使用 CL 编译器选项查看 C++ 类内存布局--转
今天查资料的时候发现 VS 编译器 CL 的一个编译选项可以查看 C++ 类的内存布局,非常有用。使用如下,从开始程序菜单找到 Visual Stdio 2008/2005 Command Prompt,选择 VS 的命令行工具,按如下格式使用:
>cl –d1reportSingleClassLayout[classname] test.cpp
而使用 –d1reportAllClassLayout 则可以查看源文件中所有类及结构体的内存布局。
其中,classname 为类名,-d1reportSingleClassLayout[classname] 之间没有空格。编写程序测试:
比较奇怪,加上 #include <iostream> 后,测试结构体的时候就会出现很输出,应该是库中的类,看起来真麻烦,所以这里去掉它。
1: //test: >cl Test.cpp /d1reportSingleClassLayout[className]
2: //#include <iostream>
3:
4: //using namespace std;
5:
6: struct S
7: {
8: char x;
9: int y;
10: double z;
11: };
12: class TestClass
13: {
14: private:
15: char y;
16: double z;
17: int x;
18: };
19: //base
20: class Base
21: {
22: private:
23: int x;
24: public:
25: virtual void f1();
26: virtual int g1();
27: };
28: //Derived
29: class Derived: public Base
30: {
31: private:
32: char y;
33: public:
34: virtual float f2();
35: };
36: //Derived2
37: class Derived2: public Base
38: {
39: private:
40: double z;
41: public:
42: virtual void f1();
43: virtual float v2();
44: int f3();
45: };
46: //
47: class Base2
48: {
49: private:
50: int yy;
51: public:
52: virtual void g2();
53: };
54: //多重继承
55: class Derived3: public Base, public Base2
56: {
57: private:
58: double zz;
59: public:
60: virtual void g3();
61: };
62: //
63: int main()
64: {
65: return 0;
66: }
//测试,1:测试结构体 S:>cl Test.cpp /d1reportSingleClassLayoutS

可以看到,VC 默认情况下,结构体内使用字节对齐,char x, 和 int y 之间填充了 3 个字节的空间。默认情况,VC 对结构体内的字节按最大字节对齐,成员变量之间的顺序不同,结构体所占空间也可能不同。
2. 测度类 TestClass: >cl Test.cpp /d1reportSingleClassLayoutTestClass
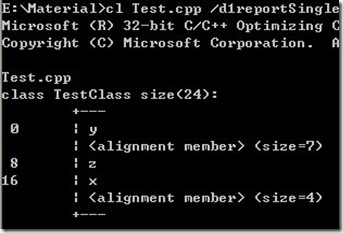
同样可以看到,类 TestClass 中数据成员的按最大数据成员字节对齐,char y 和 double z 之间插入了 7 个字节,double z 和 int x 之间插入了 4 个字节,按 double 型对齐,32 位机器上, sizeof(double) = 8。
3.测试有虚函数的类 Base: >cl Test.cpp /d1reportSingleClassLayoutBase

其中{vfptr}是虚函数表,可以看到,VC 将虚函数表地址放在了对象的头 4 个字节,接着才是数据成员。虚函数表是一个数组,里面存放的是类中虚函数的地址,可以看到虚函数成员的地址是按照声明的顺序存放的。
4.测试子类 Derived:>cl Test.cpp /d1reportSingleClassLayoutDerived

可以看到,基类的虚函数存放在虚表的前面,子类中自己声明的虚函数按顺序存放在后面。
5.测试子类Derived2: >cl Test.cpp /d1reportSingleClassLayoutDerived2

可以看到,子类 Derived2 中重写了基类 Base 中的虚函数 f1(),因此 Devried2 的虚表中 f1() 的位置被 Derived2 重写的 f1() 代替,因此便实现了多态。非虚函数地址不存放在虚表中。
6.测试多重继承的类Derived3: >cl Test.cpp /d1reportSingleClassLayoutDerived3

可以看到VC中对多重继承的处理,子类 Derived3 的对象中,前 4 个字节存放的是第一个基类的 虚表,然后是第一个基类的数据成员。接着是第 2 个基类的虚表及数据成员。最后才是自己的数据成员。其中,Derived3::$vftable@Base2@: -8, -8 表示第 2 个基类相对于虚表相对于 Derived3 的偏移量 offset。
//测试结构体的字节对齐,以及 #pragma pack(1), offsetof(struct,number) 的用法。
1: #include <iostream>
2:
3: using namespace std;
4:
5: struct st1
6: {
7: short number;
8: float grade;
9: float grade2;
10: float grade3;
11: char level;
12: }; //20
13:
14: struct st2
15: {
16: char level;
17: short number;
18: float grade;
19: float grade2;
20: float grade3;
21: };//16
22:
23: #pragma pack(1)
24: struct st3
25: {
26: char level;
27: short number;
28: float grade;
29: float grade2;
30: float grade3;
31: }; //15
32: #pragma pack()
33:
34: void TestSizeOf()
35: {
36: cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
37:
38: cout << " sizeof(short)= " << sizeof(short) << endl << endl;
39:
40: cout << " sizeof(st1)= " << sizeof (st1) << endl;
41: cout << " offsetof(st1,number) " << offsetof(st1,number) << endl;
42: cout << " offsetof(st1,grade) " << offsetof(st1,grade) << endl;
43: cout << " offsetof(st1,grade2) " << offsetof(st1,grade2) << endl;
44: cout << " offsetof(st1,grade3) " << offsetof(st1,grade3) << endl;
45: cout << " offsetof(st1,level) " << offsetof(st1,level) << endl << endl;
46:
47: cout << " sizeof(st2)= " << sizeof (st2) << endl;
48: cout << " offsetof(st2,level) " << offsetof(st2,level) << endl;
49: cout << " offsetof(st2,number) " << offsetof(st2,number) << endl;
50: cout << " offsetof(st2,grade) " << offsetof(st2,grade) << endl;
51: cout << " offsetof(st2,grade2) " << offsetof(st2,grade2) << endl;
52: cout << " offsetof(st2,grade3) " << offsetof(st2,grade3) << endl << endl;
53:
54: cout << " sizeof(st3)= " << sizeof (st3) << endl;
55: cout << " offsetof(st3,level) " << offsetof(st3,level) << endl;
56: cout << " offsetof(st3,number) " << offsetof(st3,number) << endl;
57: cout << " offsetof(st3,grade) " << offsetof(st3,grade) << endl;
58: cout << " offsetof(st3,grade2) " << offsetof(st3,grade2) << endl;
59: cout << " offsetof(st3,grade3) " << offsetof(st3,grade3) << endl << endl;
60: }
61: int main()
62: {
63: TestSizeOf();
64: return 0;
65: }
其中,VC对结构体中的数据成员默认按照最大成员对齐,#pragma pack(num) 可以设置对齐字节数,可以为1、2、4、8、16 。也可以使用编译选项 /Zp[1|2|4|8|16] 修改对齐方式,取消修改用#pragma pack(),如果结构体某成员的 sizeof 大于你设置的,则按你的设置来对齐。注意 offsetof 的用法,可以很容易观察结构体的内部结构
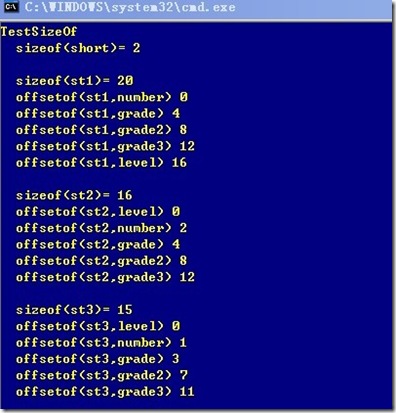
还可以使用前面所说的 cl –d1reportSingleClassLayout[classname] test.cpp 编译选项进行相互验证。
最后
以上就是俭朴大侠最近收集整理的关于使用 CL 编译器选项查看 C++ 类内存布局--转的全部内容,更多相关使用内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复