运算符重载实质上是对已有的运算符赋予多重含义,扩展c++中提供的运算符的适用范围,以用于类所表示表示得抽象数据类型
返回值类型 operator 运算符 (形参表)在程序编译时,把运算符的表达式转换为对运算符函数的调用。把运算符的操作数,作为运算符函数的参数进行传递。当运算符发生重载时,根据实参的类型决定调用对应的运算符函数。
运算符可以被重载为普通函数,也可以被定义为类的成员函数。
重载为普通函数
重载为普通函数时,参数个数为运算符目数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex
{
public:
double real,imaginary;
Complex(double r=0,double i=0 )
{
real=r;
imaginary=i;
}
};
Complex operator + (const Complex &a,const Complex &b)
{
return Complex(a.real+b.real,a.imaginary+b.imaginary);
}
int main()
{
Complex a(1,2),b(2,3),c;
c=a+b;
return 0;
}
重载为成员函数
重载为成员函数时,参数个数为运算符目数减一
赋值运算的重载
赋值运算符两边的类型可以不匹配
当遇到以下情况时,需要重载赋值运算符
把一个int类型的变量赋值给一个Complex对象
把一个char*类型的字符串赋值给一个字符串对象
对于赋值运算符,只能把它重载为成员函数
例子:
编写一个长度可变的字符串类String
在该类中包含一个char*类型的成员变量,指向动态分配的存储空间。该存储空间用于存放以’�’结尾的字符串
#include <iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
class String
{
char *str;
public:
String():str(NULL){};
const char * c_str(){return str;};
char *operator=(const char *s);
~String();
};
char *String::operator=(const char *s)
{
if(str) delete[] str;
if(s)
{
str=new char[strlen(s)+1];
strcpy(str,s);
}
else
str=NULL;
return str;
}
String::~String()
{
if(str) delete[]str;
}
int main()
{
String s;
s="Good Luck";
cout<<s.c_str()<<endl;
}
重载赋值运算符的意义:潜复制和深复制
潜复制:执行逐个字节的复制工作
MyString S1,S2;
S1="this";
S2="that";
S1=S2;实现了以下操作
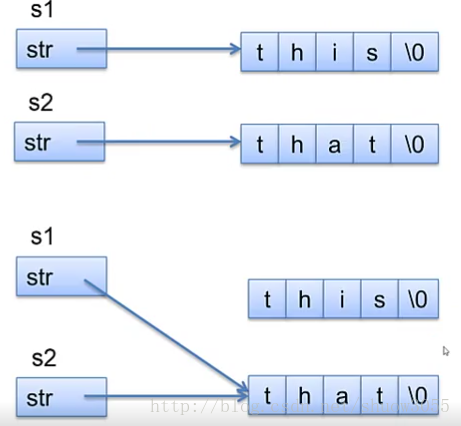
无指针指向”this”的内存空间,变成垃圾内存,而有两个指针指向“that”,这样在这块内存消亡时,会消亡两次,这也许会导致发生不可预知的内存错误。
深复制
将一个对象中指针变量所指向的内容,复制到另一个对象中指针成员对象指向的地方
即
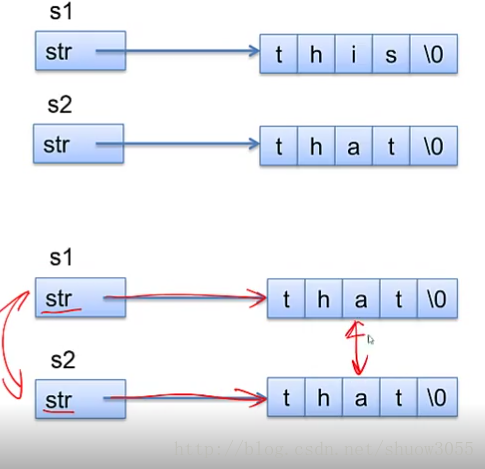
String &String::operator=(const String &s)
{
if(str==s.str) return *this;
if(str) delete[] str;
str=new char[strlen(s.str)+1];
strcpy(str,s.str);
return *this;
}流插入运算符的重载
cout实在iostream中定义的,ostream类的对象。
“<<”在iostream中对”<<”进行了重载。
例子
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class Complex
{
double real,imag;
public:
Complex(double r=0,double i=0):real(i),imag(i){};
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os,const Complex &c);
friend istream &operator>>(istream &is,const Complex &c);
};
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os,const Complex &c)
{
os<<c.real<<"+"<<c.imag<<"i";
return os;
}
istream &operator>>(istream &is,const Complex &c)
{
string s;
is>>s;
int pos=s.find("+",0);
string sTmp;
sTmp=s.substr(0,pos);
c.real=atof(sTmp.c_str());
sTMP=s.substr(pos+1,s.length()-pos-2);
c.imag=atof(sTmp.c_str());
return is;
}
int main()
{
Complex c;
cin>>c;
cout<<c;
return 0;
}
最后
以上就是糊涂过客最近收集整理的关于运算符的重载的全部内容,更多相关运算符内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复