题1
#include <iostream>
void swap(int& x, int& y);
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i ,j;
std::cin >> i >> j;
swap(i,j);
cout<<i<<j<<endl;
return 0;
}
void swap(int& x ,int& y)
{
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
结果: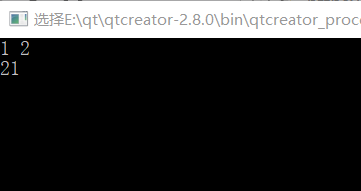
题2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
int count(T a[], int n, const T& value)
{
int theCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (a[i] == value)
theCount++;
return theCount;
}
int main()
{
int x[5]={3,2,3,4,5};
int result;
result = count(x,5,3);
cout<<result<<endl;
return 0;
}
结果:2
题10
#include <iostream>
int abc(int a,int b,int c);
using namespace std;
int main()
{
try {
//cout << abc(2,1,2)<<endl;
cout << abc(0,0,0)<<endl;
cout << abc(-2,-2,-2)<<endl;
}
catch(exception& e)//捕获基类型exception以及其派生的类型(例如bad_alloc和ba_typeid)
{
cout <<"a"<<endl;
}
catch(int e)
{
if(e==2)
cout<<"this is 2"<<endl;
if(e==1)
cout<<"e==1"<<endl;
}
catch(...)//捕捉异常,不管什么类型
{
cout<<"..."<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
int abc(int a,int b,int c)
{
if(a<0&&b<0&&c<0)
throw 1;
if(a==0&&b==0&&c==0)
throw 2;
return a+b*c;
}
结果: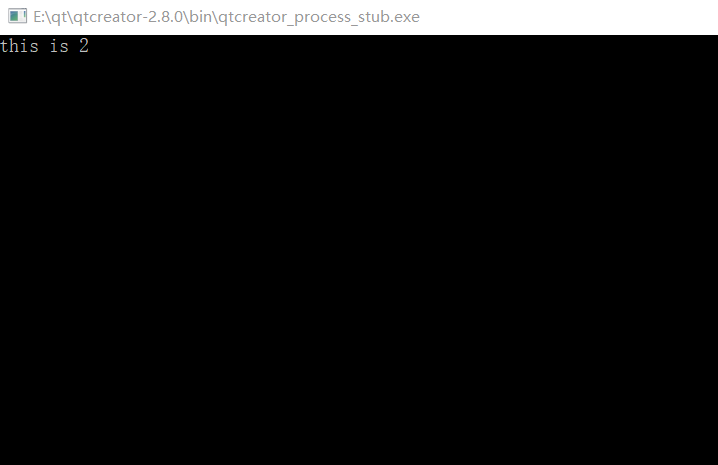
发生异常,程序终止,所以只会输出第一个异常。
题11
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
int count(T a[], int n, const T& value)
{
if(n<7)
throw "n must be >= 1";
int theCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (a[i] == value)
theCount++;
return theCount;
}
int main()
{
int x[5]={3,2,3,4,5};
int result;
result = count(x,5,3);
cout<<result<<endl;
return 0;
}
结果: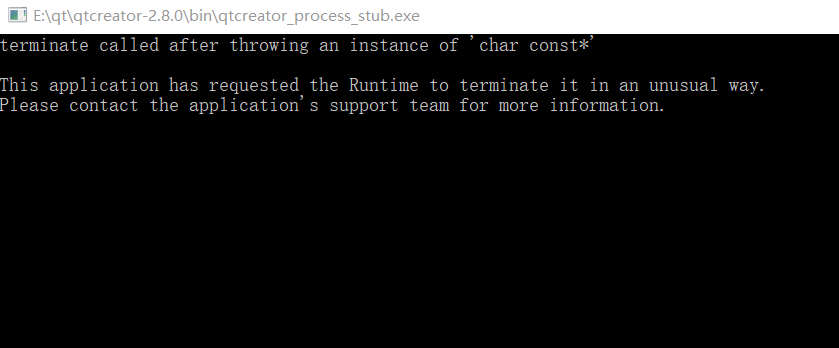 且window系统报错
且window系统报错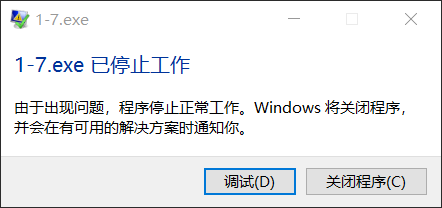
最后
以上就是平淡水杯最近收集整理的关于数据结构,算法与应用 c++语言描述答案的全部内容,更多相关数据结构,算法与应用内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复