用,现在我们就来动手自己编写一个RPC框架,通过这篇文章的学习,你将学习到
- 分布式系统的概念
- RPC远程方法调用的应用
- Dubbo的原理深入理解
当然,如果要完全自己编写一个RPC框架,我们需要掌握以下知识点
- 网络编程(网络通信) 本文将使用netty4网络通信框架
- 多线程相关知识
- 反射相关知识
- jdk的动态代理
- Spring框架的相关知识
如果对于上述的知识点有一部分不是很理解,也不会影响你阅读本文和对Dubbo的RPC调用原理的理解
好了,我们先来简单的描述一下整个RPC调用的业务流程图
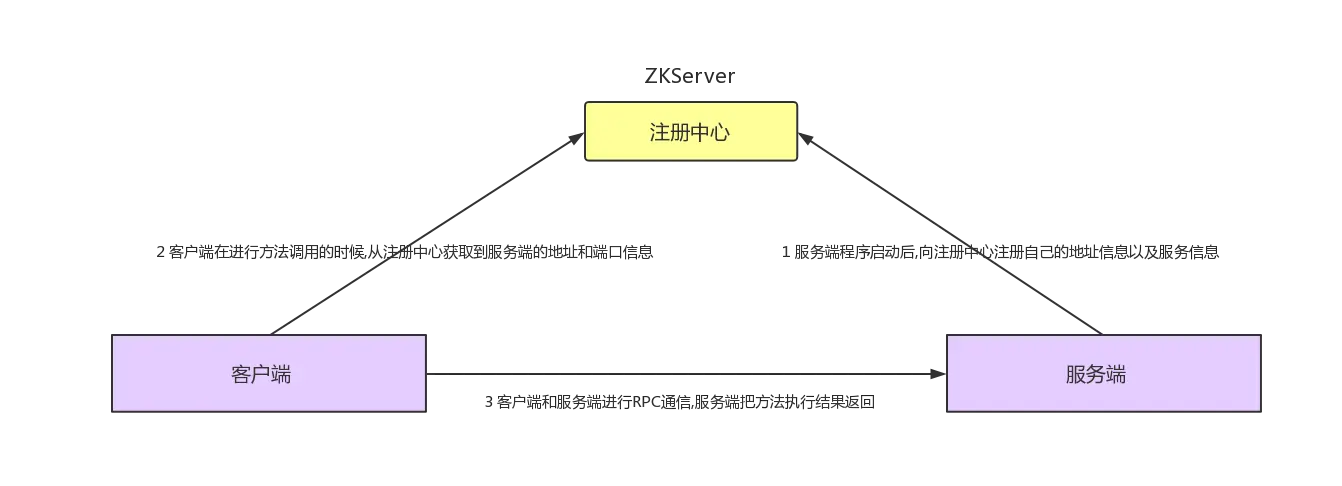
为了可以实现上面的RPC调用,我们创建的RPC框架的模块之间的关系图如下:
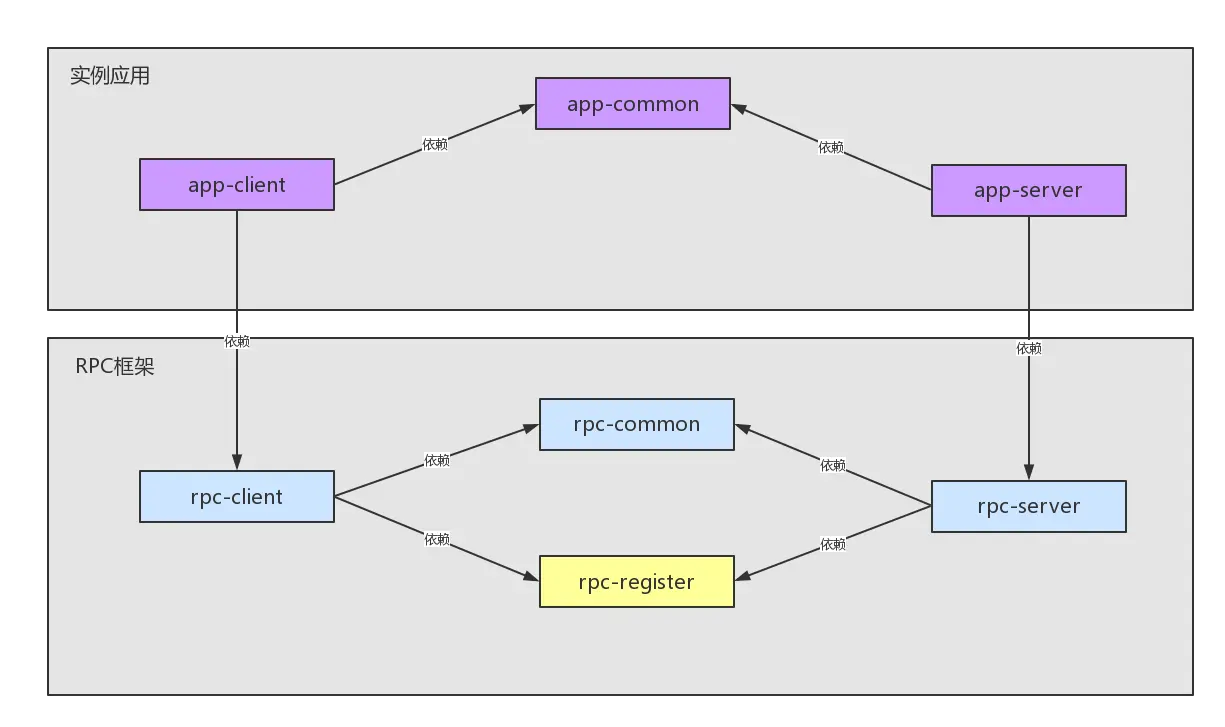
对于上面的每个模块的具体作用,使用一个表格简单的进行描述
| 模块名称 | 主要功能 |
|---|---|
| rpc-register | 主要完成可注册中心Zookeeper的交互<br />RPC服务端使用该模块往注册中心注册地址和端口<br />RPC客户端通过该模块获取实时已近注册的服务地址和端口 |
| rpc-common | 定义RPC通信的请求消息和响应消息的规则,以及消息的序列化和反序列化的帮助类 |
| rpc-server | RPC服务端,启动RPC服务,扫描app-server中的所有可以提供的服务列表并保存<br />接受RPC客户端的消息并且通过反射调用具体的方法<br/>响应RPC客户端,把方法执行结果返回到RPC客户端 |
| rpc-client | RPC客户端,通过网络通信往RPC服务端发送请求调用消息<br/>接受服务端的响应消息<br/>配置动态代理类,所有的方法调用都通过网络调用发送到RPC服务端 |
| app-common | 具体的应用中的接口和JavaBean对象,类似于service模块和bean模块 |
| app-server | 通过Spring的配置启动SpringContext,并且配置RpcServer和RpcRegistry Bean对象的创建<br />实现app-common中的接口,并且在接口上添加注解@RpcService(IProductService.class)可以让RPCServer识别到该服务<br />启动服务 |
| app-client | 通过Spring的配置创建RpcDiscover对象和RpcProxy对象,其中RpcDiscover用于从注册中心获取到服务的地址信息,RpcProxy用于创建类的动态代理对象 |
接下来我们来看一下具体的实现代码
-
rpc-register
这个模块用户和注册中心进行交互,主要包括三个类
- Constant常量定义,设置连接ZKServer的相关参数
- RpcRegistry:往注册中心ZKServer设置地址信息,RPC-Server需要使用
- RpcDiscover: 从注册中心ZKServer获取服务端的网络地址信息 RPC-client需要使用
具体的实现代码
package cn.wolfcode.rpc.register; public interface Constant { //定义客户端连接session会话超时时间,单位为毫秒,该值的设置和zkServer设置的心跳时间有关系 int SESSION_TIMEOUT=4000; // 定义用于保存rpc通信服务端的地址信息的目录 String REGISTRY_PATH="/rpc"; // 定义数据存放的具体目录 String DATA_PATH=REGISTRY_PATH+"/data"; }package cn.wolfcode.rpc.register; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import lombok.Setter; import org.apache.zookeeper.*; import org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; @Setter@Getter @AllArgsConstructor() @NoArgsConstructor public class RpcRegistry { public static final Logger LOGGER=LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcRegistry.class); //zkServer的地址信息 private String registryAddress; //zk客户端程序 private ZooKeeper zooKeeper; public void createNode(String data) throws Exception{ //创建一个客户端程序, 对于注册可以不用监听事件 zooKeeper= new ZooKeeper(registryAddress, Constant.SESSION_TIMEOUT, new Watcher() { @Override public void process(WatchedEvent event) { } }); if(zooKeeper!=null){ try{ //判断注册的目录是否存在 Stat stat = zooKeeper.exists(Constant.REGISTRY_PATH, false); if(stat==null){ //如果不存在, 创建一个持久的节点目录 zooKeeper.create(Constant.REGISTRY_PATH,null,ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,CreateMode.PERSISTENT); } //创建一个临时的序列节点,并且保存数据信息 zooKeeper.create(Constant.DATA_PATH,data.getBytes(),ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL); }catch (Exception e){ LOGGER.error("",e); e.printStackTrace(); } }else{ LOGGER.debug("zooKeeper connect is null"); } } //测试程序 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { RpcRegistry rpcRegistry = new RpcRegistry(); rpcRegistry.setRegistryAddress("192.168.158.151:2181"); rpcRegistry.createNode("testdata"); //让程序等待输入,程序一直处于运行状态 System.in.read(); } }package cn.wolfcode.rpc.register; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import org.apache.zookeeper.WatchedEvent; import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher; import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooKeeper; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; @Setter @Getter //地址发现,用于实时的获取最新的RPC服务信息 public class RpcDiscover { public static final Logger LOGGER=LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcRegistry.class); //服务端地址 zkServer的地址 private String registryAddress; //获取到的所有提供服务的服务器列表 private volatile List<String> dataList=new ArrayList<>(); private ZooKeeper zooKeeper=null; //初始化zkClient客户端 public RpcDiscover(String registryAddress) throws Exception { this.registryAddress = registryAddress; zooKeeper=new ZooKeeper(registryAddress, Constant.SESSION_TIMEOUT, new Watcher() { @Override public void process(WatchedEvent watchedEvent) { if(watchedEvent.getType()==Event.EventType.NodeChildrenChanged){ //监听zkServer的服务器列表变化 watchNode(); } } }); //获取节点相关数据 watchNode(); } // 从dataList列表随机获取一个可用的服务端的地址信息给rpc-client public String discover(){ int size=dataList.size(); if(size>0){ int index= new Random().nextInt(size); return dataList.get(index); } throw new RuntimeException("没有找到对应的服务器"); } //监听服务端的列表信息 private void watchNode(){ try{ //获取子节点信息 List<String> nodeList = zooKeeper.getChildren(Constant.REGISTRY_PATH, true); List<String> dataList=new ArrayList<>(); for (String node : nodeList) { byte[] bytes = zooKeeper.getData(Constant.REGISTRY_PATH + "/" + node, false, null); dataList.add(new String(bytes)); } this.dataList=dataList; }catch (Exception e){ LOGGER.error("",e); e.printStackTrace(); } } //测试程序 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //打印获取到的连接地址信息 System.out.println(new RpcDiscover("192.168.158.151:2181").discover()); System.in.read(); } } -
rpc-common
定义RPC通信的请求消息和响应消息的规则,以及消息的序列化和反序列化的帮助类,主要包括
- RpcRequest 请求消息封装对象
- RpcResponse 响应消息封装对象
- SerializationUtil 消息的序列化,烦序列化帮助类
- RpcEncoder 把消息对象转换为字节数组进行通信
- RpcDecoder 把获取到的字节数组转换为对应的消息对象
具体代码如下
package cn.wolfcode.rpc.common; import lombok.*; @Setter @Getter @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @ToString //RPC通信的数据请求规则 public class RpcRequest { // 请求消息的消息Id private String requestId; // 请求的具体的类名(接口名称) private String className; // 请求的具体的方法名称 private String methodName; // 请求的方法参数类型列表 private Class<?>[] parameterTypes; // 请求的方法参数列表 private Object[] parameters; }package cn.wolfcode.rpc.common; import lombok.*; @Setter @Getter @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @ToString //RPC通信消息的响应数据规则 public class RpcResponse { //响应的消息id private String responseId; //请求的消息id private String requestId; // 响应的消息是否成功 private boolean success; // 响应的数据结果 private Object result; // 如果有异常信息,在该对象中记录异常信息 private Throwable throwable; }package cn.wolfcode.rpc.common; import com.dyuproject.protostuff.LinkedBuffer; import com.dyuproject.protostuff.ProtostuffIOUtil; import com.dyuproject.protostuff.Schema; import com.dyuproject.protostuff.runtime.RuntimeSchema; import org.objenesis.Objenesis; import org.objenesis.ObjenesisStd; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; /** * 序列化工具类(基于 Protostuff 实现) 用于把对象序列化字节数组, 把字节数组反序列化对象 */ public class SerializationUtil { private static Map<Class<?>, Schema<?>> cachedSchema = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, Schema<?>>(); private static Objenesis objenesis = new ObjenesisStd(true); private SerializationUtil() { } /** * 获取类的schema * @param cls * @return */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private static <T> Schema<T> getSchema(Class<T> cls) { Schema<T> schema = (Schema<T>) cachedSchema.get(cls); if (schema == null) { schema = RuntimeSchema.createFrom(cls); if (schema != null) { cachedSchema.put(cls, schema); } } return schema; } /** * 序列化(对象 -> 字节数组) */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static <T> byte[] serialize(T obj) { Class<T> cls = (Class<T>) obj.getClass(); LinkedBuffer buffer = LinkedBuffer.allocate(LinkedBuffer.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE); try { Schema<T> schema = getSchema(cls); return ProtostuffIOUtil.toByteArray(obj, schema, buffer);//序列化 } catch (Exception e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } finally { buffer.clear(); } } /** * 反序列化(字节数组 -> 对象) */ public static <T> T deserialize(byte[] data, Class<T> cls) { try { /* * 如果一个类没有参数为空的构造方法时候,那么你直接调用newInstance方法试图得到一个实例对象的时候是会抛出异常的 * 通过ObjenesisStd可以完美的避开这个问题 * */ T message = (T) objenesis.newInstance(cls);//实例化 Schema<T> schema = getSchema(cls);//获取类的schema ProtostuffIOUtil.mergeFrom(data, message, schema); return message; } catch (Exception e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } } }package cn.wolfcode.rpc.common; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder; //对传递的消息进行编码, 因为是请求/响应对象的传递,先编码为字节数组在发送到服务器解码 public class RpcEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder { // 传递的数据的对象类型 private Class genericClass; public RpcEncoder(Class genericClass) { this.genericClass = genericClass; } @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception { if(genericClass.isInstance(msg)){ //序列化请求消息为字节数组 byte[] bytes = SerializationUtil.serialize(msg); // 把数据写入到下一个通道(channel)或者是发往服务端 out.writeBytes(bytes); } } }package cn.wolfcode.rpc.common; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageDecoder; import java.util.List; //对传递的消息进行解码, 接受到的数据是字节数组,需要把数组转换为对应的请求/响应消息对象 public class RpcDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder { private Class<?> genericClass; public RpcDecoder(Class<?> genericClass) { this.genericClass = genericClass; } @Override //解码方法,把字节数组转换为消息对象 protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception { //消息的长度 int size=in.readableBytes(); if(size<4){//保证所有的消息都完全接受完成 return; } byte[] bytes =new byte[size]; //把传递的字节数组读取到bytes中 in.readBytes(bytes); // 反序列化为对象(RPCRequest/RPCResponse对象) Object object = SerializationUtil.deserialize(bytes, genericClass); //输出对象 out.add(object); //刷新缓存 ctx.flush(); } } -
rpc-server
RPC服务端,启动RPC服务,扫描app-server中的所有可以提供的服务列表并保存,接受RPC客户端的消息并且通过反射调用具体的方法,响应RPC客户端,把方法执行结果返回到RPC客户端
主要包括:
- RpcService 定义一个注解,用于标记服务程序的提供者,通过Spring扫描出所有的服务并且保存
- RpcServerHandler 处理RPC客户端请求,调用服务提供者的具体方法,响应执行结果
- RpcServer 扫描所有的服务(标记了@RPCService的类),启动RPC服务
package cn.wolfcode.rpc.server; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * 这个注解用于贴在每个提供服务的实现类, * 在Spring容器启动的时候,自动扫描到贴了该注解的所有的服务 */ @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) public @interface RpcService { public Class<?> value(); }package cn.wolfcode.rpc.server; import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcDecoder; import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcEncoder; import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcRequest; import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcResponse; import cn.wolfcode.rpc.register.RpcRegistry; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import lombok.Setter; import org.apache.commons.collections4.MapUtils; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; @Setter @Getter @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor //RPC服务端启动,实现Spring的感知接口 public class RpcServer implements ApplicationContextAware,InitializingBean { //用于保存所有提供服务的方法, 其中key为类的全路径名, value是所有的实现类 private final Map<String,Object> serviceBeanMap=new HashMap<>(); //rpcRegistry 用于注册相关的地址信息 private RpcRegistry rpcRegistry; //提供服务的地址信息 格式为 192.168.158.151:9000 类似 private String serverAddress; //在Spring容器启动完成后会执行该方法 @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { //获取到所有贴了RpcService注解的Bean对象 Map<String, Object> serviceBeanMap = applicationContext.getBeansWithAnnotation(RpcService.class); if(MapUtils.isNotEmpty(serviceBeanMap)){ for (Object object : serviceBeanMap.values()) { //获取到类的路径名称 String serviceName = object.getClass().getAnnotation(RpcService.class).value().getName(); //把获取到的信息保存到serviceBeanMap中 this.serviceBeanMap.put(serviceName,object); } } System.out.println("服务器: "+serverAddress +" 提供的服务列表: "+ serviceBeanMap ); } // 初始化完成后执行 @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { //创建服务端的通信对象 ServerBootstrap server = new ServerBootstrap(); // 创建异步通信的事件组 用于建立TCP连接的 NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // 创建异步通信的事件组 用于处理Channel(通道)的I/O事件 NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try{ //开始设置server的相关参数 server.group(bossGroup,workerGroup) //启动异步ServerSocket .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //初始化通道信息 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new RpcDecoder(RpcRequest.class))//1 解码请求参数 .addLast(new RpcEncoder(RpcResponse.class))//2 编码响应信息 .addLast(new RpcServerHandler(serviceBeanMap));//3 请求处理 } }).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);; String host=serverAddress.split(":")[0] ;//获取到主机地址 int port=Integer.valueOf(serverAddress.split(":")[1]);//端口 ChannelFuture future = server.bind(host, port).sync();//开启异步通信服务 System.out.println("服务器启动成功:"+future.channel().localAddress()); rpcRegistry.createNode(serverAddress); System.out.println("向zkServer注册服务地址信息"); future.channel().closeFuture().sync();//等待通信完成 }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //优雅的关闭socket bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
package cn.wolfcode.rpc.server;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcRequest;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcResponse;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
@Setter
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
public class RpcServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
private Map<String,Object> serviceBeanMap;
public RpcServerHandler(Map<String, Object> serviceBeanMap) {
this.serviceBeanMap = serviceBeanMap;
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("RpcServerHandler.channelRead");
System.out.println(msg);
RpcRequest rpcRequest= (RpcRequest) msg;
RpcResponse rpcResponse=handler(rpcRequest);
//告诉客户端,关闭socket连接
ctx.writeAndFlush(rpcResponse).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
private RpcResponse handler(RpcRequest rpcRequest) {
//创建一个响应消息对象
RpcResponse rpcResponse =new RpcResponse();
//设置响应消息ID
rpcResponse.setResponseId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
//请求消息ID
rpcResponse.setRequestId(rpcRequest.getRequestId());
try{
//获取到类名(接口名称)
String className = rpcRequest.getClassName();
//获取到方法名
String methodName = rpcRequest.getMethodName();
//获取到参数类型列表
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = rpcRequest.getParameterTypes();
//获取到参数列表
Object[] parameters = rpcRequest.getParameters();
//获取到具字节码对象
Class<?> clz = Class.forName(className);
//获取到实现类
Object serviceBean = serviceBeanMap.get(className);
if(serviceBean==null){
throw new RuntimeException(className+"没有找到对应的serviceBean:"+className+":beanMap:"+serviceBeanMap);
}
//反射调用方法
Method method = clz.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
if(method==null)
throw new RuntimeException("没有找到对应的方法");
Object result = method.invoke(serviceBean, parameters);
rpcResponse.setSuccess(true);
//设置方法调用的结果
rpcResponse.setResult(result);
}catch (Exception e){
rpcResponse.setSuccess(false);
rpcResponse.setThrowable(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
return rpcResponse;
}
}
-
rpc-client
RPC客户端,通过网络通信往RPC服务端发送请求调用消息,接受服务端的响应消息,配置动态代理类,所有的方法调用都通过网络调用发送到RPC服务端
其中包括的主要代码:
- RpcProxy 对于每一个类都创建一个动态代理对象,并且在invoke方法创建rpc客户端并且发送网络通信请求
- RpcClient RPC通信客户端,启动RPC通信服务,创建TCP连接,发送请求,接受响应
具体实现代码:
package cn.wolfcode.rpc.client;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcDecoder;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcEncoder;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcRequest;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcResponse;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.register.RpcDiscover;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
//RPC通信客户端,往服务端发送请求,并且接受服务端的响应
public class RpcClient extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponse> {
//消息响应对象
private RpcResponse rpcResponse;
//消息请求对象
private RpcRequest rpcRequest;
// 同步锁 资源对象
private Object object=new Object();
// 用于获取服务地址列表信息
private RpcDiscover rpcDiscover;
//构造函数
public RpcClient(RpcRequest rpcRequest,RpcDiscover rpcDiscover) {
this.rpcDiscover = rpcDiscover;
this.rpcRequest=rpcRequest;
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponse msg) throws Exception {
this.rpcResponse=msg;//响应消息
synchronized (object){
ctx.flush();//刷新缓存
object.notifyAll();//唤醒等待
}
}
//发送消息
public RpcResponse send() throws Exception {
//创建一个socket通信对象
Bootstrap client = new Bootstrap();
//创建一个通信组,负责Channel(通道)的I/O事件的处理
NioEventLoopGroup loopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
client.group(loopGroup)//设置参数
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//使用异步socket通信
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new RpcEncoder(RpcRequest.class))//编码请求对象
.addLast(new RpcDecoder(RpcResponse.class))//解码响应对象
.addLast(RpcClient.this);//发送请求对象
}
}).option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);;
String serverAddress = rpcDiscover.discover();//获取一个服务器地址
String host=serverAddress.split(":")[0];
int port=Integer.valueOf(serverAddress.split(":")[1]);
ChannelFuture future = client.connect(host,port).sync();
System.out.println("客户端准备发送数据:"+rpcRequest);
future.channel().writeAndFlush(rpcRequest).sync();
synchronized (object){
object.wait();//线程等待,等待客户端响应
}
if (rpcResponse != null) {
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();//等待服务端关闭socket
}
return rpcResponse;
}finally {
loopGroup.shutdownGracefully();//优雅关闭socket
}
}
/**
* 异常处理
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}
package cn.wolfcode.rpc.client;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcRequest;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.common.RpcResponse;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.register.RpcDiscover;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.UUID;
@Setter
@Getter
//动态代理类,用于获取到每个类的代理对象
//对于被代理对象的所有的方法调用都会执行invoke方法
public class RpcProxy {
//用于获取到RPC-Server的地址信息
private RpcDiscover rpcDiscover;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public <T> T getInstance(Class<T> interfaceClass){
T instance = (T)Proxy.newProxyInstance(interfaceClass.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{interfaceClass}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//创建请求对象
RpcRequest rpcRequest = new RpcRequest();
//获取到被调用的类名 和RPC-Server中的serviceMap中的key进行匹配
String className=method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
//获取到方法的参数列表
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
//生成一个请求的id
rpcRequest.setRequestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
rpcRequest.setClassName(className);//类名
rpcRequest.setParameterTypes(parameterTypes);//参数类型列表
rpcRequest.setParameters(args);//参数列表
rpcRequest.setMethodName(method.getName());//调用的放方法名称
RpcResponse rpcResponse = new RpcClient(rpcRequest, rpcDiscover).send();//创建一个RPCclient对象,并且发送消息到服务端
//返回调用结果
return rpcResponse.getResult();
}
});
//返回一个代理对象
return instance;
}
}
-
app-common
这是具体应用的通用模块,和具体的项目结构有关系,这里主要包括接口定义和JavaBean对象的定义
具体代码为:
package cn.wolfcode.app.common; public interface IProductService { /** * 保存产品 * @param product */ void save(Product product); /** * 根据产品id删除产品 * @param productId */ void deleteById(Long productId); /** * 修改产品信息 * @param product */ void update(Product product); /** * 根据产品id获取到产品信息 * @param productId * @return */ Product get(Long productId); }package cn.wolfcode.app.common; import lombok.*; import java.math.BigDecimal; /** * 产品信息 */ @Setter @Getter @ToString @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Product { private Long id;//id private String sn;//产品编号 private String name;//产品名称 private BigDecimal price;//产品价格 } -
app-server
这个模块主要是定义服务的具体实现和启动Spring容器,在启动Spring容器的时候需要创建RpcRegistry,RpcServer对象
具体代码实现:
package cn.wolfcode.app.server; import cn.wolfcode.app.common.IProductService; import cn.wolfcode.app.common.Product; import cn.wolfcode.rpc.server.RpcService; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.math.BigDecimal; @Component @RpcService(IProductService.class) public class ProductServiceImpl implements IProductService { @Override public void save(Product product) { System.out.println("产品保存成功: "+product); } @Override public void deleteById(Long productId) { System.out.println("产品删除成功: "+ productId); } @Override public void update(Product product) { System.out.println("产品修改成功: "+ product); } @Override public Product get(Long productId) { System.out.println("产品获取成功"); return new Product(1L,"001","笔记本电脑",BigDecimal.TEN); } }package cn.wolfcode.app.server; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class BootAppServer { public static void main(String[] args) { //启动Spring容器 new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:application.xml"); } }其中配置文件:
- application.xml Spring的配置文件
- log4j.properties 日志配置文件
- rpc.properties 服务提供者的地址和端口 以及zkServer的连接地址和端口
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.wolfcode.app.server"/> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:rpc.properties"/> <bean id="serviceRegistry" class="cn.wolfcode.rpc.register.RpcRegistry"> <property name="registryAddress" value="${registry.address}"/> </bean> <bean id="rpcServer" class="cn.wolfcode.rpc.server.RpcServer"> <property name="serverAddress" value="${server.address}"/> <property name="rpcRegistry" ref="serviceRegistry"/> </bean> </beans>log4j.rootLogger=ERROR,console log4j.appender.console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.console.target=System.out log4j.appender.console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=%m%n log4j.logger.cn.wolfcode.rpc=DEBUG# zookeeper server registry.address=192.168.158.151:2181 # rpc server server.address=192.168.158.1:9090
-
app-client
通过Spring的配置创建RpcDiscover对象和RpcProxy对象,其中RpcDiscover用于从注册中心获取到服务的地址信息,RpcProxy用于创建类的动态代理对象
测试类:使用Spring的Junit进行测试
package cn.wolfcode.app.client;
import cn.wolfcode.app.common.IProductService;
import cn.wolfcode.app.common.Product;
import cn.wolfcode.rpc.client.RpcProxy;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
//模拟客户端启动
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:application.xml")
public class APP {
@Autowired
private RpcProxy rpcProxy;
private IProductService productService;
@Before
public void init() {
productService = rpcProxy.getInstance(IProductService.class);
}
@Test
public void testSave() throws Exception {
productService.save(new Product(2L,"002","内衣",BigDecimal.TEN));
}
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
productService.deleteById(2L);
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
productService.update(new Product(2L,"002","内衣",BigDecimal.ONE));
}
@Test
public void testGet() throws Exception {
Product product = productService.get(1L);
System.out.println("获取到的产品信息为:"+product);
}
}
配置文件信息
application.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.wolfcode.app.client"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:rpc.properties"/>
<bean id="serviceRpcDiscover" class="cn.wolfcode.rpc.register.RpcDiscover">
<constructor-arg name="registryAddress" value="${registry.address}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="rpcProxy" class="cn.wolfcode.rpc.client.RpcProxy">
<property name="rpcDiscover" ref="serviceRpcDiscover"/>
</bean>
</beans>
log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=ERROR,console
log4j.appender.console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.target=System.out
log4j.appender.console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=%m%n
log4j.logger.cn.wolfcode.rpc=DEBUG
rpc.properties
# zookeeper server
registry.address=192.168.158.151:2181
对于本文的完整代码下载地址为 https://gitee.com/heshengjun/rpcdemo.git
如果要正常运行,请部署一个zookeeper注册中心,修改rpc.properites的地址即可
- 先运行app-server中的BootAppServer
- 在运行app-client中的APP测试用例

最后
以上就是虚拟手链最近收集整理的关于解密Dubbo:自己动手编写RPC框架的全部内容,更多相关解密Dubbo内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复