
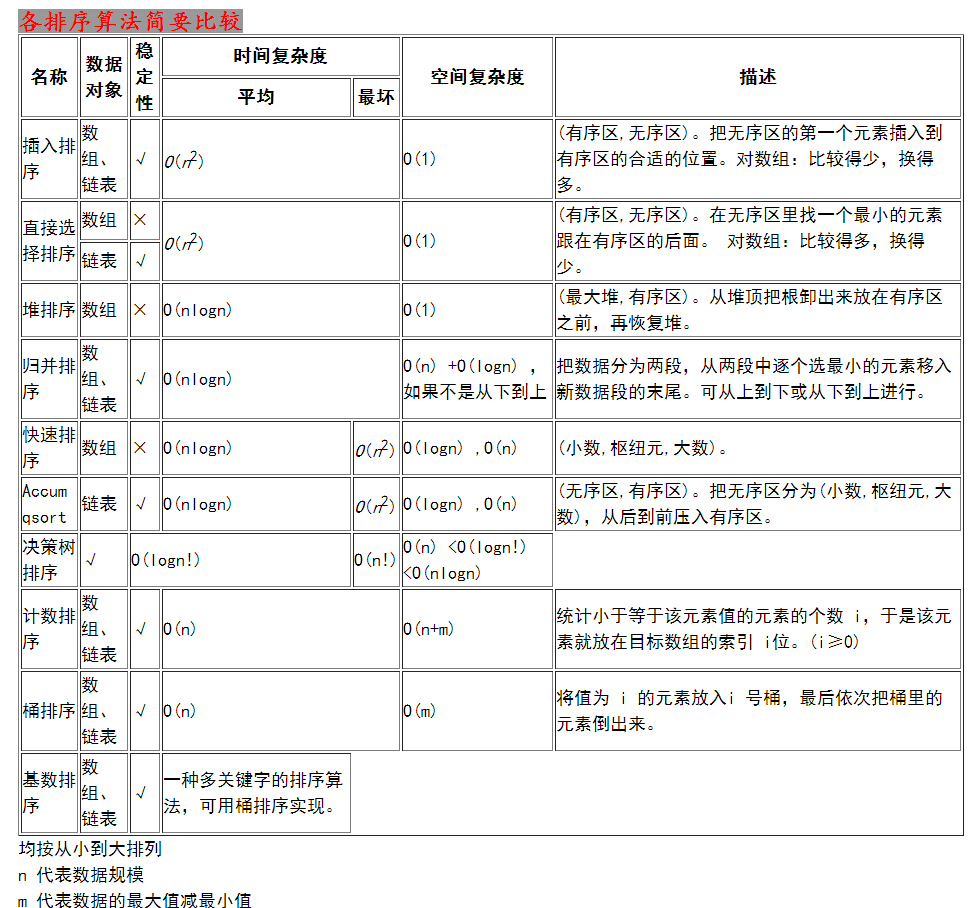
下面简要总结了常用的一些排序算法。如有错误,还请大家指正
插入排序
是一个对少量元素进行排序的有效算法。实现比较简单。时间复杂度:O(n^2),空间复杂度:O(1)。是稳定的排序方法。
代码:
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
//insertion sort
#`include <iostream>`
using namespace std;
//insertion sort
void InsertionSort(int *a,int n)
{
int temp;
for(int i = 1;i < n;++i)
{
temp = *(a + i);
int j = i - 1;
while(j >= 0 && *(a + j) > temp)
{
*(a + j + 1) = *(a + j);
--j;
}
*(a + j + 1) = temp;
}
}
int main()
{
int n,temp;
cout<<"please input the number of the values that need to sort:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
int *a = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
cout<<"please input each value:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
{
cin>>temp;
*(a + i) = temp;
}
/*
//insertion sort
for(int i = 1;i < n;++i)
{
temp = *(a + i);
int j = i - 1;
while(j >= 0 && *(a + j) > temp)
{
*(a + j + 1) = *(a + j);
--j;
}
*(a + j + 1) = temp;
}*/
InsertionSort(a,n);
cout<<"the values after sort:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
cout<<*(a + i)<<" ";
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
free(a);
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
}
数据测试:
上述代码可以改进的一个地方是:在查找插入位置的时候可以采用二分查找,但是这样依然不可以把时间复杂度降低为O(nlogn),因为移动元素的复杂度没有降低。所以时间复杂度仍然是O(n^2)。
做此改进需要添加函数InsertLoc用于二分查找需要插入的位置,以及修改函数InsertionSort的实现。具体如下:
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
//改进:用二分查找来找到插入的位置
//在数组a[low]---a[high]查找val插入的位置
int InsertLoc(int *a,int low,int high,int val)
{
if(low == high)
{
if(val > *(a + low))return (low + 1);
else
return low;
}
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if(val > *(a + mid) && val > *(a + mid + 1))
return InsertLoc(a,mid + 1,high,val);
else if(val < *(a + mid) && val < *(a + mid + 1))
return InsertLoc(a,low,mid,val);
else
return mid;
}
void InsertionSort(int *a,int n)
{
int temp,insert_location;
for(int i = 1;i < n;++i)
{
temp = *(a + i);
int j = i - 1;
insert_location = InsertLoc(a,0,j,temp);
cout<<"insert_location:"<<insert_location<<endl;
while(j >= insert_location)
{
*(a + j + 1) = *(a + j);
--j;
}
*(a + insert_location) = temp;
for(int m = 0;m <= i;++m)
cout<<*(a + m)<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
}
选择排序
第一次找出A[0,…,n-1]的最小的元素,与A[0]交换,接着,找出A[1,…,n-1]的次小得元素,与A[1]互换。对A中头n-1个元素执行这一过程。时间复杂度:O(n^2),空间复杂度O(1)。是不稳定的排序方法。比如序列5 8 5 2 9,第一遍选择第1个元素5会和2交换,那么原序列中2个5的相对前后顺序就被破坏了,所以选择排序是不稳定的排序算法。
但是严蔚敏的《数据结构》书上面Page289页说,所有时间复杂度为O(n^2)的简单排序都是稳定的。不知道为什么?求指导~~
其给出的简单排序的伪代码:
void SelectSort(SqList &L)
{
//对顺序表L做简单排序
for(i = 1;i < L.length;++i)//选择第i小得记录,并交换到位
{
j = SelectMinKey(L,i);//在L.r[i..L.length]中选择key最小的记录
if(i != j)//与第i个记录交换
{
temp = L.r[i];
L.r[i] = L.r[j];
L.r[j] = temp;
}
}
}
代码:
//选择排序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void ChoseSort(int* a,int n)
{
int temp,minVal,minIndex;
for(int i = 0;i < n - 1;++i)
{
minVal = *(a + i);//记录a[i,...,n-1]之间的最小值
minIndex = i;//记录a[i,...,n-1]之间的最小值的下标
for(int j = i + 1;j < n;++j)
{
if(minVal > *(a + j))
{
minVal = *(a + j);
minIndex = j;
}
}
//交换a[i]和a[i,...,n-1]之间的最小值最小值
if(minIndex != i)
{
temp = *(a + i);
*(a + i) = *(a + minIndex);
*(a + minIndex) = temp;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n,temp;
cout<<"please input the number of the values that need to sort:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
int *a = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
cout<<"please input each value:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
{
cin>>temp;
*(a + i) = temp;
}
ChoseSort(a,n);
cout<<"the values after sort:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
cout<<*(a + i)<<" ";
free(a);
}
合并排序
采用分治法。将n个元素分成各含n/2个元素的子序列,用合并排序法对两个子序列递归的排序(子序列长度为1时递归结束),最后合并两个已排序的子序列得到结果。时间复杂度:O(nlogn),空间复杂度:O(n)。是稳定的排序方法。
代码:
//合并排序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VALUE 100000//用于设置哨兵,避免检查是否每一个堆都是空的
//合并两个子数组的函数
void Merge(int *a,int p,int q,int r)
{
int num1,num2;
num1 = q - p + 1;
num2 = r - q;
int *a1 = (int*)malloc((num1 + 1) * sizeof(int));
int *a2 = (int*)malloc((num2 + 1) * sizeof(int));
for(int i = 0;i < num1;++i)
*(a1 + i) = *(a + p + i);
*(a1 + num1) = MAX_VALUE;//设置哨兵元素
for(int i = 0;i < num2;++i)
*(a2 + i) = *(a + q + 1 + i);
*(a2 + num2) = MAX_VALUE;//设置哨兵元素
//进行排序
int index1 = 0;
int index2 = 0;
for(int i = p;i <= r;++i)
{
if(*(a1 + index1) < *(a2 + index2))
{
*(a + i) = *(a1 + index1);
++index1;
}
else
{
*(a + i) = *(a2 + index2);
++index2;
}
}
free(a1);
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
free(a2);
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
}
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
//递归合并排序算法
void MergeSort(int *a,int p,int r)
{
if(p < r)
{
int q = (p + r) / 2;
MergeSort(a,p,q);
MergeSort(a,q + 1,r);
Merge(a,p,q,r);
}
}
int main()
{
int n,temp;
cout<<"please input the number of the values that need to sort:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
int *a = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
cout<<"please input each value:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
{
cin>>temp;
*(a + i) = temp;
}
MergeSort(a,0,n - 1);
cout<<"the values after sort:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
cout<<*(a + i)<<" ";
free(a);
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
}
如果不使用哨兵元素,需要修改Merge函数,如下:
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
//合并两个子数组的函数(不使用哨兵元素)
void Merge(int *a,int p,int q,int r)
{
int num1,num2;
num1 = q - p + 1;
num2 = r - q;
int *a1 = (int*)malloc(num1 * sizeof(int));
int *a2 = (int*)malloc(num2 * sizeof(int));
for(int i = 0;i < num1;++i)
*(a1 + i) = *(a + p + i);
for(int i = 0;i < num2;++i)
*(a2 + i) = *(a + q + 1 + i);
//进行排序
int index1 = 0;
int index2 = 0;
int index = p;
while(index1 < num1 && index2 <num2)
{
if(*(a1 + index1) < *(a2 + index2))
{
*(a + index) = *(a1 + index1);
++index;
++index1;
}
else{
*(a + index) = *(a2 + index2);
++index;
++index2;
}
}
while(index1 < num1)
{
*(a + index) = *(a1 + index1);
++index;
++index1;
}
while(index2 < num2)
{
*(a + index) = *(a2 + index2);
++index;
++index2;
}
free(a1);
free(a2);
}
冒泡排序
每一趟都比较相邻两个元素,若是逆序的,则交换。结束的条件应该是“在一趟排序过程中没有进行过交换元素的操作”。时间复杂度:O(n^2),空间复杂度O(1)。是稳定的排序。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void BubbleSort(int *a,int n)
{
int flag,temp;//标记是否进行过交换操作
for(int i = 0;i < n - 1;++i)
{
flag = 0;
for(int j = 0;j < n - 1 - i;++j)
{
if(*(a + j) > *(a + j + 1))
{
temp = *(a + j);
*(a + j) = *(a + j + 1);
*(a + j + 1) = temp;
flag = 1;
}
}
if(flag == 0)break;
}
}
int main()
{
int n,temp;
cout<<"please input the number of the values that need to sort:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
int *a = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
cout<<"please input each value:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
{
cin>>temp;
*(a + i) = temp;
}
BubbleSort(a,n);
cout<<"the values after sort:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
cout<<*(a + i)<<" ";
free(a);
}
快速排序
它是对冒泡排序的一种改进。它的基本思想是:通过一趟排序将待排序元素分成两个部分,其中一部分元素比另一部分元素小。再分别对这两部分元素进行排序。以达到整个元素序列有序。时间复杂度:O(nlogn),空间复杂度O(logn),是不稳定的算法。
代码
//Quick Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std```
Partition(int *a,int low,int high)
{
int pivotKey = *(a + high);
int i = low - 1;
for(int j = low;j <= high - 1;++j)
{
if (*(a + j) < pivotKey)
{
++i;
int tmp = *(a + i);
*(a + i) = *(a + j);
*(a + j) = tmp;
}
}
int tmp = *(a + i + 1);
*(a + i + 1) = *(a + high);
*(a + high) = tmp;
return (i + 1);
}
void QuickSort(int *a,int low,int high)
{
if(low < high)
{
int PivotLoc = Partition(a,low,high);
QuickSort(a,low,PivotLoc - 1);
QuickSort(a,PivotLoc + 1,high);
}
main()
{
int n,temp;
cout<<"please input the number of the values that need to sort:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
int *a = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
cout<<"please input each value:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
{
cin>>temp;
*(a + i) = temp;
}
QuickSort(a,0,n - 1);
cout<<"the values after sort:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
cout<<*(a + i)<<" ";
free(a);
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int Partition(int *a,int low,int high)
{
int PivotKey = *(a + low);//用第一个元素做枢轴
while(low < high)
{
while(low < high && *(a + high) > PivotKey)--high;
*(a + low) = *(a + high);
while(low < high && *(a + low) < PivotKey)++low;
*(a + high) = *(a + low);
}
*(a + low) = PivotKey;
return low;
}
void QuickSort(int *a,int low,int high)
{
if(low < high)
{
int PivotLoc = Partition(a,low,high);
QuickSort(a,low,PivotLoc - 1);
QuickSort(a,PivotLoc + 1,high);
}
}
int main()
{
int n,temp;
cout<<"please input the number of the values that need to sort:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
int *a = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
cout<<"please input each value:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
{
cin>>temp;
*(a + i) = temp;
}
QuickSort(a,0,n - 1);
cout<<"the values after sort:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i)
cout<<*(a + i)<<" ";
free(a);
}
堆排序:
参考链接:堆排序思想讲解及编程实现
计数排序
计数排序的思想是对每一个输入元素x,确定出小于x的元素的个数。然后我们就可以直接把它放在嘴中输出数组中相应的位置上。
但是计数排序基于这样一个假设:n个输入元素的每一个大小范围都是[0,k]。
代码:
这里写代码片
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//Counting Sort Algorithm
//A:array before sorting
//B:array after sorting
//n:the number of A
//k:all the elements is in [0,k]
void CountintSort(int A[],int *B,int n,int k,int *C)
{
//初始化C数组
for (int i = 0;i <= k;++i)
{
C[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0;i < n;++i)
{
++C[A[i]];//C[i]:值等于i的元素的个数
}
for (int i = 1;i <= k;++i)
{
C[i] += C[i - 1];//C[i]:值小于等于i的元素的个数
}
for (int i = n - 1;i >= 0;--i)
{
B[C[A[i]] - 1] = A[i];//注意:下标索引从0开始!
--C[A[i]];
}
}
int main()
{
int A[6] = {2,7,1,4,0,3};
int n = 6;
int k = 7;
int *B = (int *)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
int *C = (int *)malloc((k + 1) * sizeof(int));
cout << "排序之前的元素:" << endl;
for (int i = 0;i < n;++i)
{
cout << A[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
CountintSort(A,B,n,k,C);
cout << "排序之后的元素:" << endl;
for (int i = 0;i < n;++i)
{
cout << B[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
free(B);
free(C);
}
时间复杂度是O(k + n)。一般,当k = O(n)时,常常采用计数排序。这时候的运行时间为O(n)。
计数排序是稳定的排序。
参考资料:
不同排序算法间的比:http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:SortingAlgoComp.png
一些排序算法的 C 及 Pascal 实现 :
http://www.nocow.cn/index.php/%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95
最后
以上就是俏皮裙子最近收集整理的关于排序算法实现与比较插入排序的全部内容,更多相关排序算法实现与比较插入排序内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复