内核目录树建立(完整版)
<?xml:namespace prefix = o ns = "urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" />
致读者:
很高兴和大家一起分享我的一些实践经历,下面我将要介绍给大家的是驱动程序以模块方式加载进内核开发环境的搭建,即内核目录树的建立;请读者注意当你想开始动手做时,请先了解一些内核驱动的基本知识,我在这里就不说了。同时要安装的内核源代码最好与你的
linux
内核版本相同,这样不会出现很多不必要的问题,要记住:“我们是做开发,而不是做环境”。
一、首先将源码包解压,如下:
[root@localhost /]# rpm -Uvh kernel-2.6.11-1.1369_FC4.src.rpm
这个命令将 RPM 内容写到路径
/usr/src/redhat/SOURSE
和
/usr/src/redhat/SPECS
/usr/src/redhat/SOURSE
和
/usr/src/redhat/SPECS
执行效果如下:
warning: kernel-2.6.11-1.1369_FC4.src.rpm: Header V3 DSA signature: NOKEY, key ID 4f2a6fd2
1:kernel ########################################### [100%]
二、
build
源码包
进入到如下目录:
# cd /usr/src/redhat/SPECS
[root@localhost SPECS]# pwd
/usr/src/redhat/SPECS
[root@localhost SPECS]# ls
kernel-2.6.spec
[root@localhost SPECS]#
然后执行:
# rpmbuild -bp --target i686 kernel-2.6.spec
这个命令将会把内核源码树放到如下目录,如下:
[root@localhost linux-2.6.11]# pwd
[root@localhost linux-2.6.11]# pwd
/usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11
注:再没有执行上面语句时,BUILD目录为空,执行后该目录下生成了kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11,目录下内容如下:
[root@localhost linux-2.6.11]# ls
arch Documentation ipc mm security
configs drivers kernel net sound
COPYING fs lib README usr
CREDITS include MAINTAINERS REPORTING-BUGS
crypto init Makefile scripts
[root@localhost linux-2.6.11]#
三、配置内核
Fedora Core
附带的内核配置文件在
/usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11/configs 目录下
/usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11/configs 目录下
例如,i686 SMP 配置文件被命名为
configs/kernel-version-i686-smp.config。
configs/kernel-version-i686-smp.config。
源代码目录如下:
[root@localhost configs]# pwd
/usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11/configs //配置文件目录
[root@localhost configs]# ls //内容如下:
kernel-2.6.11-i586.config kernel-2.6.11-i686-xen0.config
kernel-2.6.11-i686.config kernel-2.6.11-i686-xenU.config
kernel-2.6.11-i686-smp.config
[root@localhost configs]#
然后,使用下列命令来将需要的配置文件复制到合适的位置,用来编译:
# cd /usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11
# cp configs/kernel-version-i686.config .config //记住要养成备份的好习惯!
# cd /usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11
# cp configs/kernel-version-i686.config .config //记住要养成备份的好习惯!
上面我们选择了kernel-version-i686-smp.config这个配置文件,用户可以根据自己的需求来选择configs目录下的内核配置文件。
[root@localhost linux-2.6.11]# cp configs/kernel-2.6.11-i686-smp.config .config
cp:是否覆盖‘.config’? y
上面的命令执行以后会将linux-2.6.11目录下的.config文件覆盖。
如果你不是多处理器不要选择kernel-2.6.11-i686-smp.config,如果你选错了,在后面之安装驱动文件的时候会出现如下错误:
[root@localhost hello]# insmod hello.ko
insmod: error inserting 'hello.ko': -1 Invalid module format
然后查看日志信息:
[root@localhost hello]# cat /var/log/messages
|
Nov 22 18:27:10 localhost kernel: hello: version magic '2.6.11-1.1369_FC4
SMP
686 REGPARM 4KSTACKS gcc-4.0' should be '2.6.11-1.1369_FC4 686 REGPARM 4KSTACKS gcc-4.0'
|
也许当你看到这条信息的时候,你应该明白了,我不想读者跟我犯一样的错误。
接下来执行
#make menuconfig(图片无法显示,请查看附件)
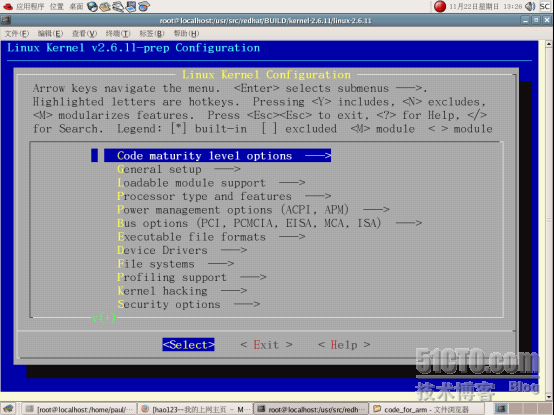
<?xml:namespace prefix = v ns = "urn:schemas-microsoft-com:vml" />
然后选择Loadable module supportà,读者可以默认配置选项。同时读者也可以根据自己的需求来配置
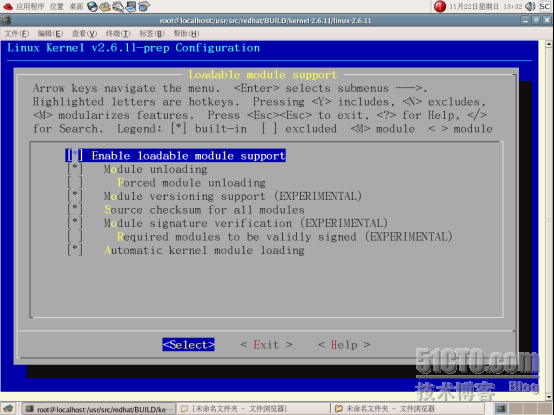
注:第一项必须选择,因为它可以使驱动程序已模块的方式加载到内核中,同时读者还应该注意有几个选项后面有EXPERIMENTAL字样,说明不是很稳定,建议去掉。
配置好后就保存退出即可。
四、
修改Makefile:
每个内核的名字都包含了它的版本号,这也是 uname -r 命令显示的值。内核Makefile 的前四行定义了内核的名字。为了保护官方的内核不被破坏,Makefile经过了修改,以生成一个与运行中的内核不同的名字。在一个模块插入运行中的内核前,这个模块必须针对运行中的内核进行编译。为此,
您必须编辑内核的Makefile 。
例如,如果 uname -r 返回字符串 2.6.11-1.1369_FC4,就将 EXTRAVERSION 定义从:
EXTRAVERSION = -prep
修改为:
EXTRAVERSION = -1.1369_FC4
每个内核的名字都包含了它的版本号,这也是 uname -r 命令显示的值。内核Makefile 的前四行定义了内核的名字。为了保护官方的内核不被破坏,Makefile经过了修改,以生成一个与运行中的内核不同的名字。在一个模块插入运行中的内核前,这个模块必须针对运行中的内核进行编译。为此,
您必须编辑内核的Makefile 。
例如,如果 uname -r 返回字符串 2.6.11-1.1369_FC4,就将 EXTRAVERSION 定义从:
EXTRAVERSION = -prep
修改为:
EXTRAVERSION = -1.1369_FC4
执行如下:
[root@localhost linux-2.6.11]# uname -r
2.6.11-1.1369_FC4
[root@localhost linux-2.6.11]#Vim Makefile
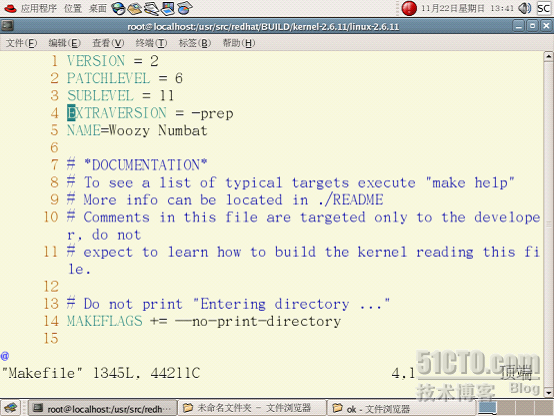
读者只需修改第四行即可。
五. 编译内核:跟普遍的编译方法一样,执行如下:
# make bzImage 编译内核
# make bzImage 编译内核
最后结果:
。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。省略
HOSTCC arch/i386/boot/tools/build
BUILD arch/i386/boot/bzImage
Root device is (8, 3)
Boot sector 512 bytes.
Setup is 7290 bytes.
System is 1513 kB
Kernel: arch/i386/boot/bzImage is ready
[root@localhost linux-2.6.11]#
# make modules 编译模块
安装模块,即编译.config文件中以M选项的代码
。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。省略
CC sound/synth/snd-util-mem.mod.o
LD [M] sound/synth/snd-util-mem.ko
CC sound/usb/snd-usb-audio.mod.o
LD [M] sound/usb/snd-usb-audio.ko
CC sound/usb/snd-usb-lib.mod.o
LD [M] sound/usb/snd-usb-lib.ko
CC sound/usb/usx2y/snd-usb-usx2y.mod.o
LD [M] sound/usb/usx2y/snd-usb-usx2y.ko
[root@localhost linux-2.6.11]#
# make modules_install 安装编译
编译结果:
。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。省略
INSTALL sound/usb/snd-usb-audio.ko
INSTALL sound/usb/snd-usb-lib.ko
INSTALL sound/usb/usx2y/snd-usb-usx2y.ko
if [ -r System.map -a -x /sbin/depmod ]; then /sbin/depmod -ae -F System.map 2.6.11-1.1369_FC4; fi
六、 完成“内核树”的安装
目录“/usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/kernel-2.6.11.686/”就是所谓的“内核代码树”但是“/lib/modules/2.6.11-1.1369_FC4/build”是个符号链接,也指向这个目录,所以这里也可以叫做“内核代码树”。
查看如下:
[root@localhost 2.6.11-1.1369_FC4]# pwd
/lib/modules/2.6.11-1.1369_FC4
[root@localhost 2.6.11-1.1369_FC4]# ll
总用量 1048
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 48 11月 22 15:10 build -> /usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11
drwxr-xr-x 9 root root 4096 11月 22 15:11 kernel
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 10月 22 20:53 misc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 193905 11月 22 15:13 modules.alias
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 69 11月 22 15:13 modules.ccwmap
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 233305 11月 22 15:13 modules.dep
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 813 11月 22 15:13 modules.ieee1394map
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 357 11月 22 15:13 modules.inputmap
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 16284 11月 22 15:13 modules.isapnpmap
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 168540 11月 22 15:13 modules.pcimap
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 89298 11月 22 15:13 modules.symbols
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 267526 11月 22 15:13 modules.usbmap
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 48 11月 22 15:10 source -> /usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11
[root@localhost 2.6.11-1.1369_FC4]#
七、测试
首先编写hello.c源文件,如下:
1 #include <linux/init.h>
2 #include <linux/module.h>
3
4 MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
5
6 static int hello_init(void)
7 {
8 printk(KERN_ALERT"Hello worldn");
9 return 0;
10 }
11
12 static void hello_exit(void)
13 {
14 printk(KERN_ALERT"Goodbyen");
15 }
16
17 module_init(hello_init);
18 module_exit(hello_exit);
编写Makefile内容如下:
1 ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
2 obj-m:=hello.o
3 else
4 KERNELDIR ?=/lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
5 PWD :=$(shell pwd)
6 default:
7 $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
8 endif
请注意Makefile的语法规则。
执行效果如下:
[root@localhost hello]# pwd
/hello
[root@localhost hello]# ls
hello.c Makefile
[root@localhost hello]# make
make -C /lib/modules/2.6.11-1.1369_FC4/build M=/hello modules
make[1]: Entering directory `/usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11'
CC [M] /hello/hello.o
Building modules, stage 2.
MODPOST
CC /hello/hello.mod.o
LD [M] /hello/hello.ko
make[1]: Leaving directory `/usr/src/redhat/BUILD/kernel-2.6.11/linux-2.6.11'
[root@localhost hello]#
[root@localhost hello]# ls
hello.c hello.ko hello.mod.c hello.mod.o hello.o Makefile
读者可以看到在hello目录下生成了hello.ko文件,这个就是2.6内核的驱动文件名。
八、安装编译好的hello驱动。
# insmod hello.ko
应该可以看到返回的信息: Hello world
然后再运行命令:
# rmmod hello
应该可以看到返回的信息:Goodbye
应该可以看到返回的信息: Hello world
然后再运行命令:
# rmmod hello
应该可以看到返回的信息:Goodbye
如果你没有看到,那么你可以看日志信息:
#cat /var/log/messages
补充:
可以用lsmod命令看到hello这个驱动的加载情况,同时可以看到系统自动分配的主次设备号!
总之:学习靠自己,继续努力吧!
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/zyg0227/231955
最后
以上就是聪慧香烟最近收集整理的关于内核目录树建立(完整版)的全部内容,更多相关内核目录树建立(完整版)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复