384 void onMagnificationChanged(@NonNull Region region,
385 float scale, float centerX, float centerY);
386 void onSoftKeyboardShowModeChanged(int showMode);
387 void onPerformGestureResult(int sequence, boolean completedSuccessfully);
388 void onFingerprintCapturingGesturesChanged(boolean active);
389 void onFingerprintGesture(int gesture);
390 void onAccessibilityButtonClicked();
391 void onAccessibilityButtonAvailabilityChanged(boolean available);
392 }
下面的图可能清晰一点。
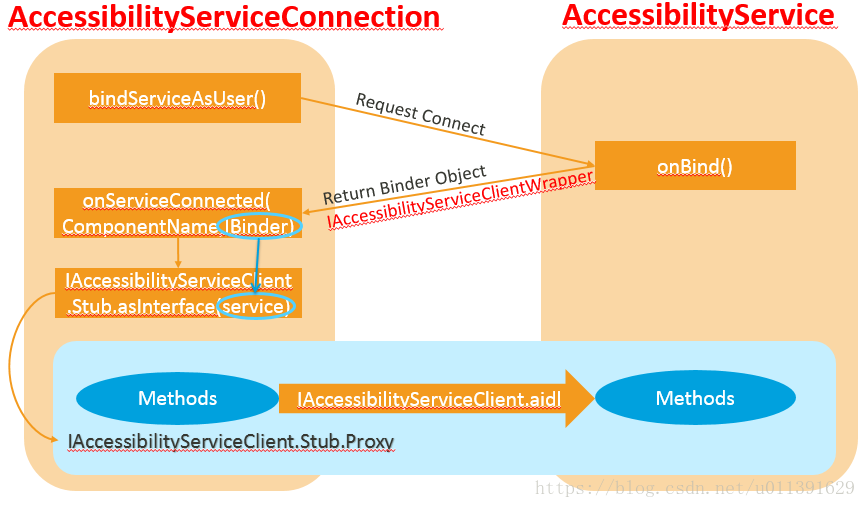
以上就是AMS和AS连接的过程。
AM与AMS联系
其实也是一个Binder的过程啦,AM通过IAccessibilityManager(AMS的本地Binder)与AMS跨进程通信。AMS通过IAccessibilityManagerClient(AM的本地Binder)与AM通信。
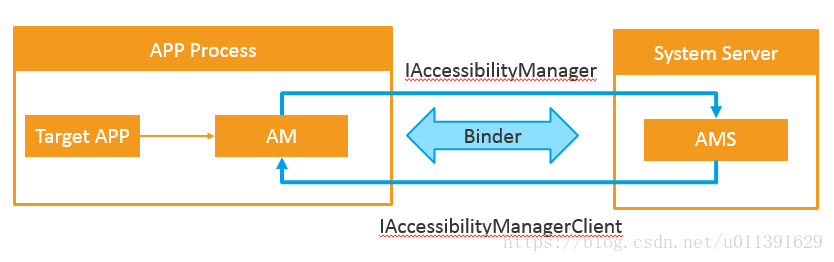
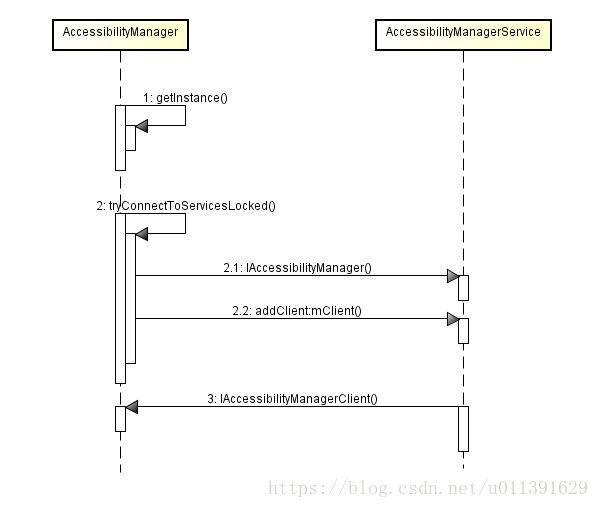
来看代码,当Target APP触发一个AccessibilityEvent(这个等会详细说),它会new一个AM的实例。
321 public static AccessibilityManager getInstance(Context context) {
322 synchronized (sInstanceSync) {
323 if (sInstance == null) {
324 final int userId;
325 if (Binder.getCallingUid() == Process.SYSTEM_UID
326 || context.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(
327 Manifest.permission.INTERACT_ACROSS_USERS)
328 == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED
329 || context.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(
330 Manifest.permission.INTERACT_ACROSS_USERS_FULL)
331 == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
332 userId = UserHandle.USER_CURRENT;
333 } else {
334 userId = context.getUserId();
335 }
336 sInstance = new AccessibilityManager(context, null, userId);
337 }
338 }
339 return sInstance;
340 }
AccessibilityManager的构造函数,然后会调用tryConnectToServiceLocked()函数。
AccessibilityManager.java – AccessibilityManager()
351 public AccessibilityManager(Context context, IAccessibilityManager service, int userId) {
352 // Constructor can't be chained because we can't create an instance of an inner class
353 // before calling another constructor.
354 mCallback = new MyCallback();
355 mHandler = new Handler(context.getMainLooper(), mCallback);
356 mUserId = userId;
357 synchronized (mLock) {
358 tryConnectToServiceLocked(service);
359 }
360 }
在tryConnectToServiceLocked()中,不仅会得到AMS的本地Binder(函数中的service),会通过addClient(mClient, mUserId)这个函数把自己的信息注册进去。
AccessibilityManager.java – tryConnectToServiceLocked()
1115 private void tryConnectToServiceLocked(IAccessibilityManager service) {
1116 if (service == null) {
1117 IBinder iBinder = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICE);
1118 if (iBinder == null) {
1119 return;
1120 }
1121 service = IAccessibilityManager.Stub.asInterface(iBinder);
1122 }
1123
1124 try {
1125 final long userStateAndRelevantEvents = service.addClient(mClient, mUserId);
1126 setStateLocked(IntPair.first(userStateAndRelevantEvents));
1127 mRelevantEventTypes = IntPair.second(userStateAndRelevantEvents);
1128 mService = service;
1129 } catch (RemoteException re) {
1130 Log.e(LOG_TAG, "AccessibilityManagerService is dead", re);
1131 }
1132 }
mClient是一个IAccessibilityManagerClient类型的本地Binder
276 private final IAccessibilityManagerClient.Stub mClient =
277 new IAccessibilityManagerClient.Stub()
下面的图也许更清楚一点,但总感觉哪里有点不对劲。
AccessibilityEvent Dispatch
整个过程从事件触发一直到响应,走过了很长的路,因此我把它分成三个部分:
- AccessibilityEvent Trigger
- AccessibilityEvent Dispatch
- AccessibilityEvent Response
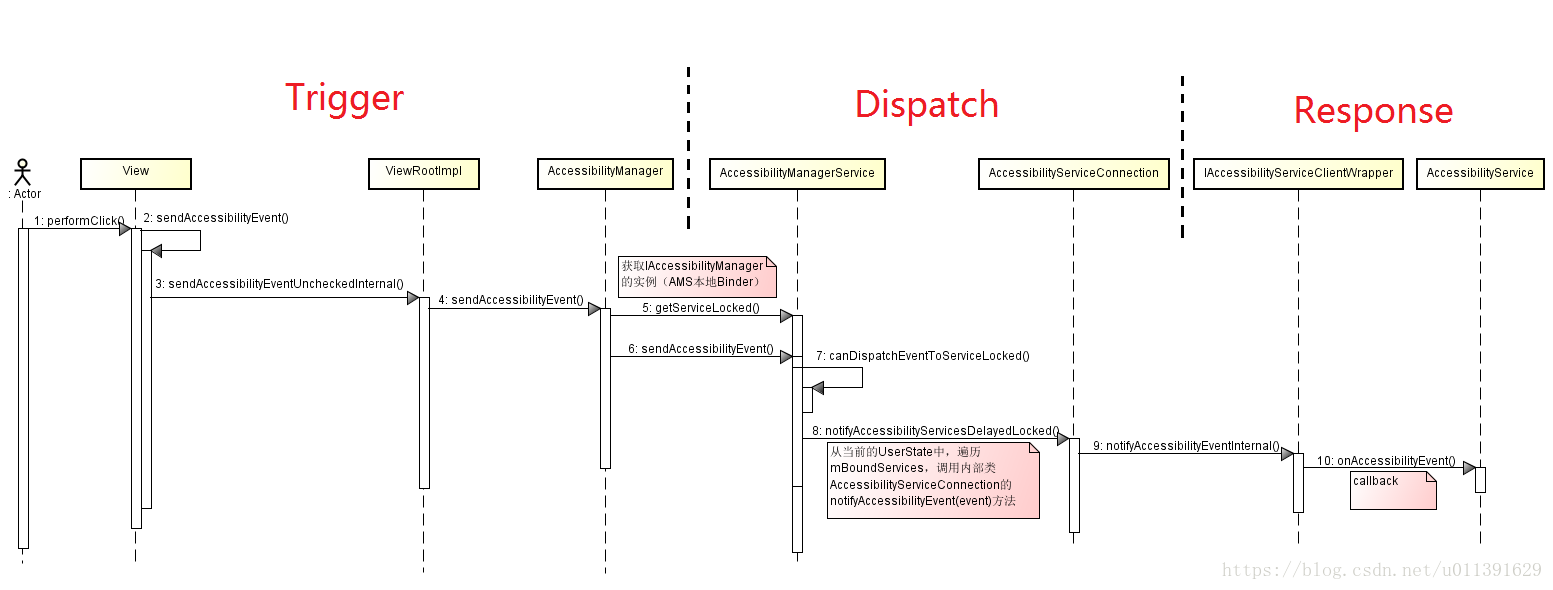
AccessibilityEvent Trigger
这一部分,是当有一个AccessibilityEvent触发后,怎么到的AMS里面。先来看看AccessibilityEvent哪些类型。这些类型包括很多种,比如点击,手势,焦点等等。

当用户的一些操作比如click,触发了Event(这时还不是AccessibilityEvent),会调用sendAccessibilityEvent()。
View.java – performClick()
6590 public boolean performClick() {
6591 // We still need to call this method to handle the cases where performClick() was called
6592 // externally, instead of through performClickInternal()
6593 notifyAutofillManagerOnClick();
6594
6595 final boolean result;
6596 final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
6597 if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {
6598 playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
6599 if (ViewDebugManager.DEBUG_TOUCH) {
6600 Log.d(VIEW_LOG_TAG, "(View)performClick, listener = " + li.mOnClickListener
6601 + ",this = " + this);
6602 }
6603 li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);
6604 result = true;
6605 } else {
6606 result = false;
6607 }
6608
6609 sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
6610
6611 notifyEnterOrExitForAutoFillIfNeeded(true);
6612
6613 return result;
6614 }
再来看sendAccessibilityEvent()里面做了什么,这个AccessibilityDelegate我不知道具体是什么意思,可看官网解释,这里可以暂时先不用管它,然后可以看到它调用了sendAccessibilityEventInternal()。
View.java – sendAccessibilityEvent()
7374 public void sendAccessibilityEvent(int eventType) {
7375 if (mAccessibilityDelegate != null) {
7376 mAccessibilityDelegate.sendAccessibilityEvent(this, eventType);
7377 } else {
7378 sendAccessibilityEventInternal(eventType);
7379 }
7380 }
在sendAccessibilityEventInternal()中,创建了一个AM的实例,在AM与AMS联系这一节讲到,创建实例的时候会与AMS通过Binder连接,然后这里会判断是否enable状态,再调用sendAccessibilityEventUnchecked()函数。
View.java – sendAccessibilityEventInternal()
7409 public void sendAccessibilityEventInternal(int eventType) {
7410 if (AccessibilityManager.getInstance(mContext).isEnabled()) {
7411 sendAccessibilityEventUnchecked(AccessibilityEvent.obtain(eventType));
7412 }
7413 }
在sendAccessibilityEventUnchecked()中又会调用sendAccessibilityEventUncheckedInternal()。
View.java – sendAccessibilityEventUnchecked()
7430 public void sendAccessibilityEventUnchecked(AccessibilityEvent event) {
7431 if (mAccessibilityDelegate != null) {
7432 mAccessibilityDelegate.sendAccessibilityEventUnchecked(this, event);
7433 } else {
7434 sendAccessibilityEventUncheckedInternal(event);
7435 }
7436 }
在sendAccessibilityEventUncheckedInternal()中,会调用onInitializeAccessibilityEvent()初始化一些event信息,比如className/packageName/source等,然后会调用getParent().requestSendAccessibilityEvent(this, event)将event分发给ParentView。
View.java – sendAccessibilityEventUncheckedInternal()
7445 public void sendAccessibilityEventUncheckedInternal(AccessibilityEvent event) {
7446 // Panes disappearing are relevant even if though the view is no longer visible.
7447 boolean isWindowStateChanged =
7448 (event.getEventType() == AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_WINDOW_STATE_CHANGED);
7449 boolean isWindowDisappearedEvent = isWindowStateChanged && ((event.getContentChangeTypes()
7450 & AccessibilityEvent.CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_PANE_DISAPPEARED) != 0);
7451 if (!isShown() && !isWindowDisappearedEvent) {
7452 return;
7453 }
7454 onInitializeAccessibilityEvent(event);
7455 // Only a subset of accessibility events populates text content.
7456 if ((event.getEventType() & POPULATING_ACCESSIBILITY_EVENT_TYPES) != 0) {
7457 dispatchPopulateAccessibilityEvent(event);
7458 }
7459 // In the beginning we called #isShown(), so we know that getParent() is not null.
7460 ViewParent parent = getParent();
7461 if (parent != null) {
7462 getParent().requestSendAccessibilityEvent(this, event);
7463 }
7464 }
这里不管ParentView是哪一个,最终会到View层次中的顶层,也就是ViewRootImpl的requestSendAccessibilityEvent()。这里,会对一些特殊Type的AccessibilityEvent做特殊处理,最终是调用到mAccessibilityManager.sendAccessibilityEvent(event),也就是到了AM。
ViewRootImpl.java – requestSendAccessibilityEvent()
7788 public boolean requestSendAccessibilityEvent(View child, AccessibilityEvent event) {
7789 if (mView == null || mStopped || mPausedForTransition) {
7790 return false;
7791 }
7792
7793 // Immediately flush pending content changed event (if any) to preserve event order
7794 if (event.getEventType() != AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED
7795 && mSendWindowContentChangedAccessibilityEvent != null
7796 && mSendWindowContentChangedAccessibilityEvent.mSource != null) {
7797 mSendWindowContentChangedAccessibilityEvent.removeCallbacksAndRun();
7798 }
7799
7800 // Intercept accessibility focus events fired by virtual nodes to keep
7801 // track of accessibility focus position in such nodes.
7802 final int eventType = event.getEventType();
7803 switch (eventType) {
7804 case AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUSED: {
7805 final long sourceNodeId = event.getSourceNodeId();
7806 final int accessibilityViewId = AccessibilityNodeInfo.getAccessibilityViewId(
7807 sourceNodeId);
7808 View source = mView.findViewByAccessibilityId(accessibilityViewId);
7809 if (source != null) {
7810 AccessibilityNodeProvider provider = source.getAccessibilityNodeProvider();
7811 if (provider != null) {
7812 final int virtualNodeId = AccessibilityNodeInfo.getVirtualDescendantId(
7813 sourceNodeId);
7814 final AccessibilityNodeInfo node;
7815 node = provider.createAccessibilityNodeInfo(virtualNodeId);
7816 setAccessibilityFocus(source, node);
7817 }
7818 }
7819 } break;
7820 case AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS_CLEARED: {
7821 final long sourceNodeId = event.getSourceNodeId();
7822 final int accessibilityViewId = AccessibilityNodeInfo.getAccessibilityViewId(
7823 sourceNodeId);
7824 View source = mView.findViewByAccessibilityId(accessibilityViewId);
7825 if (source != null) {
7826 AccessibilityNodeProvider provider = source.getAccessibilityNodeProvider();
7827 if (provider != null) {
7828 setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
7829 }
7830 }
7831 } break;
7832
7833
7834 case AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED: {
7835 handleWindowContentChangedEvent(event);
7836 } break;
7837 }
7838 mAccessibilityManager.sendAccessibilityEvent(event);
7839 return true;
7840 }
在AM和AMS的联系一节中讲到,AM会用AMS的本地BinderIAccessibilityManager去和AMS通信,在AM的sendAccessibilityEvent()可以看到定义了一个IAccessibilityManager类型的service,通过getServiceLocked()获取本地Binder,然后通过service.sendAccessibilityEvent(dispatchedEvent, userId)去调用AMS的sendAccessibilityEvent方法。到这里Trigger的部分就结束了,然后是AMS的分发过程。
AccessibilityManager.java – sendAccessibilityEvent()
456 public void sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) {
457 final IAccessibilityManager service;
458 final int userId;
459 final AccessibilityEvent dispatchedEvent;
460 synchronized (mLock) {
461 service = getServiceLocked();
462 if (service == null) {
463 return;
464 }
465 event.setEventTime(SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
466 if (mAccessibilityPolicy != null) {
467 dispatchedEvent = mAccessibilityPolicy.onAccessibilityEvent(event,
468 mIsEnabled, mRelevantEventTypes);
469 if (dispatchedEvent == null) {
470 return;
471 }
472 } else {
473 dispatchedEvent = event;
474 }
475 if (!isEnabled()) {
476 Looper myLooper = Looper.myLooper();
477 if (myLooper == Looper.getMainLooper()) {
478 throw new IllegalStateException(
479 "Accessibility off. Did you forget to check that?");
480 } else {
481 // If we're not running on the thread with the main looper, it's possible for
482 // the state of accessibility to change between checking isEnabled and
483 // calling this method. So just log the error rather than throwing the
484 // exception.
485 Log.e(LOG_TAG, "AccessibilityEvent sent with accessibility disabled");
486 return;
487 }
488 }
489 if ((dispatchedEvent.getEventType() & mRelevantEventTypes) == 0) {
490 if (DEBUG) {
491 Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Not dispatching irrelevant event: " + dispatchedEvent
492 + " that is not among "
493 + AccessibilityEvent.eventTypeToString(mRelevantEventTypes));
494 }
495 return;
496 }
497 userId = mUserId;
498 }
499 try {
500 // it is possible that this manager is in the same process as the service but
501 // client using it is called through Binder from another process. Example: MMS
502 // app adds a SMS notification and the NotificationManagerService calls this method
503 long identityToken = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
504 try {
505 service.sendAccessibilityEvent(dispatchedEvent, userId);
506 } finally {
507 Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(identityToken);
508 }
509 if (DEBUG) {
510 Log.i(LOG_TAG, dispatchedEvent + " sent");
511 }
512 } catch (RemoteException re) {
513 Log.e(LOG_TAG, "Error during sending " + dispatchedEvent + " ", re);
514 } finally {
515 if (event != dispatchedEvent) {
516 event.recycle();
517 }
518 dispatchedEvent.recycle();
519 }
520 }
AccessibilityEvent Dispatch
在AMS的sendAccessibilityEvent()中,会调用notifyAccessibilityServicesDelayedLocked()。
AccessibilityManagerService.java – sendAccessibilityEvent()
519 public void sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event, int userId) {
520 boolean dispatchEvent = false;
521
522 synchronized (mLock) {
523 if (event.getWindowId() ==
524 AccessibilityWindowInfo.PICTURE_IN_PICTURE_ACTION_REPLACER_WINDOW_ID) {
525 // The replacer window isn't shown to services. Move its events into the pip.
526 AccessibilityWindowInfo pip = mSecurityPolicy.getPictureInPictureWindow();
527 if (pip != null) {
528 int pipId = pip.getId();
529 event.setWindowId(pipId);
530 }
531 }
532
533 // We treat calls from a profile as if made by its parent as profiles
534 // share the accessibility state of the parent. The call below
535 // performs the current profile parent resolution.
536 final int resolvedUserId = mSecurityPolicy
537 .resolveCallingUserIdEnforcingPermissionsLocked(userId);
538
539 // Make sure the reported package is one the caller has access to.
540 event.setPackageName(mSecurityPolicy.resolveValidReportedPackageLocked(
541 event.getPackageName(), UserHandle.getCallingAppId(), resolvedUserId));
542
543 // This method does nothing for a background user.
544 if (resolvedUserId == mCurrentUserId) {
545 if (mSecurityPolicy.canDispatchAccessibilityEventLocked(event)) {
546 mSecurityPolicy.updateActiveAndAccessibilityFocusedWindowLocked(
547 event.getWindowId(), event.getSourceNodeId(),
548 event.getEventType(), event.getAction());
549 mSecurityPolicy.updateEventSourceLocked(event);
550 dispatchEvent = true;
551 }
552 if (mHasInputFilter && mInputFilter != null) {
553 mMainHandler.sendMessage(obtainMessage(
554 AccessibilityManagerService::sendAccessibilityEventToInputFilter,
555 this, AccessibilityEvent.obtain(event)));
556 }
557 }
558 }
559
560 if (dispatchEvent) {
561 // Make sure clients receiving this event will be able to get the
562 // current state of the windows as the window manager may be delaying
563 // the computation for performance reasons.
564 if (event.getEventType() == AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_WINDOW_STATE_CHANGED
565 && mWindowsForAccessibilityCallback != null) {
566 WindowManagerInternal wm = LocalServices.getService(WindowManagerInternal.class);
567 wm.computeWindowsForAccessibility();
568 }
569 synchronized (mLock) {
570 notifyAccessibilityServicesDelayedLocked(event, false);
571 notifyAccessibilityServicesDelayedLocked(event, true);
572 mUiAutomationManager.sendAccessibilityEventLocked(event);
573 }
574 }
575
576 if (OWN_PROCESS_ID != Binder.getCallingPid()) {
577 event.recycle();
578 }
579 }
在AMS绑定AS这一节讲到,AMS会维护一个绑定AS的List(mBoundServices),List中每一个AccessibilityServiceConnection对应一个绑定的AS,因此遍历mBoundServices,然后去到AccessibilityServiceConnection的notifyAccessibilityEvent()函数。
AccessibilityManagerService.java – notifyAccessibilityServicesDelayedLocked()
1378 private void notifyAccessibilityServicesDelayedLocked(AccessibilityEvent event,
1379 boolean isDefault) {
1380 try {
1381 UserState state = getCurrentUserStateLocked();
1382 for (int i = 0, count = state.mBoundServices.size(); i < count; i++) {
1383 AccessibilityServiceConnection service = state.mBoundServices.get(i);
1384
1385 if (service.mIsDefault == isDefault) {
1386 service.notifyAccessibilityEvent(event);
1387 }
1388 }
1389 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException oobe) {
1390 // An out of bounds exception can happen if services are going away
1391 // as the for loop is running. If that happens, just bail because
1392 // there are no more services to notify.
1393 }
1394 }
AccessibilityServiceConnection是继承AbstractAccessibilityServiceConnection的,这里notifyAccessibilityEvent()会发送一个message。
AbstractAccessibilityServiceConnection.java – notifyAccessibilityEvent()
967 public void notifyAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) {
968 synchronized (mLock) {
969 final int eventType = event.getEventType();
970
971 final boolean serviceWantsEvent = wantsEventLocked(event);
972 final boolean requiredForCacheConsistency = mUsesAccessibilityCache
973 && ((AccessibilityCache.CACHE_CRITICAL_EVENTS_MASK & eventType) != 0);
974 if (!serviceWantsEvent && !requiredForCacheConsistency) {
975 return;
976 }
977
978 // Make a copy since during dispatch it is possible the event to
979 // be modified to remove its source if the receiving service does
980 // not have permission to access the window content.
981 AccessibilityEvent newEvent = AccessibilityEvent.obtain(event);
982 Message message;
983 if ((mNotificationTimeout > 0)
984 && (eventType != AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED)) {
985 // Allow at most one pending event
986 final AccessibilityEvent oldEvent = mPendingEvents.get(eventType);
987 mPendingEvents.put(eventType, newEvent);
988 if (oldEvent != null) {
989 mEventDispatchHandler.removeMessages(eventType);
990 oldEvent.recycle();
991 }
992 message = mEventDispatchHandler.obtainMessage(eventType);
993 } else {
994 // Send all messages, bypassing mPendingEvents
995 message = mEventDispatchHandler.obtainMessage(eventType, newEvent);
996 }
997 message.arg1 = serviceWantsEvent ? 1 : 0;
998
999 mEventDispatchHandler.sendMessageDelayed(message, mNotificationTimeout);
1000 }
1001 }
在AbstractAccessibilityServiceConnection的构造函数中,有对消息的处理,它最终会调用notifyAccessibilityEventInternal()。
AbstractAccessibilityServiceConnection.java – AbstractAccessibilityServiceConnection()
241 public AbstractAccessibilityServiceConnection(Context context, ComponentName componentName,
242 AccessibilityServiceInfo accessibilityServiceInfo, int id, Handler mainHandler,
243 Object lock, SecurityPolicy securityPolicy, SystemSupport systemSupport,
244 WindowManagerInternal windowManagerInternal,
245 GlobalActionPerformer globalActionPerfomer) {
246 mContext = context;
247 mWindowManagerService = windowManagerInternal;
248 mId = id;
249 mComponentName = componentName;
250 mAccessibilityServiceInfo = accessibilityServiceInfo;
251 mLock = lock;
252 mSecurityPolicy = securityPolicy;
253 mGlobalActionPerformer = globalActionPerfomer;
254 mSystemSupport = systemSupport;
255 mInvocationHandler = new InvocationHandler(mainHandler.getLooper());
256 mEventDispatchHandler = new Handler(mainHandler.getLooper()) {
257 @Override
258 public void handleMessage(Message message) {
259 final int eventType = message.what;
260 AccessibilityEvent event = (AccessibilityEvent) message.obj;
261 boolean serviceWantsEvent = message.arg1 != 0;
262 notifyAccessibilityEventInternal(eventType, event, serviceWantsEvent);
263 }
264 };
265 setDynamicallyConfigurableProperties(accessibilityServiceInfo);
266 }
在notifyAccessibilityEventInternal()中,listener是AS的本地Binder(IAccessibilityServiceClient类型),最终是回调到了AS的onAccessibilityEvent()。到这里Dispatch的部分就结束了。
AbstractAccessibilityServiceConnection.java – notifyAccessibilityEventInternal()
1040 private void notifyAccessibilityEventInternal(
1041 int eventType,
1042 AccessibilityEvent event,
1043 boolean serviceWantsEvent) {
1044 IAccessibilityServiceClient listener;
1045
1046 synchronized (mLock) {
1047 listener = mServiceInterface;
1048
1049 // If the service died/was disabled while the message for dispatching
1050 // the accessibility event was propagating the listener may be null.
1051 if (listener == null) {
1052 return;
1053 }
1054
1055 // There are two ways we notify for events, throttled AND non-throttled. If we
1056 // are not throttling, then messages come with events, which we handle with
1057 // minimal fuss.
1058 if (event == null) {
1059 // We are throttling events, so we'll send the event for this type in
1060 // mPendingEvents as long as it it's null. It can only null due to a race
1061 // condition:
1062 //
1063 // 1) A binder thread calls notifyAccessibilityServiceDelayedLocked
1064 // which posts a message for dispatching an event and stores the event
1065 // in mPendingEvents.
1066 // 2) The message is pulled from the queue by the handler on the service
1067 // thread and this method is just about to acquire the lock.
1068 // 3) Another binder thread acquires the lock in notifyAccessibilityEvent
1069 // 4) notifyAccessibilityEvent recycles the event that this method was about
1070 // to process, replaces it with a new one, and posts a second message
1071 // 5) This method grabs the new event, processes it, and removes it from
1072 // mPendingEvents
1073 // 6) The second message dispatched in (4) arrives, but the event has been
1074 // remvoved in (5).
1075 event = mPendingEvents.get(eventType);
1076 if (event == null) {
1077 return;
1078 }
1079 mPendingEvents.remove(eventType);
1080 }
1081 if (mSecurityPolicy.canRetrieveWindowContentLocked(this)) {
1082 event.setConnectionId(mId);
1083 } else {
1084 event.setSource((View) null);
1085 }
1086 event.setSealed(true);
1087 }
1088
1089 try {
1090 listener.onAccessibilityEvent(event, serviceWantsEvent);
1091 if (DEBUG) {
1092 Slog.i(LOG_TAG, "Event " + event + " sent to " + listener);
1093 }
1094 } catch (RemoteException re) {
1095 Slog.e(LOG_TAG, "Error during sending " + event + " to " + listener, re);
1096 } finally {
1097 event.recycle();
1098 }
1099 }
Accessibility Response
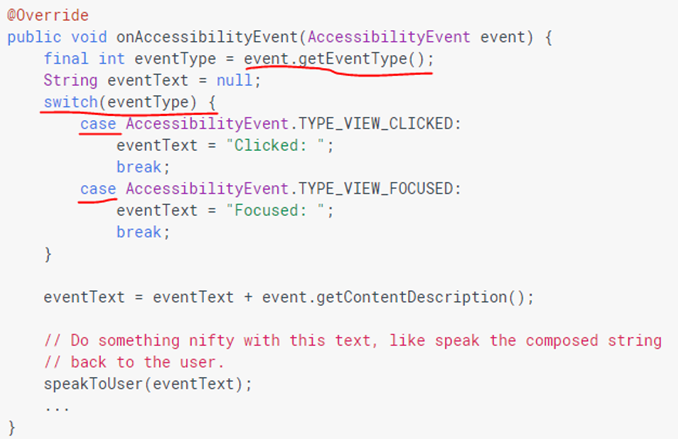
至于这里AS的onAccessibilityEvent()就看实际需求写了,官网给了一个简单的例子:
这里根据AccessibilityEvent的类型来判断,然后case语句,每一步去做什么。
那如果要回到View去操作怎么办呢?比如WeChat的例子,我还要回到View中去模拟点击Open按钮怎么办呢?
其实这里我没有具体去深入研究过,不过我找到两篇博客,有兴趣可以看一看。简略的说来就是Dispatch的逆过程了。
- AccessibilityService分析与防御
- 從源碼角度看AccessibilityService
最后
以上就是呆萌往事最近收集整理的关于Android 9.0源码学习-AccessibilityManagerAccessibility ArchitectureAccessibility FlowAM与AMS联系AccessibilityEvent Dispatch的全部内容,更多相关Android内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复