1、构建环境
参考mmsegmentation使用说明:
创建虚拟环境
conda create -n mmsegmentation python=3.8
进入虚拟环境
conda activate mmsegmentation
安装torch/torchvision
conda install pytorch torchvision -c pytorch
安装mim
pip install -U openmim
安装mmcv-full ## 注意本地环境的cuda与mmcv-full的版本对应
mim install mmcv-full
linux安装有git+网络畅通,可以直接下载mmsegmentation
git clone -b [version] https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmsegmentation.git
or 没网的情况 则下载对应的.zip包进行解压
进入mmsegmentation
cd mmsegmentation
pip install -v -e. or python setup.py develop
如果缺陷包,可以安装requirement.txt里面的对应包
pip install -r requirement.txt
按照上述步骤可搭建完成mmsegmentation的conda基础环境
2、制作数据集
- 搭建labelme环境并标注数据
pip install labelme
然后直接运行labelme
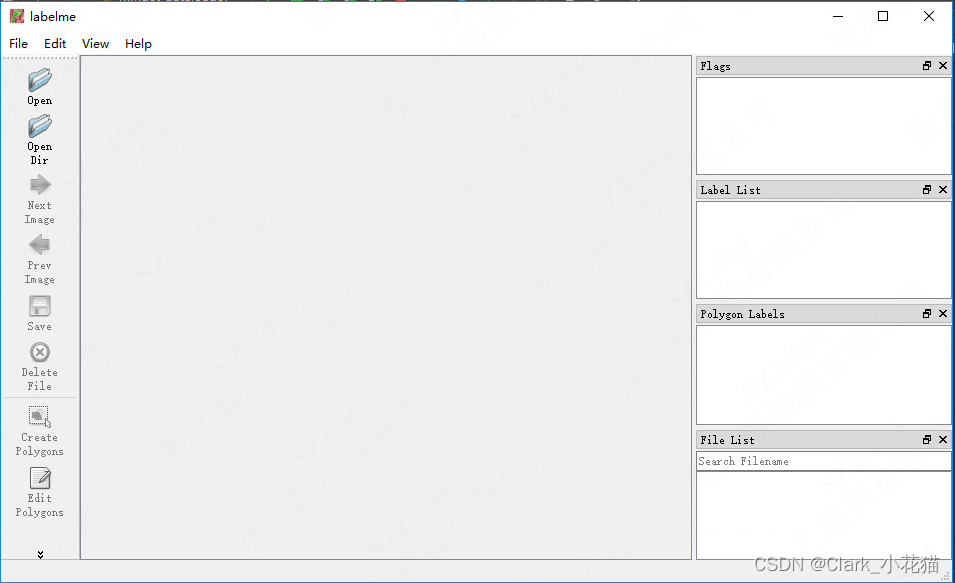
labelme
可以看到如下消息以及对应窗口

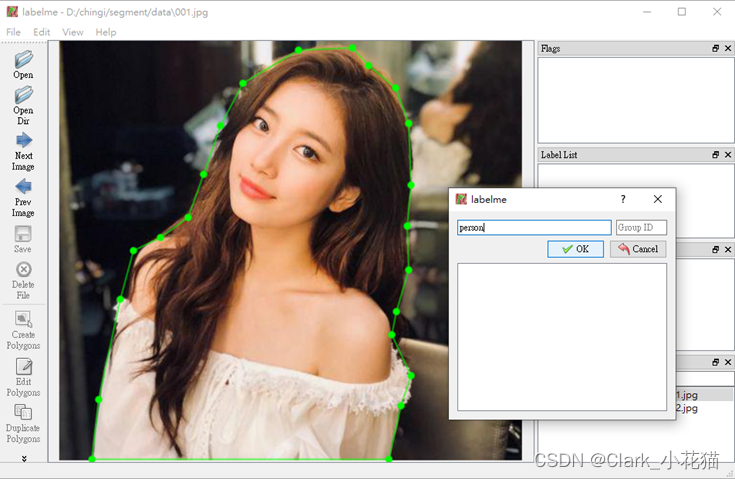
按照标记点的方式,标记出对应的object,并给与不同的label(盗个别人的美女图)
- 使用labelme源码中的labelme2voc.py进行数据转换
(1)新建labels.txt,并在其中添加你的类别,如下,我只有一个类别line ,默认需要添加__ignore__以及_background_两个默认类别

(2)准备如下源码
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import glob
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import imgviz
import numpy as np
import labelme
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
)
parser.add_argument("input_dir", help="input annotated directory")
parser.add_argument("output_dir", help="output dataset directory")
parser.add_argument("--labels", help="labels file", required=True)
parser.add_argument(
"--noviz", help="no visualization", action="store_true"
)
args = parser.parse_args()
if osp.exists(args.output_dir):
print("Output directory already exists:", args.output_dir)
sys.exit(1)
os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages"))
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClass"))
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassPNG"))
if not args.noviz:
os.makedirs(
osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassVisualization")
)
print("Creating dataset:", args.output_dir)
class_names = []
class_name_to_id = {}
for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):
class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1
class_name = line.strip()
class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
if class_id == -1:
assert class_name == "__ignore__"
continue
elif class_id == 0:
assert class_name == "_background_"
class_names.append(class_name)
class_names = tuple(class_names)
print("class_names:", class_names)
out_class_names_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "class_names.txt")
with open(out_class_names_file, "w") as f:
f.writelines("n".join(class_names))
print("Saved class_names:", out_class_names_file)
for filename in glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.json")):
print("Generating dataset from:", filename)
label_file = labelme.LabelFile(filename=filename)
base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(filename))[0]
out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages", base + ".jpg")
out_lbl_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "SegmentationClass", base + ".npy"
)
out_png_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassPNG", base + ".png"
)
if not args.noviz:
out_viz_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir,
"SegmentationClassVisualization",
base + ".jpg",
)
with open(out_img_file, "wb") as f:
f.write(label_file.imageData)
img = labelme.utils.img_data_to_arr(label_file.imageData)
lbl, _ = labelme.utils.shapes_to_label(
img_shape=img.shape,
shapes=label_file.shapes,
label_name_to_value=class_name_to_id,
)
labelme.utils.lblsave(out_png_file, lbl)
np.save(out_lbl_file, lbl)
if not args.noviz:
viz = imgviz.label2rgb(
lbl,
imgviz.rgb2gray(img),
font_size=15,
label_names=class_names,
loc="rb",
)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_viz_file, viz)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
(3)直接运行labelme2voc.py
python --input_dir [你的标注数据的地址jpg and annotation ] --output_dir [输出的数据] --labels [刚才准备的labels.txt] --novis [是否显示结果图,默认True]
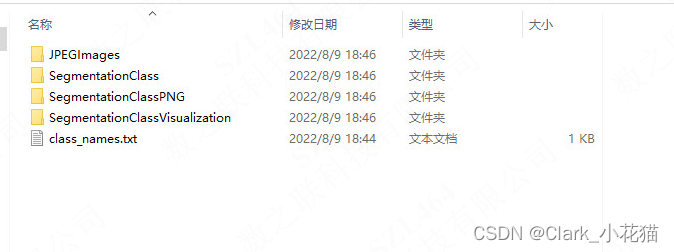
- 输出如下
JPEGImages----原始图片
SegmentationClass----npy格式存储的数据
SegmentationClassPNG----训练所需要的Label数据(annotation)
SegmentationClassVisualization----原图叠加masks数据的显示图
class_names.txt----包含所有的label,包含了_background_
以上即准备好了数据
但是label的数值不是我们通常认知的的1,2,3,4等,可进行适当修改,完成自己的定制需求
3、模型训练
-
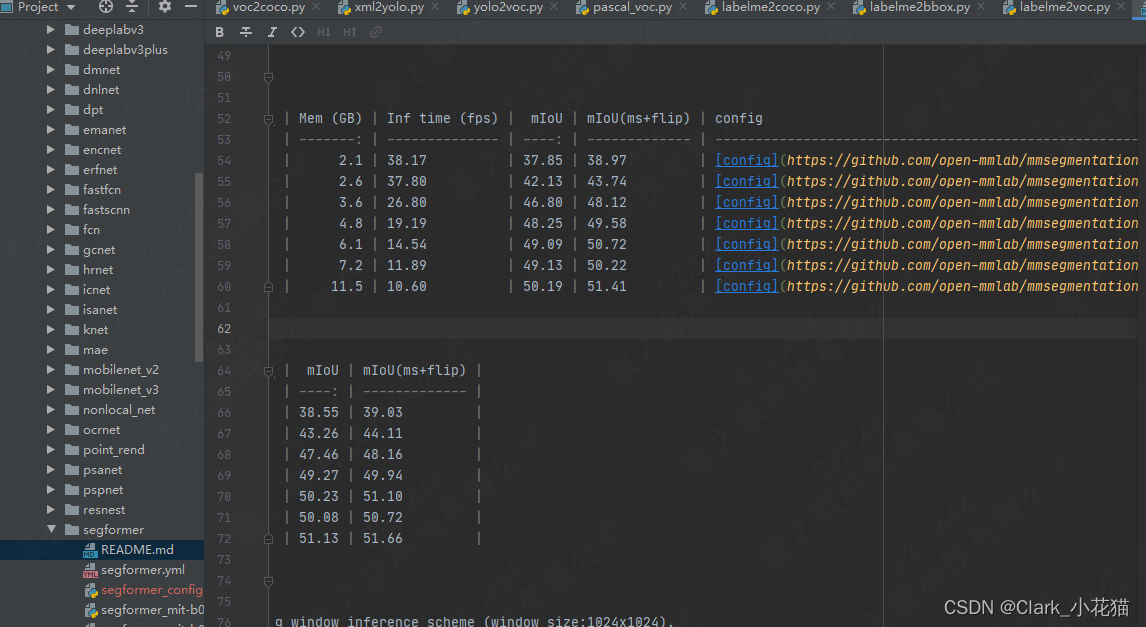
选择想要进行试验的模型,下载预训练权重和对应的config
进入config/segformer里面的README.md ,找到对应的config配置以及对应的权重文件位置
-
更改config文件和相应的源码位置
(1)修改类别数, 类别数=你的类别数+1
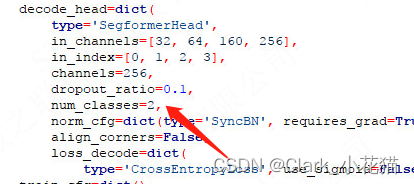
(2)更改你的预训练模型地址
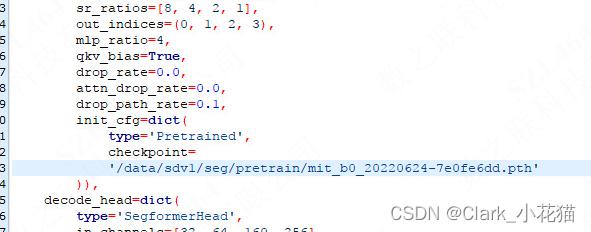
(3)配置数据类型+图片和label地址
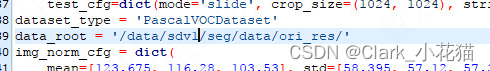

-
配置结果存储路径
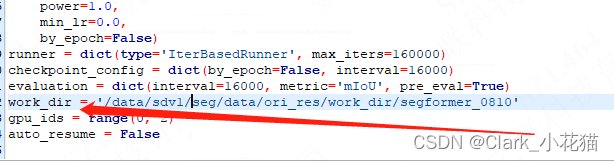
-
源码相应更新
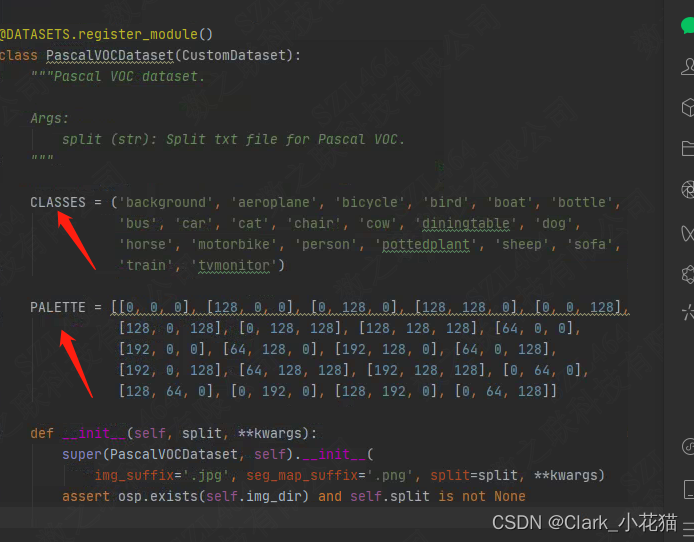
找到mmsegmentation/mmseg/datasets,因我们的数据类型为voc,因此打开voc.py,修改其中的CLASSES为你的类别名称,PALETTE为为每个类别对应的颜色
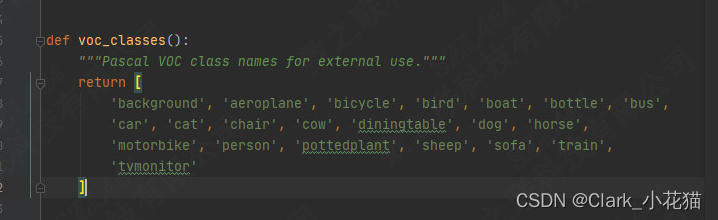
进入mmsegmentation/mmseg/core/evaluation中,找到class_names.py,更改voc_classes函数中的类别为自己数据集的类别,防止在评估阶段出错
-
训练模型
cd mmsegmentation
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES='1,2' bash /tools/dist_train.py [your config] [GPU nums]

4、模型测试
from mmseg.api import init_segmentor,inference_segmentor,show_result_plot
import cv2
config_file = '/data/sdv1/your_config.py'
checkpoint = '/data/sdv1/your_checkpoint.pth'
img_path = '/data/sdv1/you_img.jpg'
model = init_segmentor(config_file, checkpoint, device='cuda:0')
result = inference_segmentor(mdoel, img_path )
show_result_plot(model,img_path,result,out_file='输出图片地址')
–END–
如有问题,敬请指出
最后
以上就是爱听歌大米最近收集整理的关于图像分割之--mmsegmentation使用的全部内容,更多相关图像分割之--mmsegmentation使用内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复