1.PM2.5:if,if
def main():
PM=eval(input("What is today's PM2.5?"))
if PM>75:
print("UNhealth")
if PM<35:
print("Good")
main()2.二次方程求解:if else
import math
def main():
print("This program finds the real solutions to a quadraticn")
a,b,c=eval(input("Please enter the coefficients(a,b,c):"))
delta=b*b-4*a*c
if delta<0:
print("This quadratic has no real roots! ")
else:
delta=math.sqrt(delta)
root1=(-b+delta)/(2*a)
root2=(-b-delta)/(2*a)
print("nThe solution are:",root1,root2)
main()升级版1 二次方程求解:if elif elif else
无根,有一个根,有两个相等的根,有两个不等的根。
import math
def main():
print("This program finds the real solutions to a quadraticn")
a,b,c=eval(input("Please enter the coefficients(a,b,c):"))
delta=b*b-4*a*c
if a==0:
x=-b/c
print("There is a solution")
elif delta<0:
print("This quadratic has no real roots! ")
elif delta==0:
x=-b/(2*a)
print("There is a double root at",x)
else:
delta=math.sqrt(delta)
x1=(-b+delta)/(2*a)
x2=(-b-delta)/(2*a)
print("nThe solutions are:",x1,x2)
main()升级版2 二次方程求解 异常处理(try…except…)
try:
<body>
except <errortype1>:
<handler1>
except <errortype2>:
<handler2>
当Python解释器遇到一个try语句,它会尝试执行 try语句体<body>内的语句
如果没有错误,控制转到try-except后面的语句
如果发生错误,Python解释器会寻找一个符合该错误 的异常语句,然后执行处理代码
import math
def main():
print("This program finds the real solutions to a quadraticn")
try:
a,b,c=eval(input("Please enter the coefficients(a,b,c):"))
discRoot= math.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c)
root1 = (-b + discRoot) / (2 * a)
root2 = (-b - discRoot) / (2 * a)
print("nThe solutions are:", root1, root2)
except ValueError as exc0bj:
if str(exc0bj)=="math domain error":
print("no real roots.")
else:
print("You didn't give me the right number of coefficients.")
except NameError:
print("nYou didn't enter three numbers.")
except TypeError:
print("nYour inputs were not all numbers.")
except SyntaxError:
print("nYour inputs was not in the correct form.Missing comma?")
except:
print("nSomething went wrong.sorry")
3.循环结构(求三者最大,求平均数)
求最大值


求平均数
a.简单for循环

b.交互式循环是无限循环的一种 允许用户通过交互的方式重复程序的特定部分 让我们以交互循环的视角重新审视求平均数程序,伪码 如下: 初始化sum为0 初始化count为0 初始化moredata为"yes" 当moredata值为"yes"时 输入数字x 将x加入sum count值加1 询问用户是否还有moredata需要处理 输出sum/count


c.哨兵循环
执行循环直到遇到特定的值,循环语句才终止执行的循 环结构设计方法 哨兵循环是求平均数的更好方案,思路如下: 设定一个哨兵值作为循环终止的标志 任何值都可以做哨兵,但要与实际数据有所区别 伪码如下: 接收第一个数据 while这个数据不是哨兵 程序执行相关语句 接收下一个数据项 在求考试分数平均数的程序中,可以设定负数为哨兵
没有那么多yes/no的干扰,执行结果更加清晰 但不能包含负数的平均数计算,为了更加通用化需要引 入字符串
利用非数字字符串表示输入结束 所有其他字符串将被转换成数字作为数据处理 空字符串以””(引号中间没有空格)代表,可以作为哨 兵,用户输入回车Python就返回空字符串 伪码如下: 初始化sum为0 初始化count为0 接受输入的字符串数据,xStr while xStr非空 将xStr转换为数字x 将x加入sum count值加1 接受下个字符串数据,xStr 输出sum/count
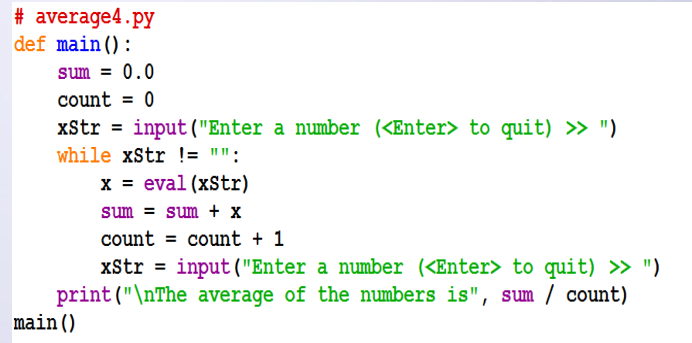
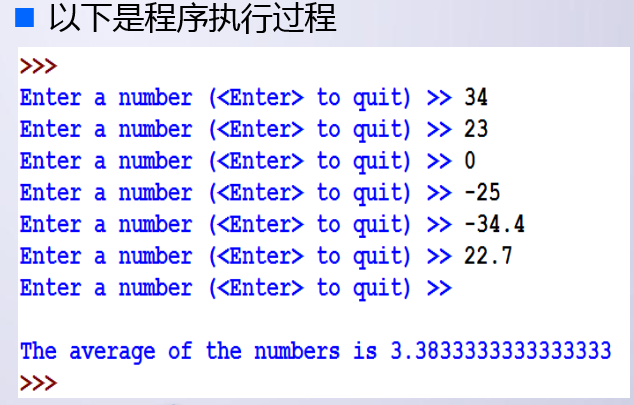
d.文件循环
面向文件的方法是数据处理的典型应用 之前求平均数的数字都是用户输入的,如果几百个数求 平均,输入困难且容易出错 可以事先将数据录入到文件中,然后将这个文件作为程 序的输入,避免人工输入的麻烦,便于编辑修改
def main():
yy="yy.txt"
infile=open(yy,'r')
sum=0
count=0
line=infile.readline()
while line!="":
sum=sum+eval(line)
count=count+1
line=infile.readline()
print("nThe average of the nummbers is",sum/count)
main()
先要把yy.txt文件放在当前目录下,然后用yy="yy.txt"读入文件
e.嵌套循环
嵌套循环
决策和循环互相嵌套可以实现复杂算法 之前实例中文件每行只存一个数字,这一次数字以逗号 分隔出现在文件的同一行上
下面是处理一行的代码片段:


最后
以上就是爱笑棒球最近收集整理的关于//Python学习// 第4周 简单分支、多分支、异常处理、循环结构的全部内容,更多相关//Python学习//内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复